Chapter: Medicine and surgery: Dermatology and soft tissues
Lichen planus - Lichenoid lesions
Lichenoid lesions
Lichen planus
Definition
Lichen planus is pruritic skin disorder causing bluish purple papules involving flexor surfaces, mucous membranes and genitalia symmetrically.
Age
Most common between 30–60 years. Uncommon in very young and very old.
Sex
M = F
Aetiology/pathophysiology
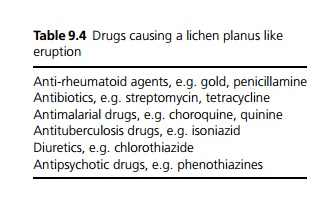
The exact cause is unknown but it is thought that there is a T cell autoimmune reaction to keratinocytes. There is also some evidence of an association with HLA DR1. There is a lichen planus like eruption, associated with many drugs (see Table 9.4).
Clinical features
Patients develop small, flat, polygonal, bluish purple papules often affecting the wrists, shins and lower back. On close inspection there are white, lacy patterns on the surface of the papules; these are termed Wickham’s striae. Patients often describe severe pruritus, and healing results in hyperpigmentation. Hypertrophic lichen planus is a variant with hyper-keratotic plaques seen on the legs.
Lichen planus of the scalp is termed lichen planopilaris, which can cause a scarring alopecia.
Nail involvement ranges from mild dystrophy to nail loss.
Mucous membrane involvement may be Wickham’s striae in the mouth, or plaques or erosive ulceration.
Anogenital lichen planus results in bluish purple papules on the glans penis or vulva. An erosive lichen planus affecting the orogenital regions is seen in women termed vulvovaginalgingival syndrome.
Management
High potency topical steroids are the mainstay of treatment. Refractory cases may respond to systemic steroids, oral retinoids, ciclosporin or azathioprine.
Prognosis
Most lesions clear within 2 years leaving hyperpigmented patches. Hypertrophic, anogenital and mucosal involvement is more persistent and more refractory to treatment.
Related Topics