Terminology, Types of separation or concentration of an ore - Metallurgy | 10th Science : Chapter 8 : Periodic Classification of Elements
Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 8 : Periodic Classification of Elements
Metallurgy
METALLURGY
Human life is associated
with various metals. We use metals in our day to day activities. It is the
utmost need to have some metals like sodium, potassium, calcium, iron, etc. in
the human body. Deficiency of these metals affects the metabolic activities
thereby causing diseases. So, metals play a vital role in our life. In this
section, let us discuss how metals are obtained from various sources by the
process of metallurgy.
Metallurgy is a science of extracting metals from their ores and
modifying the metals into alloys for various uses, based on their physical and
chemical properties and their structural arrangement of atoms. A metallurgical process
involve three main steps as follows:
(i) Concentration or Separation
of the ore: It is the process of removal of impuries from the ore.
(ii) Production of the
metal: It
is the convertion of the ore into metal.
(iii) Refining of the
metal: It
is the process of purification of the metal.
![]()
![]()
1. Terminology in metallurgy
Minerals: A mineral may be a
single compound or a complex mixture of various compounds of metals
found in the Earth.
Ore: The mineral from which a
metal can be readily and economically extracted on a large scale is said
to be an ore.

For example: Clay (Al2O
3. 2 SiO 2. 2 H2O) and
bauxite (Al2O3 .2 H2O) are the two minerals of
aluminium, but aluminium can be profitably extracted only from bauxite. Hence,
bauxite is an ore of aluminium and clay is its mineral.
Mining: The process of
extracting the ores from the Earth's crust is called mining.
Gangue or Matrix: The rocky impurity associated
with an ore is called gangue or matrix.
Flux: It is the substance
added to the ore to reduce the fusion temperature and to remove the
impurities. E.g. Calcium oxide (basic), Silica (acidic). If the gangue is
acidic, then basic flux is added and vice versa.
Slag: It is the fusible
product formed when a flux reacts with a gangue during the extraction of
metals.
Flux + Gangue → Slag
Smelting: Smelting is the process
of reducing the roasted metallic oxide from the metal in its molten
condition. In this process, impurities are removed as slag by the addition of
flux.
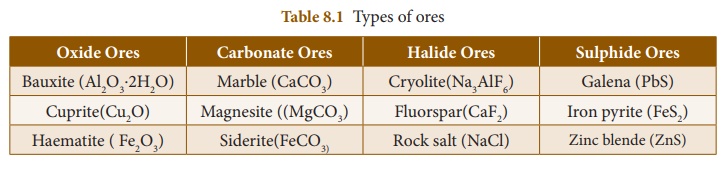
2. Types of separation or concentration of an ore
There are four major
types of separation of ores based on the nature of the ore. The different kinds
of ores of metals are given in Table 8.1
Concentration of the
crushed ore is done mainly by the following methods: -
(i) Hydraulic (Gravity Separation) method
Principle:
The difference in the
densities or specific gravities of the ore and the gangue is the main principle
behind this method. Oxide ores are purified by this method. e.g., Haematite
Fe2O3 the ore of iron.
Method:
The ore is poured over a
sloping,vibrating corrugated table with grooves and a jet of water is allowed
to flow over it. The denser ore particles settle down in the grooves and
lighter gangue particles are washed down by water.
(ii) Magnetic separation method
Principle:
The magnetic properties
of the ores form the basis of separation. When either the ore or the gangue is
magnetic, this method is employed. e.g., Tinstone SnO2, the ore of tin.
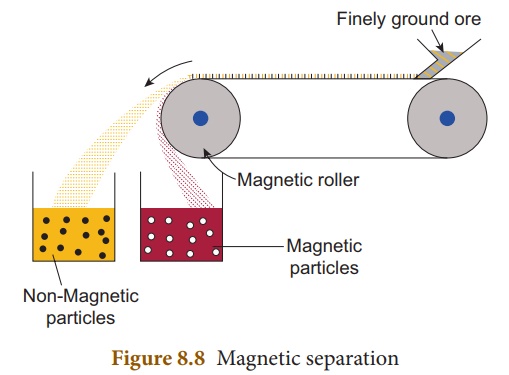
Method: The crushed ore is
placed over a conveyer belt which rotates around two metal wheels, one of which
is magnetic. The magnetic particles are attracted to the magnetic wheel and
fall separately apart from the non- magnetic particles.
(iii) Froth floatation
Principle:
This process depends on
the preferential wettability of the ore with oil (pine oil) and the gangue
particles by water. Lighter ores, such as sulphide ores, are concentrated by
this method. e.g., Zinc blende (ZnS).
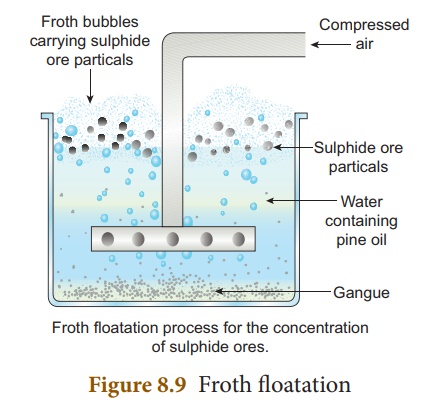
Method:
The crushed ore is taken
in a large tank containing oil and water and agitated with a current of
compressed air. The ore is wetted by the oil and gets separated from the gangue
in the form of froth. Since the ore is lighter, it comes on the surface with
the froth and the impurities are left behind. e.g., Zinc blende (ZnS).
(iv) Chemical method or Leaching
This method is employed
when the ore is in a very pure form.
Extraction of metal from metal oxide can be categorized into three types.

The ore is treated with
a suitable reagent such that the ore is soluble in it but the impurities are
not. The impurities are removed by filtration. The solution of the ore, ie.,
the filtrate is treated with a suitable reagent which precipitates the ore.
E.g. Bauxite Al2O3.2H2O, the ore of aluminium.
Related Topics