Chapter: Mechanical : Metrology and Measurements : Linear and Angular Measurements
Sine bar
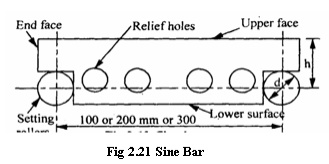
SINE BAR
Sine bars are always used along with
slip gauges as a device for the measurement of angles very precisely. They are
used to
1) Measure
angles very accurately.
2) Locate
the work piece to a given angle with very high precision.
Generally, sine bars
are made from high carbon, high chromium, and corrosion resistant steel. These
materials are highly hardened, ground and stabilized. In sine bars, two
cylinders of equal diameter are attached at lie ends with its axes are mutually
parallel to each other. They are also at equal distance from the upper surface
of the sine bar mostly the distance between the axes of two cylinders is 100mm,
200mm or 300mm. The working surfaces of the rollers are finished to 0.2┬Ąm
R value. The cylindrical holes are provided to reduce the weight of the sine
bar.
Working principle of
sine bar
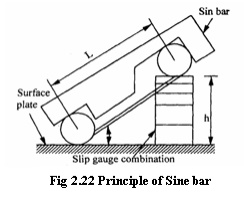
The working of sine bar
is based on trigonometry principle. To measure the angle of a given
specimen, one roller of the sine bar is placed on the surface plate and another
one roller is placed over the surface of slip gauges. Now, ŌĆśh be the he slip
gauges and ŌĆśLŌĆÖ becenters,thenthe angledistancecalculatedas between
Use of Sine Bar
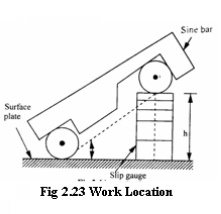
Locating anyŌĆÖ
work to a
given angle
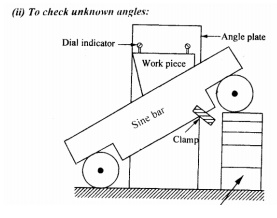
1) Before checking the unknown angle of the
specimen, first the angle (0) of given specimen is found approximately by bevel
protractor.
2) Then
the sine bar
is set at
angle of 0
and clamped on the angle plate.
3) Now, the work is placed on the sine bar
and the dial indicator set at one end of the work is moved across the work
piece and deviation is noted.
4) Slip gauges are adjusted so that the dial
indicator reads zero throughout the work surface.
Limitations
of sine bars
1) Sine
bars are fairly reliable for angles than 15┬░.
2) It
is physically difficult to hold in position.
3) Slight
errors in sine bar cause larger angular errors.
4)
A difference of deformation occurs at
the point of roller contact with the surface plate and to the gauge blocks.
5) The
size of parts to be inspected by sine bar is limited.
Sources
of error in sine bars
The
different sources of errors are listed below:
1) Error
in distance between roller centers.
2) Error
in slip gauge combination.
3) Error
in checking of parallelism.
4) Error
in parallelism of roller axes with each other.
5) Error in flatness of the upper surface of sine bar.
Related Topics