Chapter: 10th Social Science : Geography : Chapter 3 : India - Agriculture
Major Crops Cultivated in India
Major Crops Cultivated in India
The major
crops of India are divided into four major categories as follows:
1. Food crops (wheat, maize, rice, millets, pulses
etc.).
2. Cash crops (sugarcane, tobacco, cotton, jute,
oilseeds etc.).
3. Plantation crops (tea, coffee and rubber).
4. Horticulture crops (fruits, flowers and
vegetables).
1. Food Crops
Due to
its large population, Indian agriculture is largely dominated by the food
crops.
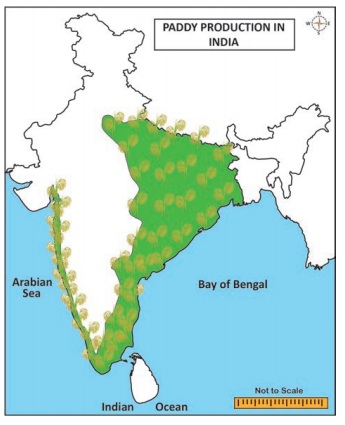
Rice
Rice is an indigenous crop. India is the second
largest producer of rice in the world after China. It is mainly a tropical
crop, growing mainly with mean temperatures of 24°C and annual rainfall of 150
cm. Deep fertile clayey or loamy soils are suited well for rice cultivation. It
also needs abundant supply of cheap labour.

Rice in
India is sown in three ways:
i) Broadcasting,
ii Ploughing or drilling
iii) Transplanting
Due to increased use of High Yielding Variety (HYV)
seeds (CR Dhan 205, AR Dhan 306, CRR 451 etc.), many of the indigenous
varieties were disappeared. In 2016, the first 10 leading rice producing states
are West Bengal (First in India) Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Tamil Nadu, Andhra
Pradesh, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Assam, and Haryana.
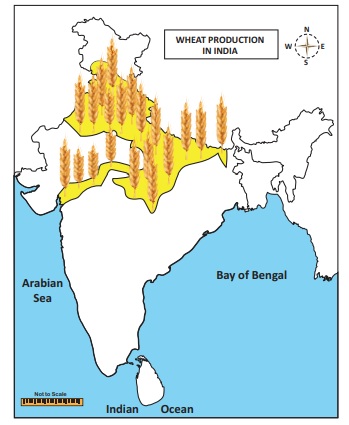
Wheat
Wheat is the second most important food crop of the
country, after rice. It accounts for 22 percent of the total area and 34
percent of the total production of food grains in the country. It requires 10-15°C
at the time of sowing and 20-25°C at the time of ripening of grains.
Over 85% of the India’s wheat production comes from
5 states namely Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh.
Apart from these regions, the black soil tract of the Deccan covering parts of
Maharashtra and Gujarat also contribute a major wheat production.
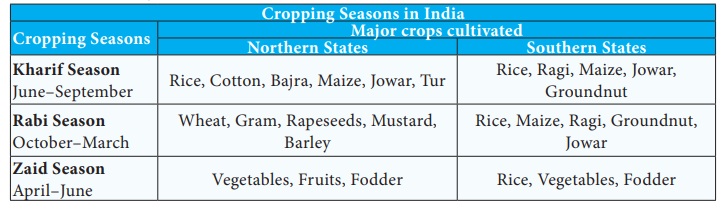
Cropping Seasons in India
Kharif Season June–September: Rice, Cotton, Bajra, Maize, Jowar, Tur Rice, Ragi, Maize, Jowar, Groundnut
Rabi Season October–March: Wheat, Gram, Rapeseeds, Mustard, Barley, Rice, Maize, Ragi, Groundnut, Jowar
Zaid Season April–June: Vegetables, Fruits, Fodder Rice, Vegetables, Fodder
Jowar
Jowar is
the third important food crop of our country. It is an indigenous plant of
Africa. The plant has a tendency to grow in adverse climatic conditions. Its
grains are rich in carbohydrates, protein, minerals, and vitamins. Hence, it
provides cheap food to the large section of the poor population. It is also
used as fodder in many parts of the country. Jowar is essentially a crop of the
Peninsular India. Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Madhya Pradesh are the leading
producers of Jowar.
Bajra
Bajra is
an indigenous plant of Africa. This forms the staple food for poor people. Its
stalks are used as fodder for cattle and for thatching purposes. Bajra is a
crop of dry region. Rajasthan is the largest producer of bajra followed by
Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Gujarat and Maharashtra.
Barley
Barley is
one of the important cereals of our country. Besides, being poor man’s diet, it
is used for making barley water, beer and whiskey. Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh
are the two leading producers of Barley.
Pulses
Pulses
include a large number of crops which are mostly leguminous and rich in
vegetable protein. They are used as human food and feeding cattle. They fix
atmospheric nitrogen in the soil and hence are usually rotated with other
crops. India is the largest producer of pulses.
2. Cash Crops
The crops which are cultivated for commercial
purpose are called cash crops. These crops include sugarcane, tobacco, fibre
crops (cotton, jute, and mesta) and oilseeds.
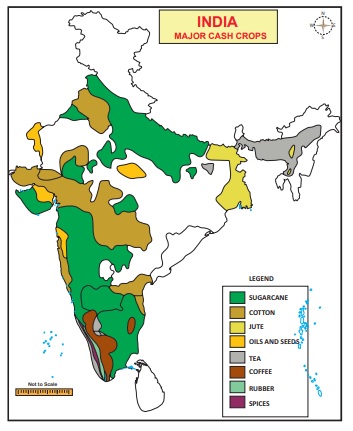
Sugarcane
It is the
second largest producer in the world. This crop provides raw material for the
sugar industry which is the second largest industrial category of our country.
Besides providing sugar, gur and khandsari, it supplies molasses for alcohol
industry and bagasse for paper industry. India is ranked third in sugar
production in the world after Cuba and Brazil. At the state level, Uttar
Pradesh is the leading producer of sugarcane followed by Maharashtra,
Karnataka, Tamil Nadu and Gujarat.
Cotton
Cotton is
the most important cash crop of India. It provides raw material to the largest
industry of India. India ranks second next to China in the production of
cotton.
About 79% of the total area and production in the
country were contributed by four states viz., Gujarat, Maharashtra, Andhra
Pradesh and Punjab.
Jute
It is a tropical fibre crops, grows well in the alluvial soil. It provides raw material for Jute industry. It is used for manufacturing of gunny bags, carpets, hessian, ropes and strings, rugs, clothes, tarpaulins, upholstery etc. West Bengal is the leading state both in cultivation and production of jute. The other cultivators of jute are Bihar, Assam and Meghalaya.
Oil Seeds
Oil
seeds, the premier source of fat in the Indian diet are derived from number of
crops like groundnut, rapeseed, mustard, sesame, linseed, sunflower, castor
seed, cotton seed, niger seed etc. These provide oil and oilcake which are used
for making lubricants, varnish, medicine, perfume, candles, soaps, manure and
cattle feed. Gujarat is India’s largest oilseeds producing state. In groundnut
production, India is the second largest producer in the world after China.
3. Plantation Crops
Plantation crops are cultivated for the purpose of
exports. These are cultivated in large estates on hilly slopes. Tea, coffee,
rubber and spices are the major plantation crops of India.
Tea
Tea is an
evergreen plant that mainly grows in tropical and subtropical climates. Tea is
a labour intensive and grows faster under light shade. Tea plants require high
rainfall but its root cannot tolerate water logging. Two major varieties of tea
are cultivated in India. They are
i) BOHEA
- originated from China
ii) ASSAMICA
- from India
A number of hybrid varieties have been developed by
mixing these two. India is the second largest producer of tea after China in
the world. Assam is the larger producer of tea in India. Other states are Tamil
Nadu, Kerala and West Bengal.
Coffee
Coffee is
grown in shade and it grows effectively in the altitudes between 1,000 and
1,500 m above mean sea level. There are two main varieties of coffee. They are
i) Arabica
(High quality-cultivated more in India)
ii) Robusta
(Inferior quality).
India is
the 7th largest producer of coffee globally. Karnataka is the leading producer
of coffee in India. It produces 71% in India, and 2.5 % in the world (source;
coffee board of India-2018).
Rubber
Rubber
plantation were first established in Kerala in 1902. It needs hot and wet
climatic conditions (temperature above 20°C and rainfall above 300cm). Most of
the land under rubber belongs to small land holders. The major rubber growing
areas are Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka and Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Spices
India has
been world famous for its spices since ancient times. These spices mostly used
for flavouring or tampering cooked food and for preparing medicines, dyes etc.
Pepper, chillies, turmeric, ginger, cardamom, clove and areca nut are the major
spices cultivated in India. Kerala is the leading producer of spices in India.
4. Horticulture Crops
It refers to the cultivation of fruits, flowers and
vegetables. Fruits and vegetables are important supplement to the human diet,
as they provide essential minerals, vitamins, and fibres required for
maintaining health. India is in the second position in the production of fruits
and vegetables.
Related Topics