Chapter: Obstetric and Gynecological Nursing : Abnormal Pregnancy
Multiple Pregnancy
Multiple Pregnancy
Definition:- When there is more than one fetus is in utero, the term,
plural or multiple pregnancy is applied.
Twin pregnancy occurs approximately 1 in 100 pregnancy Triplets occur 1
in every 8000- 9000 pregnancies.
Types:-
1. Monozygotic (Uniovular)
2. Dizygotic (Binovular)
1. Monozygotic (Uniovular)
Monozygotic or single ovum twins are known as identical twins.
Monozygotic twins develop from one ovum which has been fertilized by one
spermatozoon, always of same sex, they share one placenta and one chorion. A
few have two chorions. There is a connection between the circulations of blood
in the two babies. Finger and palm prints are identical. Errors in development
are more likely in monozygotic twins and conjoined twins are more common.
2. Dizygotic (Binovular) Twins
Diazygotic or double ova twins develop from the fertilization of two
ovum and two spermatozoa and are more common than monoazygotic twins.
These twins have two placenta may be fused to form one amniotic sacs,
two chrions and no connection between fetal circulations. The babies may or may
not be of the same sex and their physical and mental characteristics can be as
different as in any members of one family.
Table 5. Difference between monozygotic
and dizaygot twins
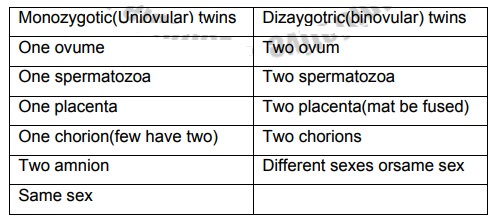
One fetus may be died and be retained in uterus until term, when it will
be expelled with the placenta as a flattened paper like fetus called a fetus
papyraceous. Twin babies are small and often preterm.
Diagnosis of twin pregnancy
Diagnosis of twin pregnancy may be difficult, although a family history
of twins should alter the midwife to the possibility. Ultrasound: -it will demonstrate two heads at 15 weeks whenthe
outline of the head will be noted
X -ray- may be used after the 12thweek of gestation.
Abdominal examination
Inspection:-the size of the uterus may be
larger thanexpected for the period of gestation after the 20th week. Palpation:-The fundal height may be greater than expectedfor the
period of gestation.
·
The presence of two fetal poles (head or breech) multiple fetal limbs.
·
Lateral palpation may reveal two fetal backs or limbs on both sides.
·
Pelvic palpation one fetus may lie behind the other and make palpation
difficult.
Auscultation:-Hearing two fetal hearts is not
diagnostic.Comparison of the heart rates should reveals difference of at least
10 beats per minutes.
Effect of Twins on Pregnancy
·
Exacerbation of minor disorder
·
Nausea, Morning Sickness and heart burn may be more persist.
·
Anaemia
·
Iron deficiency or folic acid deficiency anaemias are common. Early
growth and development of the uterus and
·
its contents make greater demands on maternal iron stores. In later
pregnancy (after the 28th
week) fetal demands for iron deplete those stores further.
· Pregnancy induced Hypertension
o
More common in twin pregnancies May be associated with the larger
placenta site or the increased hormonal out put the incidence tends to be
greater in monozygotic twin pregnancies.
·
Polyhydraminos
o
It is common and associated with monozygotic twins and with fetal
abnormalities. If acute polyhydraminos occurs it tends to lead to abortion.
·
Pressure symptoms
. Tendency to oedema of ankle and
varicose veins isincreased
. Dyspnoea and indigestion are more
marked,backache is common.
Management of Pregnancy
·
Early diagnosis is important so as to provide dietary
·
advice on iron folic acid and vitamins which help to keep her
haemoglobin level normal
·
Frequent antenatal check up to detect P.I.H.
· Admission to hospital for relief discomfort in later pregnancy.
Labour and Delivery of multiple pregnancy
Effect on labour: - Labour occurs spontaneously before term due to over
stretching of the uterus or may be induced early if complications arise.
Preterm labour, babies light for dates and malpresentation.
Management of delivery
1st stage of labour: - should be conducted normally,preparation should be made for the
reception of two immature babies. Good nursing care to alleviate minor
discomfort. If fetal distress occurs during labour, delivery will need to be
expedited, often by caesarean section. If the uterine activity is poor the use
of intravenous oxytocin may be required. If the pregnancy is preterm neonatal
care unit should be informed. Two incubators should be in readiness. The room
should be warm.
2nd stage of labour: - An obstetrician, anesthetist andpaediatrician should be present during
this stage of labour because of the risk of complication.
Resuscitation equipment should be prepared. The delivery trolley should
include equipments for episiotomy, aminiotomy forceps, and extra cord clamp and
equipment for delivery.
An elective episiotomy may be considered if there are complication like
preterm labour and fetal distress. The second stage is conducted as usual up to
the birth of the first baby. After delivery of the first twin an abdominal
examination is made to ascertain the lie, presentation and position of the
second fetus and to auscultate the fetal heart. If the lie is not longitudinal,
an attempt is made to correct it by external cephalic version.
If the presenting part is not engaged it should be pushed in to the
pelvis by fundal pressure before the second sac of membranes is ruptured.
Stimulate the contraction with IV syntocinon. When the presenting part became
visible the mother is encouraged to push with contraction to deliver the second
twin.
With three or four good contractions and effective pushing the 2nd baby has to be delivered with
in 15 minutes. The babies are labeled as ‘ Twin one ‘ and ‘Twin two’ a note of
the time of delivery and the sex of the child is made.
3rd Stage of Labour:-An oxytoxic drug has taken effect,controlled
cord traction is applied to both cords simultaneously and delivery of the
placenta should be effected with out delay. Emptying the uterus enables the
control of bleeding and the prevention of post partum haemorrhage.
The placenta should be examined for completeness and to detect deviation
from the normal. The umbilical cords should be examined for the number of cord
vessels.
Complications associated with multiple pregnancy
Delay in the birth of the second twin
After delivery of the 1st twin, contraction has to start with in 5 minutes.
• Poor uterine action
• Malpresentation of the second twin
Dangers (risk of) Delay
I. Intra uterine hypoxia, IUFD
II. Birth asphyxia following premature separation of placenta
III. Sepsis- an ascending infection may reult from from the first umblical cord which lies out side of the vulva.
IV. The cervix closes to certain extent and will have to dilate again
Managements of closed cervix
Stimulate the contraction put the baby on the breast. If the lie is longitudinal the doctor will rupture the membranes and give an oxytocic drug. When the uterus begins to contracts he may apply forceps. If there appears obstructed caesarean section may be necessary.
• Transverse lie of the second twin
If the lie is transverse call the doctor and he/she attempts external version between contraction if the membranes are intact. Also after internal version may be a breech extraction may be done with intact membrane.
Premature expulsion of the placenta or bleeding before the birth of the second twin results in hypoxia of the unborn twin.
Management - Massage the uterus and expel the 2nd twin by fundal pressure
• Post parrtum haemorrhage
• Premature rupture of the membrane
• Prolapse of the cord
• Prolonged labour - malpresentation, poor uterine action
2. Locked Twins
In the second stage of labour the after coming head of the first twin
may be prevented from descending into the pelvis by the head of the second
twin.
·
Both twins presenting by the vertex
·
Twin one - breech presentation
Twin two - vertex presentation
Danger - Obstructed labour
Management - caesarean section
Complication of Multiple Pregnancy
·
Abortion
·
Polyhydramnous,
·
Fetal abnormality
·
Malpresentaion
·
Premature rupture of membrane
·
Prolapse of cord
·
Prolonged labour
·
Locked twin
· Post partum hemorrhage
Management of Puerperium
Care of the babies maintenances of body temperature, hygiene to prevent
infection.
Related Topics