Chapter: 11th Home Science : Chapter 5 : Nutrition
Macronutrients
MACRONUTRIENTS
Macronutrients refer to the nutrients that are
needed in large quantities. They are broadly classified as carbohydrates,
pro-tein and lipids/fats.
1. Carbohydrates
Definition: Carbohydrates are
sug-ars or polymers of sugars such as starch that can be hydrolyzed to sim-ple
sugars by the action of digestive enzymes or by heating with dilute acids.
Generally but not always, the hydrogen and oxygen in them are in proportion to
form water, hence the term carbohydrate.
The predominant function of the carbohydrates
is to provide energy needed by our body. Starch found in cereals and sugar in
sugarcane and fruits are examples of carbohydrates in foods.
Classification: The dietary
carbohy-drates are classified as:
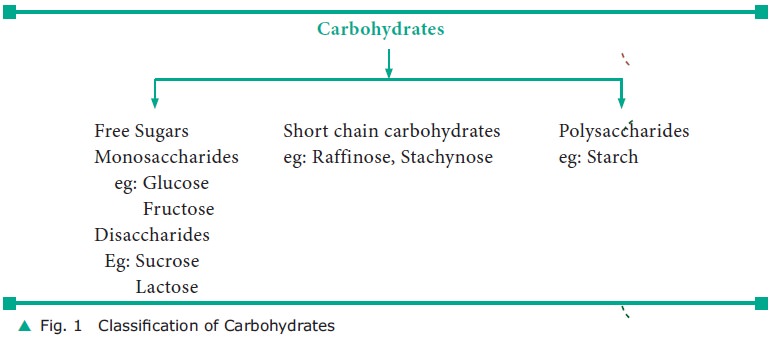
·
Functions: The functions of
carbohy-drates include
·
Carbohydrates are a source of energy. Each gram of carbohydrate
yields 4 kilo calories
·
Adequate supply of carbohydrate ensures that proteins are spared
from performing the role of giving energy.
·
Major source of energy for muscu-lar work.
·
Detoxifying action and regulating influence of protein and fat
metab-olism.

·
Source of energy for heart muscle
·
Excess calories through carbohy-drate is stored as fat in the
adipose tissue.
·
Stimulates the peristaltic move-ment in the form of dietary
fiber which helps in preventing heart diseases, diabetes mellitus and cancer.
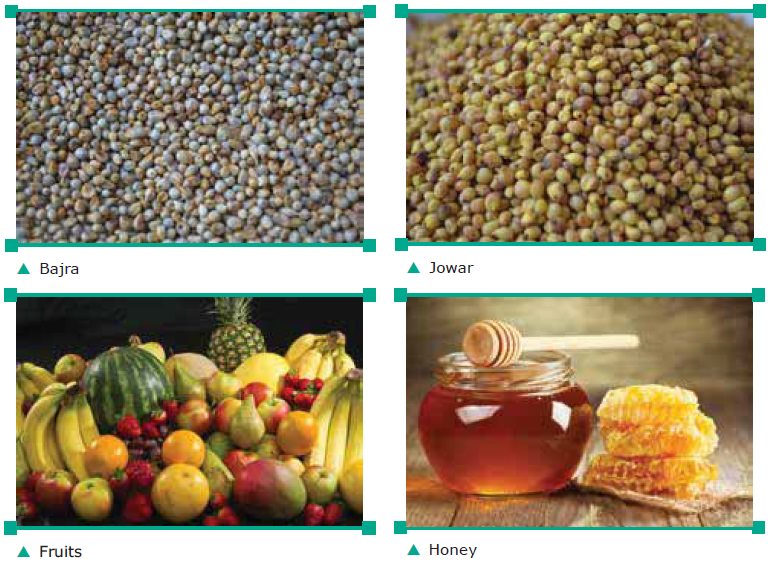
Food Sources: Carbohydrates are found in cereals like Rice, Wheat, Bajra, Jowar. Fruits, Honey
and Jag-gery are also rich sources of carbohy-drates


2. Proteins:
Definition
The word ‘protein’ is derived from the
Greek word protos meaning ‘first’. Protein is the basic chemical unit of
liv-ing organisms and is essential for nutri-tion, building of new tissues
(growth) and maintaining and repairing of those already built. Casein from
milk, albu-min in egg and gluten in wheat, are examples of proteins occurring
in foods.
Classification: The proteins are classi-fied
as:
Complete proteins e.g. Egg proteins
Partially complete proteins e.g. wheat
proteins
Incomplete proteins e.g. Gelatin or zein
Functions: Proteins perform the
fol-lowing functions;
·
Necessary for growth
·
Wear and tear of human body is repaired
For regular supply of raw materials for the
formation of digestive juices, hormones, plasma proteins, hemo-globin, vitamins
and enzymes.
·
Each gram of protein supplies 4 Kcal of energy
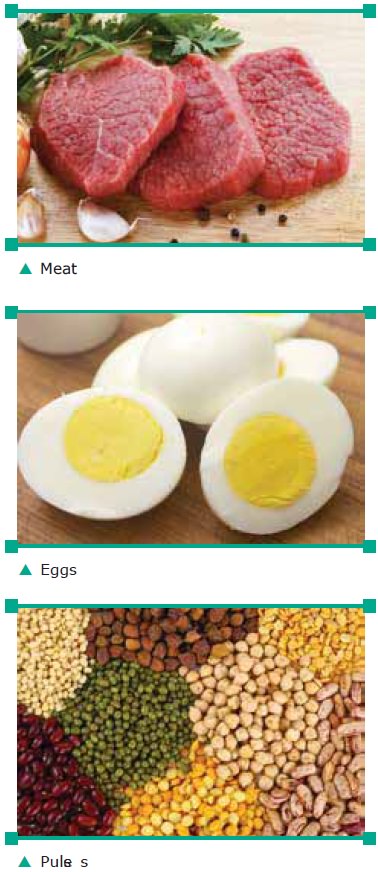
Food Sources: Animal foods like Meat, Fish, Eggs and Milk are excel-lent sources of Proteins.
Plant Sources like Pulses, Oil seeds and nuts are also good sources of Protein

Deficiency: Deficiency of protein causes protein energy malnutrition which covers a wide spectrum
of clini-cal stages ranging from the severe forms like kwashiorkor and marasmus
to the milder forms like growth retardation. Protein energy malnutrition is due
to “food gap” between the intake and requirement. The average energy deficit in
Indian children is 300kcal/day. Defi-ciency of protein is discussed in detail
in the section Protein energy malnutrition
3. Lipids/Fats
Definition: Lipids are organic
sub-stances soluble in fat solvents such as alcohol, ether, and chloroform but
not in water. The term includes fatty acids, soaps, neutral fats,
phospholipids, ste-roids and waxes. Oils found in seeds, butter from milk, and
lard from meat, are examples of fats found in foods.
Classification: Lipids are classified
as follows
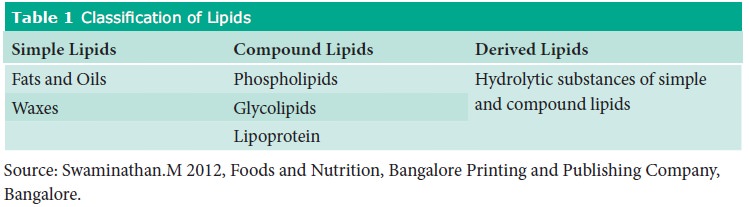
·
Functions: The functions of lipids
are to
·
Provide energy reserve and supply 9 kcal/gram.
·
Serve as a vehicle for the absorp-tion of fat-soluble vitamins
A, D, E, and K
Supply essential fatty acids neces-sary for
growth and function
·
Provide energy source so that pro-teins are spared for tissue
growth and repair
·
Gives satiety
·
Act as insulators against heat and cold.
Food Sources: Visible fat sources
are But-ter, Ghee and Oil, Invisible fat sources are Cereals, Pulses, Oil
seeds, Milk and Egg.



Related Topics