Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 11 : Transport in Plants
Measurement and Significance of transpiration in Plants
Measurement of Transpiration
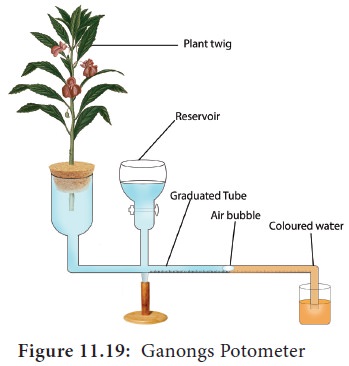
1. Ganongs potometer
Ganongs
potometer is used to measure the rate of transpiration indirectly. In this, the
amount of water absorbed is measured and assumed that this amount is equal to
the amount of water transpired.
Apparatus consists of a horizontal graduated tube which is bent in opposite directions at the ends. One bent end is wide and the other is narrow. A reservoir is fixed to the horizontal tube near the wider end. The reservoir has a stopcock to regulate water flow. The apparatus is filled with water from reservoir. A twig or a small plant is fixed to the wider arm through a split cock. The other bent end of the horizontal tube is dipped into a beaker containing coloured water. An air bubble is introduced into the graduated tube at the narrow end (Figure 11.19). keep this apparatus in bright sunlight and observe.As transpiration takes place, the air bubble will move towards the twig. The loss is compensated by water absorption through the xylem portion of the twig. Thus, the rate of water absorption is equal to the rate of transpiration.
2. Cobalt chloride (CoCl2) paper method
Select a
healthy dorsiventral leaf and clean its upper and lower surface with dry
cotton. Now place a dry Cobalt chloride (CoCl2)
strips on both surface and immediately cover the paper with glass slides and
immobilize them. It will be observed after some time that the CoCl2
strip of lower epidermis turns pink. This indicates that CoCl2
becomes hydrated (CoCl2.2H2O or CoCl2.4H2O)
due to water vapours coming out through stomata. The rate of transpiration is
more on the lower surface than in the upper surface of the dorsiventral leaf.
Significance of transpiration
Transpiration
leads to loss of water, as stated earlier in this lesson 95% of absorbed water
is lost in transpiration. It seems to be an evil process to plants. However,
number of process like absorption of water, ascent of sap and mineral
absorption directly relay on the transpiration. Moreover plants withstand
against scorching sunlight due to transpiration. Hence the transpiration is a “necessary evil” as stated by Curtis.
Related Topics