Chapter: Civil : Soil Mechanics : Soil Classification And Compaction
Compaction
Compaction
Compaction
In construction of highway
embankments, earth dams and many other engineering structures, loose soils must
be compacted to improve their strength by increasing their unit weight;
Compaction - Densification of soil by removing air voids using mechanical equipment;
the degree of compaction is measured in terms of its dry unit weight.
1 Objectives for Compaction
Ø Increasing
the bearing capacity of foundations;
Ø Decreasing
the undesirable settlement of structures;
Ø Control
undesirable volume changes;
Ø Reduction
in hydraulic conductivity;
Ø Increasing
the stability of slopes.
In general, soil densification includes compaction
and consolidation.
Compaction is one
kind of densification that is realized by rearrangement of soil particles without
outflow of water. It is realized by application of mechanic energy. It does not
involve fluid flow, but with moisture changing altering.
Consolidation
is
another kind of densification with fluid flow away. Consolidation is primarily
for clayey soils. Water is squeezed out from its pores under load.
CONSOLIDATION
It is a
gradual process of reduction of Volume under sustained, static loading.
It causes
a reduction in volume of a saturated soil due to squeezing out of water from
the soil.
Is a
process which in nature when saturated soil deposits are subjected to static
loads caused by the weight of the building
COMPACTION
It is a
rapid of reduction of volume mechanical mean such as rolling , tamping ,
vibration.
In
compaction, the volume of partially saturated soil decreases of air the voids
at the unaltered water content
Is an
artificial process which is done to increase the density of the soil to improve
its properties before it is put to any use.
2 Compaction Effect
There are 4 control factors affecting the extent of
compaction:
Ø Compaction
effort;
Ø Soil type
and gradation;
Ø Moisture
content; annd
Ø Dry unit
weight (dryy density).
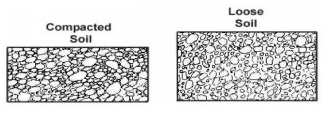
3 Effect of Water on Compaction
In soils, compaction is a funnction of water content
Water added to the soil duri ng compaction acts as a softening
agent on t he soil particles
Ø Consider
0% moistu re - Only compact so much
Ø Add a
little water - compacts better
Ø A little
more water - a little better compaction
Ø Even more
water - Soil
begins to flow
What is better compactionn?
The dry unit weight (?d) inccreases as the moisture
content increases to a point
Beyond a certain moisture
content, any increase in moisture content ten ds to reduce the dry unit weight
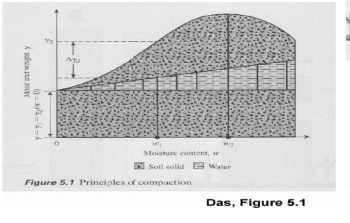
4 Standard Proctor C ompaction Test
The
standard was originall y developed to simulate field compaction in the lab
Purpose:
Find the optimum moisture content
at which the maximum dry unit weig ht is attained ASTM D 698
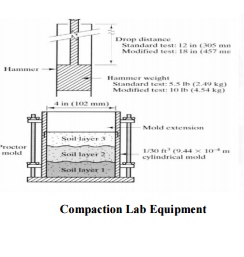
Equipments;
Standard Proctor; 1/30 ft3
mold 5.5 lb hammer; 12' drop
3 layers of soil; 25 blows / l ayer
Compaction Effort is calc ulated with the
following parameters
Mold volume = 1/30 cubic foot Compact in 3 layers
25blows/layer
5.5 lb hammer 12"
drop
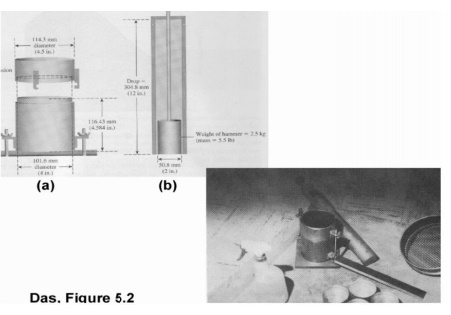
Procedure
1. Obtain 10
lbs of soil pass ing No. 4 sieve
2.
Record the weight of the Proctor mold without the
base and the (c ollar) extension, the volume of which is 1/30 ft3.
3. Assemble
the compactio n apparatus.
4.
Place the soil in the mold in 3 layers and compact
using 25 well dist ributed blows of the Proctor hammer.
5. Detach
the collar without disturbing the soil inside the mold
6. Remove
the base and determine the weight of the mold and compacte d soil.
7.
Remove the compacted soil from the mold and take a
sample (20-30 grams) of soil and find the moisture content
Place the
remainder of th e molded soil into the pan, break it down, and thoroughly remix
it with the other soil, plus 100 additional grams of water.
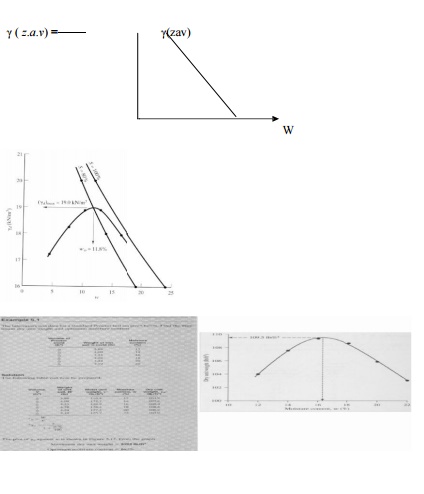
Zero-air-void unit weight:
At
certain water content, w hat is the unit weight to let no air in the voids
It is clear that in the above
equation, specific gravity of the solid and thewater density are constant, the
zero-air-void density is inversely proportional to water content w. For a given
soil and water content the best possible compaction is represented by the
zero-air-voids curve. The actual compaction curve will always be below. For dry
soils the unit weight increases as water is added to the soil because the water
lubricates t he particles making compaction easier. As moree water is added and
the water content is larg er than the optimum value, the void spaces be come
filled with water so further compac tion is not possible because water is a
kind like incompressible fluid. This is illustrated by t he shape of the
zero-air-voids curve which decre ases as water content increases.
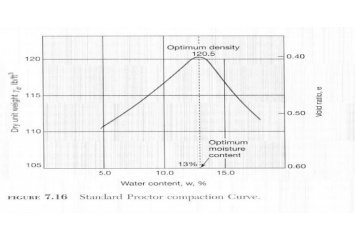
Compaction Curve
Compaction curve
plotted ?d vs. w.The peak of the
curve is the Maxim um Compaction (?d max) at Optimum Moisture Content
(wopt )
Results
Plot of dry unit weight vs m oisture content
Find
?d (max) and w and Plot
Zero-Air-Void unit weight (only S=100% )
5 Effect of Compacti on Energy
With the development of heavy
rollers and their uses in field compaction, the Standard Proctor Test was
modified t o better represent field compaction
As the compaction effort increases,
The maximum dry unit w eight of
compaction increase; the optimum moisture content decreases to some extend
Compaction energy per unit volume.
6 Compaction adopte d in the field
i) Tampers.
A hand operated tamper consists
of block iron, about 3 to 5 Kg mass, a ttached to a wooden rod. The tamper is
lifted for about 0.30m and dropped on the soil to be compressed. Mechanical
Tampers operatted by compressed air or gasoline power.
ii) Rollers
a) smooth - wheel
rollers
b) pneumatic
- tyred
rollers
c) Sheep-
foot rollers.
a) Smooth - wheel
rollers
Smooth - wheel
rollers ar e useful finishing operations after compaction of fillers and for
compacting granular base causes of highways.
b) Pnumatic - tyred
roller s
Pneumatic - tyred
rollers u se compressed air to develop the required in flation pressure.The
roller compactive the soil primarily by kneading action. These rolle srs are
effecting for compacting cohesive as we ll as cohesion less soils.
c) Sheep - foot
rollers
The sheep - foot roller con sists of a hollow drum with a large number of small projections (known as feet) on its surf ace. The drums are mounted on a steel frame. The drum can fill with water or ballast incre ases the mass. The contact pressure is gener ally between 700 to 4200 KN/m2.
Related Topics