Transport in Plants - Guttation | 11th Botany : Chapter 11 : Transport in Plants
Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 11 : Transport in Plants
Guttation
Guttation
During high humidity in the atmosphere, the rate of transpiration is much reduced. When plants absorb water in such a condition root pressure is developed due to excess water within the plant. Thus excess water exudates as liquid from the edges of the leaves and is called guttation. Example: Grasses, tomato, potato, brinjal and Alocasia. Guttation occurs through stomata like pores called hydathodes generally present in plants that grow in moist and shady places. Pores are present over a mass of loosely arranged cells with large intercellular spaces called epithem (Figure 11.18). This mass of tissue lies near vein endings (xylem and Phloem).
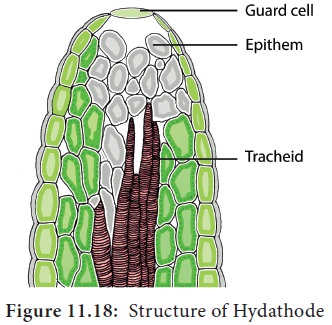
The liquid coming out of hydathode is not pure
water but a solution containing a number of dissolved substances.
Related Topics