Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Management of Patients With Cerebrovascular Disorders
Management of Patients With Cerebrovascular Disorders
Management
of Patients With Cerebrovascular Disorders
Cerebrovascular disorders” is an umbrella term that
refers to any functional abnormality of the central nervous system (CNS) that
occurs when the normal blood supply to the brain is dis-rupted. Stroke is the
primary cerebrovascular disorder in the United States and in the world.
Although preventive efforts have brought about a steady decline in incidence
over the last several years, stroke is still the third leading cause of death.
Approxi-mately 500,000 people experience a new stroke, 100,000 experi-ence a
recurrent stroke, and approximately 160,000 die of a stroke each year. With
over 4 million survivors (2.2 million men and 2.3 million women), stroke is the
leading cause of serious, long-term disability in the United States (American
Heart Asso-ciation, 2000).
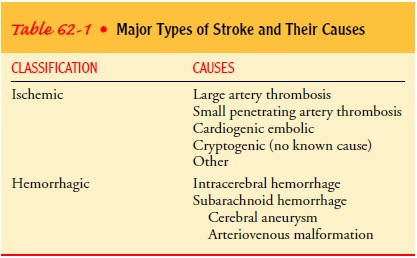
Strokes can be divided into two major categories:
ischemic (85%), in which vascular occlusion and significant hypoperfu-sion occur,
and hemorrhagic (15%), in which there is extravasa-tion of blood into the brain
(American Heart Association, 2000). Although there are some similarities
between the two broad types of stroke, overall the etiology, pathophysiology,
medical management, surgical management, and nursing care differ. Table 62-1
reviews the major types of ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes.
Related Topics