India | Geography - Agriculture | 10th Social Science : Geography : Chapter 3 : India - Agriculture
Chapter: 10th Social Science : Geography : Chapter 3 : India - Agriculture
Agriculture
Agriculture
Agriculture is the process of producing food for people, fodder for cattle, fiber and many other desired products by the cultivation of certain plants and the raising of domesticated animals (livestock).
Determinants of Agriculture
Agriculture in India is determined by a set of factors. Some of the important factors:
1. Physical factors: relief, climate and soil.
2. Institutional factors: Size of farm holdings, land tenure, and land reforms.
3. Infrastructural factors: Irrigation, power, transport, credit, market, insurance and storage facilities.
4. Technological factors: High yielding varieties of seeds, chemical fertilisers, insecticides and machinery.
Types of Farming
a) Subsistence Farming
A considerable proportion of farmers in the country practice subsistence farming. Farmers grow crops with the help of family members and consumes almost the entire farm produce with little surplus to sell in the market. Preference is given to food crops. In addition to the food crops, sugarcane, oilseeds, cotton, jute and tobacco are also cultivated. Traditional farming method results in low productivity.
b) Shifting Agriculture
This type of agriculture is performed by tribal people in a piece of forest land after clearing the trees through felling and burning the trunks and branches. Once the land is cleared, crops are grown for two to three years and the land will get abandoned as the fertility of the soil decreases. The farmers then move to new areas and the process will be repeated. They cultivate some grains and vegetable crops using the manual labour. It is also called as “Slash and burn” cultivation.
Different names of shifting agriculture in different regions in India
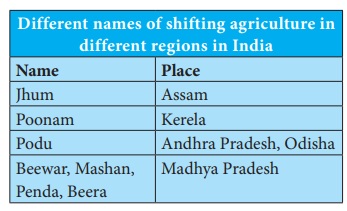
Name: Place
Jhum: Assam
Poonam: Kerela
Podu: Andhra Pradesh, Odisha
Beewar, Mashan, Penda, Beera: Madhya Pradesh
c) Intensive Farming
Intensive farming is an agricultural intensification and mechanization system that aims to maximize yields from available land through various means, such as heavy use of pesticides and chemical fertilizers.
d) Dry Farming
This type of farming is practiced in arid areas where irrigation facilities are lacking. Crops cultivated in these areas can withstand dry conditions. The crops grown generally with the help of irrigation are also grown under dry farming. In such circumstances, the yields are generally low. Most of the areas under dry cultivation entertain only one crop per year.
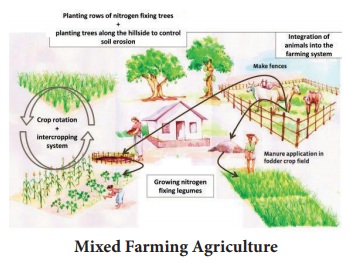
e) Mixed Farming
Mixed farming is defined as a system of farm which includes crop production, raising livestock, poultry, fisheries, bee keeping etc. to sustain and satisfy as many needs of the farmer as possible.
f) Terrace Farming
This type of cultivation is practiced specially in hilly areas, where lands are of sloping nature. The hill and mountain slopes are cut to form terraces and the land is used in the same way as in permanent agriculture. Since the availability of flat land is limited, terraces are made to provide small patches of level land. Soil erosion is also checked due to terrace formation on hill slopes.
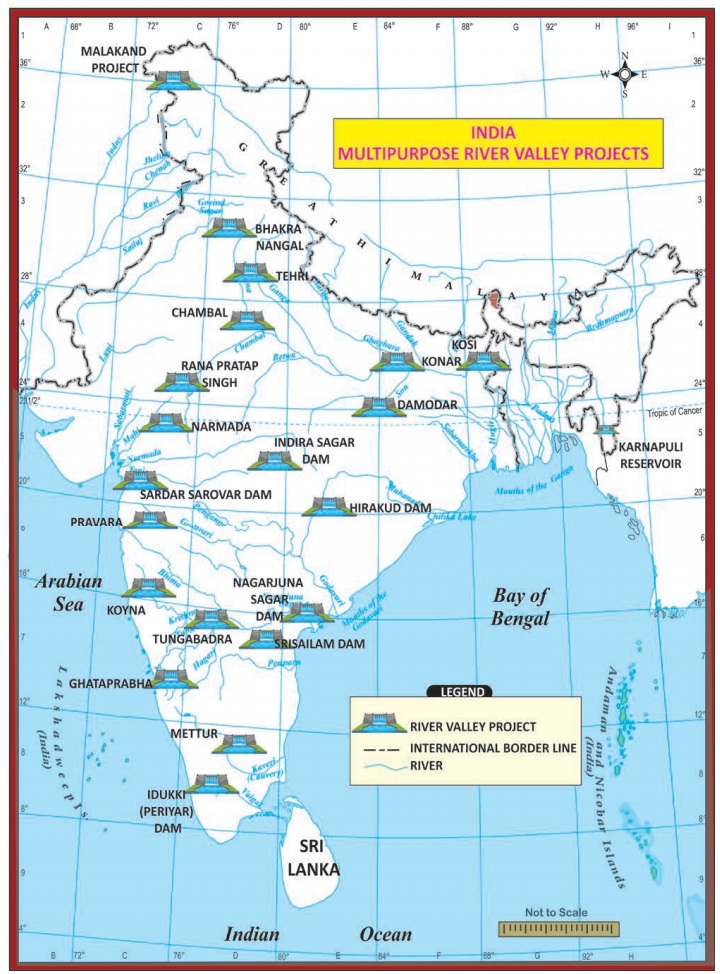
Name of projects - River -Benefit States
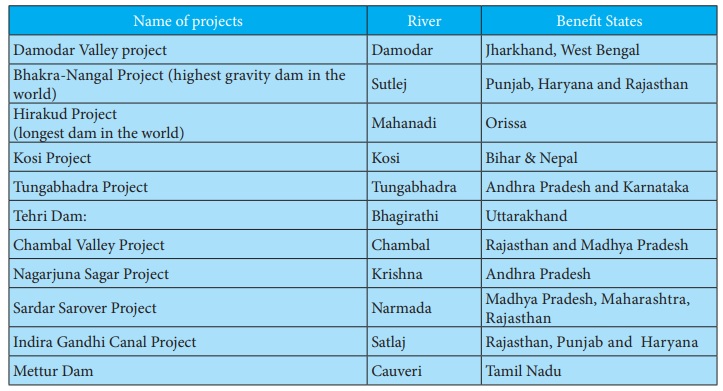
Damodar Valley project: Damodar - Jharkhand, West Bengal
Bhakra-Nangal Project (highest gravity dam in the world): Sutlej - Punjab, Haryana and Rajasthan
Hirakud Project (longest dam in the world) : Mahanadi - Orissa
Kosi Project: Kosi - Bihar & Nepal
Tungabhadra Project: Tungabhadra - Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka
Tehri Dam: Bhagirathi - Uttarakhand
Chambal Valley Project: Chambal - Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh
Nagarjuna Sagar Project: Krishna - Andhra Pradesh
Sardar Sarover Project: Narmada - Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan
Indira Gandhi Canal Project: Satlaj - Rajasthan, Punjab and Haryana
Mettur Dam: Cauveri - Tamil Nadu
Related Topics