Chapter: Satellite Communication : Satellite Applications
LEO, MEO, GEO- Low, Medium, Geosynchronous Earth Orbit
LEO:
LEO: Low
Earth Orbit satellites have a small area of coverage. They are positioned in an
orbit approximately 3000km from the surface of the earth
They complete one orbit every 90 minutes
The large majority of satellites are in low earth orbit
The Iridium system utilizes LEO satellites (780km high)
The satellite in LEO orbit is visible to a point on the earth for a very short
time
MEO:
MEO: Medium Earth Orbit satellites have orbital
altitudes between 3,000 and 30,000 km.
They are commonly used used in navigation systems such as GPS
GEO:
GEO: Geosynchronous (Geostationary) Earth Orbit
satellites are positioned over the equator. The orbital altitude is around
30,000-40,000 km
There
is only one geostationary orbit possible around the earth
Lying on the earth’s equatorial plane.
The satellite orbiting at the same speed as the rotational speed of the earth
on its axis.
They complete one orbit every 24 hours. This causes the satellite to appear
stationary with respect to a point on the earth, allowing one satellite to
provide continual coverage to a given area on the earth's surface
One GEO satellite can cover approximately 1/3 of the world’s surface
They
are commonly used in communication systems
Advantages:
Simple ground station tracking.
Nearly constant range
Very small frequency shift
Disadvantages:
Transmission delay of the order of 250 msec.
Large free space loss.
No polar coverage
Satellite orbits in terms of the
orbital height:
According
to distance from earth:
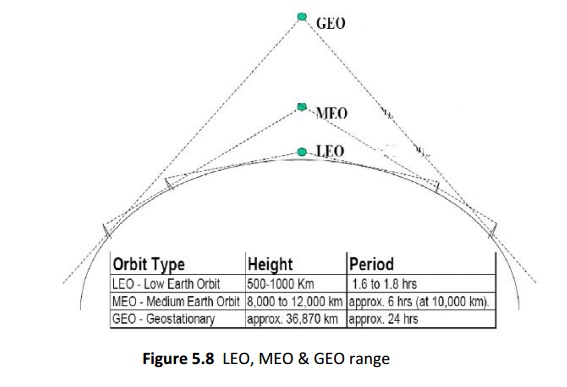
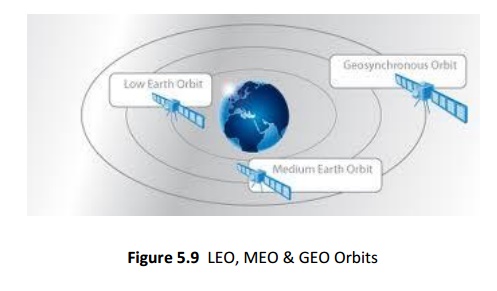
Geosynchronous Earth Orbit (GEO) ,
Medium Earth Orbit (MEO),
Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
GEO:
35,786 km above the earth, MEO: 8,000-20,000 km above the earth & LEO: 500-
2,000 km above the earth.
Related Topics