Chapter: Mechanical : Metrology and Measurements : Linear and Angular Measurements
Linear Measuring Instruments
LINEAR MEASURING
INSTRUMENTS
Linear measurement applies to
measurement of lengths, diameter, heights and thickness including external and
internal measurements. The line measuring instruments have series of accurately
spaced lines marked on them e.g. Scale. The dimensions to be measured are
aligned with the graduations of the scale. Linear measuring instruments are
designed either for line measurements or end measurements. In end measuring
instruments, the measurement is taken between two end surfaces as in
micrometers, slip gauges etc.
The
instruments used for linear measurements can be classified as:
1. Direct
measuring instruments
2. Indirect
measuring instruments
The
Direct measuring instruments are of two types:
1. Graduated
2. Non
Graduated
The graduated instruments include rules,
vernier calipers, vernier height gauges, vernier depth gauges, micrometers,
dial indicators etc.
The non graduated instruments include
calipers, trammels, telescopic gauges, surface gauges, straight edges, wire
gauges, screw pitch gauges, radius gauges, thickness gauges, slip gauges etc.
They
can also be classified as
1. Non
precision instruments such as steel rule, calipers etc.,
2. Precision
measuring instruments, such as vernier instruments, micrometers, dial gauges
etc.
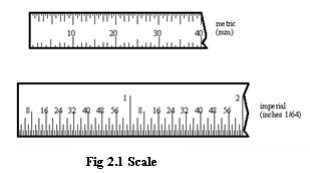
SCALES
·
The most common tool for crude
measurements is the scale (also known as rules, or rulers).
·
Although plastic, wood and other
materials are used for common scales, precision scales use tempered steel
alloys, with graduations scribed onto the surface.
·
These are limited by the human eye.
Basically they are used to compare two dimensions.
·
The metric scales use decimal divisions,
and the imperial scales use fractional divisions.
·
Some scales only use the fine scale
divisions at one end of the scale. It is advised that the end of the scale not
be used for measurement. This is because as they become worn with use, the end
of the scale will no longer be at a `zero' position.
·
Instead the internal divisions of the
scale should be used. Parallax error can be a factor when making measurements
with a scale.
CALIPERS
Caliper is an instrument used for
measuring distance between or over surfaces comparing dimensions of work pieces
with such standards as plug gauges, graduated rules etc. Calipers may be
difficult to use, and they require that the operator follow a few basic rules,
do not force them, they will bend easily, and invalidate measurements made. If
measurements are made using calipers for comparison, one operator should make
all of the measurements (this keeps the feel factor a minimal error source).
These instruments are very useful when dealing with hard to reach locations
that normal measuring instruments cannot reach. Obviously the added step in the
measurement will significantly decrease the accuracy.
VERNIER CALIPERS
The vernier instruments generally used
in workshop and engineering metrology have comparatively low accuracy. The line
of measurement of such instruments does not coincide with the line of scale.
The accuracy therefore depends upon the straightness of the beam and the
squareness of the sliding jaw with respect to the beam. To ensure the
squareness, the sliding jaw must be clamped before taking the reading. The zero
error must also be taken into consideration. Instruments are now available with
a measuring range up to one meter with a scale value of 0.1 or 0.2 mm.
Types
of Vernier Calipers
According to Indian Standard IS:
3651-1974, three types of vernier calipers have been specified to make external
and internal measurements and are shown in figures respectively. All the three
types are made with one scale on the front of the beam for direct reading.
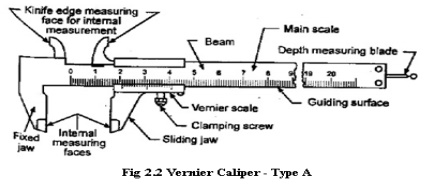
Type A: Vernier
has jaws on both sides for external and internal measurements and a
blade for depth measurement.
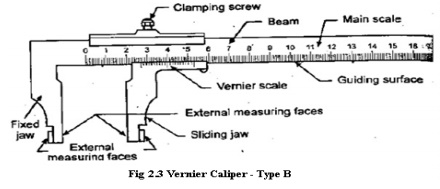
Type B: It
is provided with jaws on one side for external and internal measurements.
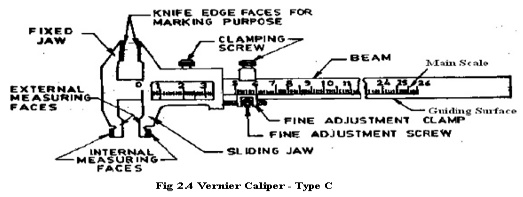
Type C: It has
jaws on both
sides for making
the measurement and
for marking
Operations
Errors
in Calipers
The degree of accuracy obtained in
measurement greatly depends upon the condition of the jaws of the calipers and
a special attention is needed before proceeding for the measurement. The
accuracy and natural wear, and warping of Vernier caliper jaws should be tested
frequently by closing them together tightly and setting them to 0-0 point of
the main and Vernier scales.
MICROMETERS
There
are two types in it.
(i) Outside
micrometer — To measure external dimensions.
(ii)
Inside micrometer — To measure internal
dimensions.
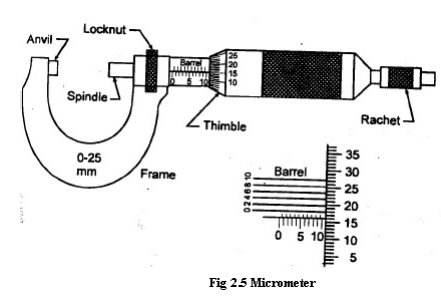
An outside micrometer is shown. It consists of two
scales, main scale and thimble scale. While the pitch of barrel screw is 0.5 mm
the thimble has graduation of 0.01 mm. The least count of this
micrometer is 0.01 mm.
The micrometer requires the use of an
accurate screw thread as a means of obtaining a measurement. The screw is
attached to a spindle and is turned by movement of a thimble or ratchet at the
end. The barrel, which is attached to the frame, acts as a nut to engage the
screw threads, which are accurately made with a pitch of 0.05mm. Each
revolution of the thimble advances the screw 0.05mm. On the barrel a datum line
is graduated with two sets of division marks.
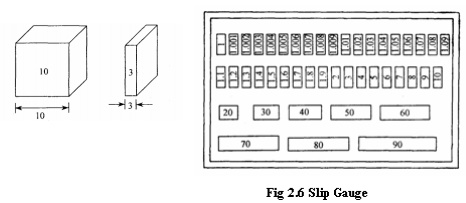
SLIP GAUGES
These may be used as reference standards for
transferring the dimension of the unit of length from the primary standard to
gauge blocks of lower accuracy and for the verification and graduation of
measuring apparatus. These are high carbon steel hardened, ground and lapped
rectangular blocks, having cross sectional area 0f 30 mm 10mm. Their opposite
faces are flat, parallel and are accurately the stated distance apart. The
opposite faces are of such a high degree of surface finish, that when the
blocks are pressed together with a slight twist by hand, they will wring
together. They will remain firmly attached to each other. They are supplied in
sets of 112 pieces down to 32 pieces. Due to properties of slip gauges, they
are built up by, wringing into combination which gives size, varying by steps
of 0.01 mm and the overall accuracy is of the order of 0.00025mm. Slip gauges
with three basic forms are commonly found, these are rectangular, square with
center hole, and square without center hole.
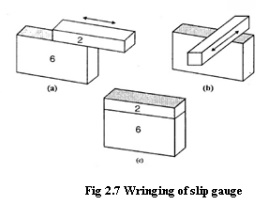
Wringing or Sliding is
nothing but combining the faces of slip gauges one over the other. Due
to adhesion property of slip gauges, they will stick together. This is because
of very high degree of surface finish of the measuring faces.
Classification of Slip Gauges
Slip
gauges are classified into various types according to their use as follows:
1) Grade
2
2) Grade
1
3) Grade
0
4) Grade
00
5) Calibration
grade.
1) Grade
2:
It is a workshop grade slip gauges used
for setting tools, cutters and checking dimensions roughly.
2)
Grade 1:
The
grade I is used for precise work in tool rooms.
3)
Grade 0:
It
is used as inspection grade of slip gauges mainly by inspection department.
4)
Grade 00:
Grade 00 mainly used in high precision
works in the form of error detection in instruments.
5)
Calibration grade:
The actual size of the slip gauge is
calibrated on a chart supplied by the manufactures.
Manufacture
of Slip Gauges
The following additional operations are
carried out to obtain the necessary qualities in slip gauges during
manufacture.
i. First
the approximate size of slip gauges is done by preliminary operations.
ii. The
blocks are hardened and wear resistant by a special heat treatment process.
iii. To
stabilize the whole life of blocks, seasoning process is done.
iv. The
approximate required dimension is done by a final grinding process..
v. To
get the exact size of slip gauges, lapping operation is done.
vi.Comparison
is made with grand master sets.
Slip
Gauges accessories
The application slip gauges can be
increased by providing accessories to the slip gauges. The various accessories
are
· Measuring
jaw
· Scriber
and Centre point.
· Holder
and base
1. Measuring
jaw:
It
is available in two designs specially made for internal and external features.
2.
Scriber and Centre point:
It
is mainly formed for marking purpose.
3.
Holder and base:
Holder is nothing but a holding device
used to hold combination of slip gauges. Base in designed for mounting the
holder rigidly on its top surface.
Related Topics