Ores, Physical and Chemical Properties, Uses - Extractive Metallurgy of Aluminium | 10th Science : Chapter 8 : Periodic Classification of Elements
Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 8 : Periodic Classification of Elements
Extractive Metallurgy of Aluminium
EXTRACTIVE METALLURGY OF
ALUMINIUM
Aluminium is the metal
found most abundantly in the Earth’s crust. Since it is a reactive metal, it
occurs in the combined state. The important ores of aluminium are as follows
Ores of Aluminium Formula
Bauxite Al2O3.2H2O
Cryolite Na3AlF6
Corundum Al2O3
Bauxite is the chief ore
of aluminium. The extraction of aluminium from bauxite involves two steps:
(i) Conversion of bauxite into alumina – Baeyer’s Process
The conversion of
Bauxite into Alumina involves the following steps:
Bauxite ore is finely
ground and heated under pressure with a solution of concentrated caustic soda
solution at 150° C to obtain sodium meta aluminate.
On diluting sodium meta
aluminate with water, a precipitate of aluminium hydroxide is formed.
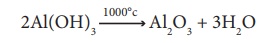
The precipitate is
filtered, washed, dried and ignited at 1000°C to get alumina.
![]()
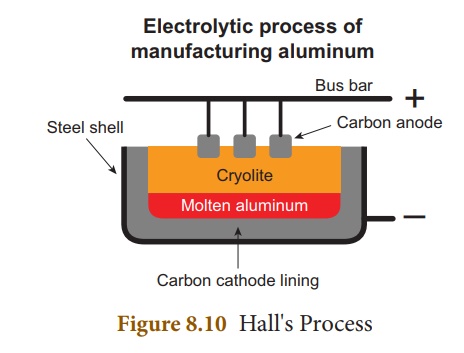
(ii) Electrolytic reduction of alumina – Hall’s Process
Aluminium is produced by
the electrolytic reduction of fused alumina (Al2O3) in
the electrolytic cell.
Cathode: Iron tank linked with
graphite
Anode: A bunch of graphite
rods suspended in molten electrolyte.
Electrolyte: Pure alumina+ molten cryolite + fluorspar
(fluorspar lowers the fusion temperature of electrolyte)
Temperature: 900 - 950 °C
Voltage used: 5-6 V
Overall reaction: 2 Al2O3
→ 4 Al +3 O2↑
Aluminium is deposited
at the cathode and oxygen gas is liberated at the anode. Oxygen combines with
graphite to form CO2.
Physical Properties of Aluminium
·
It is a silvery white metal
·
It has low density (2.7) and it is light
·
It is malleable and ductile
·
It is a good conductor of heat and electricity.
·
Its melting point is 660 °C.
·
It can be polished to produce a shiny attractive appearance.
Chemical Properties of Aluminium
i. Reaction with air: It is not affected by dry air. On heating
at 800 °C, aluminium burns very brightly forming it’s oxide and nitride.
4 Al + 3 O2 →
2 Al2O3(Aluminium oxide)
2
Al + N2 → 2 AlN (Aluminium nitride)
ii. Reaction with water: Water does not react with aluminium due
to the layer of oxide on it. When steam is passed over red hot aluminium,
hydrogen is produced.
2 Al + 3 H2O → Al2O3 + 3 H2↑
iii. Reaction with alkalis: It reacts with strong caustic alkalis
forming aluminates.
2 Al + 2 NaOH +2 H2O → 2 NaAlO2 + 3 H2↑ (Sodium meta aluminate)
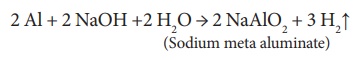
iv. Reaction with acids:
With dilute and con. HCl it liberates H2 gas.
2 Al + 6 HCl → 2 AlCl3 + 3 H2↑
(Aluminium chloride)

Aluminium liberates
hydrogen on reaction with dilute sulphuric acid. Sulphur dioxide is liberated
with hot concentrated sulphuric acid
2 Al+ 3 H2SO4
→ Al2(SO4)3 + 3 H2
2 Al + 6 H2SO4
→ Al2(SO4)3 + 6 H2O + 3 SO2
↑
v. As reducing agent: Aluminium is a powerful
reducing agent. When a mixture of aluminium powder and iron oxide is ignited,
the latter is reduced to metal. This process is known as aluminothermic
process.
Fe2O3
+ 2 Al → 2 Fe + Al2O3 + Heat.
Uses
Aluminium is used in
·
household utensils
·
electrical cable industry
·
making aeroplanes and other industrial mechine parts
Related Topics