Chapter: Civil : Soil Mechanics : Soil Classification And Compaction
Major Soil Deposits Of India
MAJOR SOIL DEPOSITS OF INDIA
The soil deposits of India can be broadly classified into the
following five types:
1. Black
cotton soils, occurring in Maharashtra, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh,
Karnataka, parts of Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu. These are expansive
in nature. On account of Fig.Flocculent structure flaky particles and
Dispersed structure high swelling and shrinkage potential these are difficult
soils to deal with in foundation design.
Marine
soils, occurring in a narrow belt all along the coast, especially in
the Rann of Kutch. These are very soft and sometimes contain organic
matter, possess low strength and high compressibility.
3. Desert
soils, occurring in Rajasthan. These are deposited by win d and are
uniformly graded.
4. Alluvial
soils, occurring in the Indo-Gangetic plain, north of the Vind
hyachal ranges.
5. Lateritic
soils, occurri ng in Kerala, South Maharashtra, Karnatak a, Orissa
and West Bengal.
Phases Relationship
The three constituen ts are
blended together to form a complex material. It is also known as block diagram.
D ry soil and saturated soil is known as two ph ase diagram.
Weight
Wt = Ww + Ws + Wg
Volume
Vt = Vv + Vs = Va + Vw + Vs + Vg
1. Volumetric Relation ships
i) Void ratio
It is
defined as the ratio of volume of voids to the volume of soli ds.
e = Vv/Vs; the
void ratio is expressed in decimal.
ii) Porosity (n) or Percentage of
voids
It is
defined as the ratio of the volume of voids to the total volum e.
n = Vv/V; Porosity is expre ssed as percentage & it is not
exceed 100%.
n = e/1+e; e = n/n-1
iii) Degree of Saturation (S)
The degree of saturation (s) is the ratio of the volume of
water to the volume of
voids.
S = Vw/Vv; The
degree of saturation is generally as a percentage . It is equal to zero when
the soil is absolutely dry & 100 % when the soil is fully saturated.
iv) Percentage of air voids (na)
It is defined a s the ratio of the volume of air to the total
v olum, .na = Va/V (it is represented as(%)
v) Air Content (ac)
It is
defined as the ratio of the volume of air to the volume of voids, .ac = Va/Ve,
Air Content is usually expressed
as percentage. Air Content and percentage of air voids are zero when the soil
is saturated.(Va=0)
na = Va/V = Va/Vv .Vv/V
na = n.ac
vi) Water content (w)
The water content (w) is defined as the ratio of the mass of
water to mass of solids.
w = Mw/Ms. It is
also known as moisture content (m); it is expressed as percentage but used as
a decimal computation.
2. Volume Mass Relationships
i) Bulk density (?)
The bulk mass density (?) is defined
as the total mass (m) per unit total volume (v)
? = m/v.It is also known as Bulk mass
density, Bulk density, Wet mass density and density.
It is expressed as kg/m3 , gm/ml (or)
mg/m3
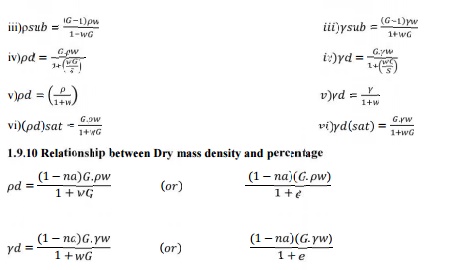
ii) Dry mass density (?d)
The dry density (?d) is defined as
the mass of solids per unit total volume.
?d
=Ms/V
iii)Saturated density(?sat)
Saturated density the bulk mass density of the soil when it is fully
saturated.
?sat=Msat/V
iv)Submerged density
When the soil exists below water
it is submerged conditions. When a volume of v of soil is submerged in water,
it displaces an equal volume of water.
v)Density
of solids
Density of solids is equal to the
ratio of the mass of solids to the volume of solids.
Rs=Ws/Vs
3. Volume-Weight Relationships
i)Bulk unit weight (?)
Bulk unit weight is defined as
total weight per unit total volume.
? =W/V
ii) Dry unit weight (?d)
It is defined as the weight of
soil solids per unit total volume. ?d= Ws/V
iii) Saturated unit weight
The saturated unit
weight is bulk unit weight when the soil is fully saturated. It is defined as weight of saturated soil solids to
the unit total volume. ?sat=Wsat/V
iv) Submerged unit
weight (?')
It is defined as the submerged weight per unit of total
volume.
?? = Wsub/V; ?sat = Wsub-?w
v) Unit weight of soil
solids (?s)
The unit weight of solids (?s) is equal to the ratio of the
weight of solids to the total volume of solids. = ?s= Ws/Vs
4
Specific gravity of solids (G)
i)
The specific gravity of solid particles is defined as the
ratio of the mass of a given volume of solids to the mass of an equal volume of
water @ 4 o C. = G =ps/pw
The specific gravity of
solids for most natural soils is range of 2.65 to 2.80.
ii)
Mass specific gravity (or) apparent specific gravity (or)
Bulk specific gravity
It is defined as the
ratio of the mass density of the soil to the mass density of water.
Gn=p/pw
iii)
Absolute specific gravity (or) True specific gravity
If all the internal
voids of the particles are exclude from the determination the true volume of
solids, then the specific gravity is called as Absolute (or) True specific
gravity.
Ga=(ps)/pw
5.
Density Index (ID)
Relative compactness of
natural soil.
It is varies from 0 to
1
ID= emax - e / emax-emin
. e max = voids ratio
in loosest state ;e min = voids ratio in densest state.
e = natural voids ratio
of deposits; When the natural state of cohesion less soil in the densest form e
= e min, ID = 1.
Relative
Density Density Description
0-15 Very loose
15-35 Loose
35-65 Medium
65-85 Dense
85-100 Very dense

Related Topics