Chapter: Operating Systems : Process and Threads
Memory Hierarchy - Operating Systems
Memory Hierarchy
Memory is categorized into volatile
and nonvolatile memories, with the former requiring constant power ON of
the system to maintain data storage.
Furthermore, a typical computer
system provides a hierarchy of different times of memories for data storage.
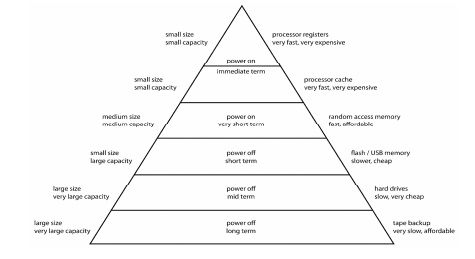
Different levels of the memory
hierarchy
ü Cache
(MB): Cache is the fastest accessible memory of a computer system.
It's access speed is in the order of a few nanoseconds. It is volatile
and expensive, so the typical cache size is in the order of megabytes.
ü Main
memory (GB): Main memory is arguably the most used memory. When
discussing computer algorithms such as quick sort, balanced binary sorted
trees, or fast Fourier transform, one typically assumes that the algorithm
operates on data stored in the main memory. The main memory is reasonably fast,
with access speed around 100 nanoseconds. It also offers larger capacity at a
lower cost. Typical main memory is in the order of 10 GB. However, the main
memory is volatile.
ü Secondary
storage (TB): Secondary storage refers to nonvolatile data
storage units that are external to the computer system. Hard drives and
solid state drives are examples of secondary storage. They offer very large
storage capacity in the order of terabytes at very low cost. Therefore, database
servers typically have an array of secondary storage devices with data stored
distributed and redundantly across these devices. Despite the continuous
improvements in access speed of hard drives, secondary storage devices are
several magnitudes slower than main memory. Modern hard drives have access
speed in the order of a few milliseconds.
ü Tertiary storage (PB): Tertiary storage refers storage designed for the purpose data backup. Examples of tertiary storage devices are tape drives are robotic driven disk arrays. They are capable of petabyte range storage, but have very slow access speed with data access latency in seconds or minutes.
Related Topics