Occurrence of Ores, Physical and Chemical Properties, Uses - Extractive Metallurgy of Iron | 10th Science : Chapter 8 : Periodic Classification of Elements
Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 8 : Periodic Classification of Elements
Extractive Metallurgy of Iron
EXTRACTIVE METALLURGY OF
IRON
Occurrence:
Iron is the second most
abundant metal available next to aluminium. It occurs in nature as oxides,
sulphides and carbonates. The ores of iron are as follows:
Ores of iron Formula
Haematite Fe2O3
Magnetite Fe3O4
Iron pyrite FeS2
Iron is chiefly
extracted from haematite ore (Fe2O3)
i. Concentration by Gravity Separation: The powdered ore
is washed with a steam of water. As a result, the lighter sand particles and
other impurities are washed away and the heavier ore particles settle down.
ii. Roasting and
Calcination: The concentrated ore is strongly heated in a limited supply
of air in a reverberatory furnace. As a result, moisture is driven out and
sulphur, arsenic and phosphorus impurities are oxidized off.
iii. Smelting (in a Blast
Furnace): The
charge consisting of roasted ore, coke and limestone in the ratio 8:4:1 is
smelted in a blast furnace by introducing it through the cup and cone
arrangement at the top. There are three important regions in the furnace.
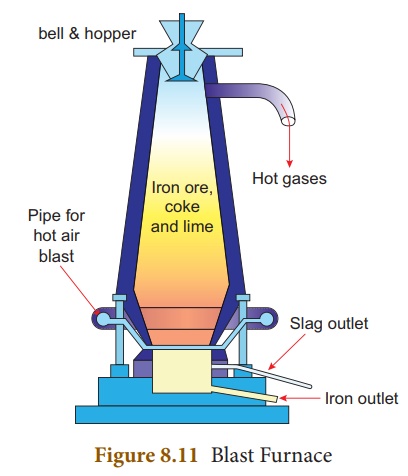
(a) The Lower Region
(Combustion Zone)-The temperature is at 1500°C. In this region, coke burns with
oxygen to form CO2 when the charge comes in contact with a hot blast
of air.
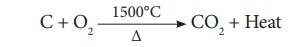
It is an exothermic
reaction since heat is liberated.
(b) The Middle Region
(Fusion Zone) – The temperature prevails at 1000°C. In this region, CO2
is reduced to CO.
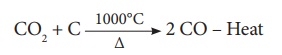
Limestone decomposes to
calcium oxide and CO2.

These two reactions are
endothermic due to absorption of heat. Calcium oxide combines with silica to
form calcium silicate slag.
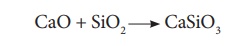
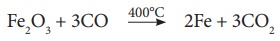
(c) The Upper Region
(Reduction Zone)- The temperature prevails at 400°C . In this region carbon
monoxide reduces ferric oxide to form a fairly pure spongy iron.
The molten iron is
collected at the bottom of the furnace after removing the slag.
The iron thus formed is
called pig iron. It is remelted and cast into different moulds. This iron is
called cast iron.
Physical properties:
·
It is a lustrous metal, greyish white in colour.
·
It has high tensility, malleability and ductility.
·
It can be magnetized.
Chemical properties:
i. Reaction with air or oxygen: Only on heating in air, iron forms
magnetic oxide.
3Fe + 2 O2 → Fe3O4 (black)
ii. Reaction with moist air: When iron is exposed to moist air, it
forms a layer of brown hydrated ferric oxide on its surface. This compound is
known as rust and the phenomenon of formation of rust is known as rusting.
4 Fe+ 3 O2 +
x H2O →2 Fe2O3 . xH2O(rust)
iii. Reaction with steam: When steam is passed over red hot iron,
magnetic oxide is formed.
3Fe + 4 H2O (steam) → Fe3O4
+ 4 H2 ↑
iv. Reaction with chlorine: Iron combines with chlorine to form
ferric chloride.
2Fe + 3Cl2 → 2FeCl3
(ferric chloride)
v. Reaction with acids: With dilute HCl and dilute H2SO4
it liberates H2 gas.
Fe + 2HCl → FeCl2
+ H2 ↑
Fe + H2SO4
→ FeSO4 + H2 ↑
With dilute HNO3
in cold condition it gives ferrous nitrate.
4 Fe + 10 HNO3
→ 4 Fe(NO3)2 + NH4NO3 + 3 H2O
With con. H2SO4
it forms ferric sulphate.
2 Fe + 6 H2SO4
→ Fe2(SO4)3 + 3 SO2 + 6 H2O
When iron is dipped in
con. HNO3 it becomes chemically passive or inert due to the
formation of a layer of iron oxide (Fe3O4) on its
surface.
Uses of iron
Pig iron (Iron with 2-4.5% of
carbon): It is used in making pipes, stoves, radiators, railings,
manhole covers and drain pipes.
Steel (Iron with < 0.25% of
carbon): It is used in the construction of buildings, machinery,
transmission cables and T.V towers and in making alloys.
Wrought iron (Iron with 0.25-2% of
wraught carbon): It is used in making springs, anchors and
electromagnets.
Related Topics