Chapter: Genetics and Molecular Biology: Lambda Phage Genes and Regulatory Circuitry
N Protein and Antitermination of Early Gene Transcription
N Protein and Antitermination of Early Gene Transcription
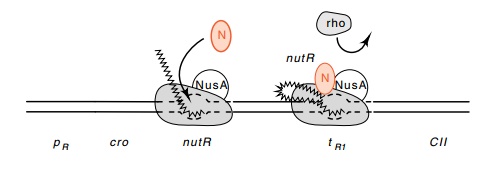
Several minutes after infection, N protein reaches
sufficiently high concentrations in the cytoplasm to function. It binds to RNA
polymerase and to a special sequence in the mRNA whose corresponding sequence
in the DNA is called the nut, for N
utilization, site. Without a functional nut
sequence, or without the NusA protein already bound to RNApolymerase, the N
protein does not bind to the polymerase. RNA polymerase with N protein bound to
it no longer terminates transcrip-tion at the sites tL1 and tR1 and instead continues across these sites to
synthesize messenger for genes CII
and CIII as well as the more distal
genes in these operons (Fig. 14.5).
It should be mentioned
at this time that a number of E. coli mutants exist in which wild-type
lambda does not grow. Some of these behave as though the lambda possessed a
mutation in the N protein. These are called nus
mutants, and the NusA protein is the product of one such gene. Presumably, NusA
protein can be altered so that it still fulfills its normal cellular function,
but lambda N protein does not properly interact with it. Consequently,
termination always occurs at tL1
and tR1 in nus mutants. Other nus mutations, nusB, nusE, and nusG, lie in RNA polymerase and in ribosomal genes. These other
proteins stabilize the N protein-RNA polymerase interaction.
Figure
14.5 A representation of how lambda N
protein could antagonize theaction of rho protein at the terminators.
Related Topics