Chapter: Operating Systems : Process and Threads
Multiprocessor and Multicore Organization
MULTIPROCESSOR AND MULTICORE
ORGANIZATION
ü Multiprocessor
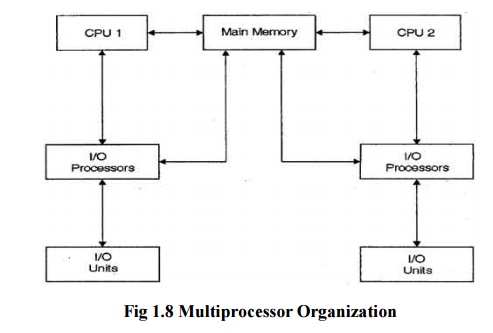
Operating System refers to the use of two or more central processing units
(CPU) within a single computer system. These multiple CPUs are in a close
communication sharing the computer bus, memory and other peripheral devices.
These systems are referred as tightly coupled systems.
ü Multiprocessing
system is based on the symmetric multiprocessing model, in which each processor
runs an identical copy of operating system and these copies communicate with
each other. In this system processor is assigned a specific task. A master
processor controls the system. This scheme defines a master-slave relationship.
ü These
systems can save money in compare to single processor systems because the
processors can share peripherals, power supplies and other devices. The main
advantage of multiprocessor system is to get more work done in a shorter period
of time. Moreover, multiprocessor systems prove more reliable in the situations
of failure of one processor. In this situation, the system with multiprocessor
will not halt the system; it will only slow it down.
ü In order
to employ multiprocessing operating system effectively, the computer system
must have the followings:
1. Motherboard Support:
A motherboard capable of handling
multiple processors. This means additional sockets or slots for the extra chips
and a chipset capable of handling the multiprocessing arrangement.
2. Processor Support:
ü Processors
those are capable of being used in a multiprocessing system.
ü The whole
task of multiprocessing is managed by the operating system, which allocates
different tasks to be performed by the various processors in the system.
ü Multiprocessor
system supports the processes to run in parallel. Parallel processing is the
ability of the CPU to simultaneously process incoming jobs. This becomes most
important in computer system, as the CPU divides and conquers the jobs.
Generally the parallel processing is used in the fields like artificial
intelligence and expert system, image processing, weather forecasting etc.
ü In a
multiprocessor system, the dynamically sharing of resources among the various processors may cause therefore, a potential bottleneck. There
are three main sources of contention that can be found in a multiprocessor
operating system:
2.1
Locking system:
v In order
to provide safe access to the resources shared among multiple processors, they
need to be protected by locking scheme. The purpose of a locking is to
serialize accesses to the protected resource by multiple processors.
Undisciplined use of locking can severely degrade the performance of system.
v This form
of contention can be reduced by using locking scheme, avoiding long critical
sections, replacing locks with lock-free algorithms, or, whenever possible,
avoiding sharing altogether.
2.2
Shared data:
v The
continuous accesses to the shared data items by multiple processors (with one
or more of them with data write) are serialized by the cache coherence
protocol. Even in a moderate-scale system, serialization delays can have
significant impact on the system performance.
v In
addition, bursts of cache coherence traffic saturate the memory bus or the
interconnection network, which also slows down the entire system. This form of
contention can be eliminated by either avoiding sharing or, when this is not
possible, by using replication techniques to reduce the rate of write accesses
to the shared data.
2.3 False
sharing:
v This form of contention arises when unrelated data items used by different processors are located next to each other in the memory and, therefore, share a single cache line: The effect of false sharing is the same as that of regular sharing bouncing of the cache line among several processors. Fortunately, once it is identified, false sharing can be easily eliminated by setting the memory layout of non-shared data.
Related Topics