Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio zoology Human Body higher secondary school
Mechanism of hearing - Human Ear
Mechanism of hearing
Functions of External Ear :- Sound waves enter the external auditory meatus, pass along the external eustachian canal and fall on the tympanic membrane (TM). This causes the TM to vibrate.
Functions of Middle Ear :- The middle ear is an air filled cavity in the temporal bone which opens via the eustachian tube into the nasopharynx. The auditory tube opens during chewing, swallowing and yawning thus keep-ing the pressures on both sides of the tympanic membrane equal.
The three auditory ossicles are localised in the middle ear. Of these, the malleus is attached to the TM, and the stapes to the membranous oval window on the medial wall. Incus articulates with these two bones. Thus vibrations of the TM are transmitted to the oval window. As the TM has an area of 90mm2 and the foot plate of the stapes 3.2mm2 and the lever system formed by the ossicles multiplies the force 1.3 times.
The vibrations of the oval window generate pressure waves in the fluid filling the vestibular canal. The pressure waves pass to the median canal and vibrate the basilar membrane. The tympanic canal is connected to a circular membrane called the round window just beneath the oval window. This arragement allows the pressure waves to transmit through the cochlear fluid.
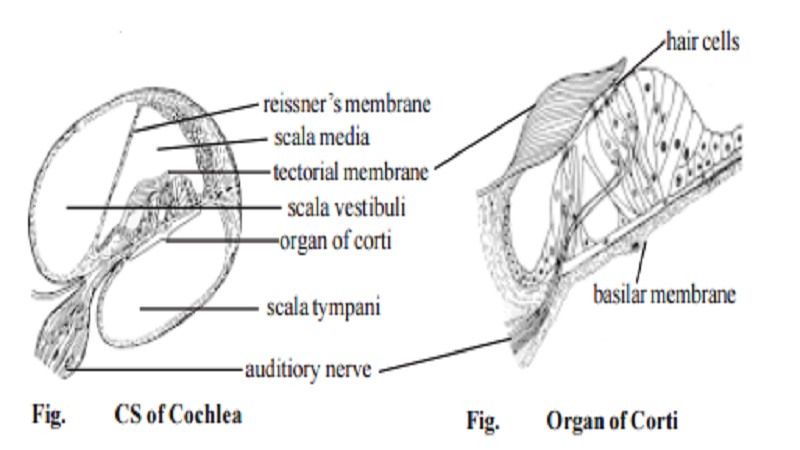
Functions of Cochlea :- The inner ear (labyrinth) is made up of the cochlea and the vestibule. The cochlear portion of the labyrinth is a tubule coiled 2.75 times. Throughout its length the cochlea is divided into three compartments by the basilar and the Reissner's membranes. The middle compartment (scala media) contains endolymph and the other two (scala vestibuli & scala tympani) contain perilymph.
Organ of Corti :
Located on the basilar membrane is the Organ of Corti which contains the auditory receptors. Four rows of hair cells arise from the basilar
membrane.
Stimulation of hair cells :- Movements of the foot plate of the stapes set up a series of waves in the perilymph of the scala vestibuli. This in turn causes vibrations of the vestibular membrane and hence of the endolymph in the scala media. These waves deflect the Reissner's membrane and this in turn produces disturbances in the basilar membrane which bend the hairs of hair cells in the organ of Corti. This leads to development of action potentials in the related nerve fibres which are transmitted along the auditory nerve.
The site of maximum distortion in the organ of Corti is determined by the frequency of sound, for high pitched sounds the maximum height of the waves is near the base of the cochlea and for low pitched near the apex. The extent of distortion is determined by the loudness of the sound. Interpretation of these impulses is made in the auditory cortex.
Sound waves � vibrate tymphanic membrane � movements in ear ossicle chain � vibration of oval window � waves in perilymph (scala vestibuli) � waves in endolymph � deflection in the Reissner's membrane � basilar membrane disturbed � bending of hair cells � action potential � transmission by auditory nerve.
Related Topics