Chapter: Satellite Communication : Satellite Applications
Direct Broadcast satellites (DBS)
Direct Broadcast
satellites (DBS):
Satellites
provide broadcast transmissions in the fullest sense of the word, because
antenna footprints can be made to cover large areas of the earth.
The
idea of using satellites to provide direct transmissions into the home has been
around for many years, and the services pro- vided are known generally as
direct broadcast satellite (DBS) services.
Broadcast
services include audio, television, and Internet services.
1. Power Rating
and Number of Transponders:
From
Table 1.4 it will be seen that satellites primarily intended for DBS have a
higher [EIRP] than for the other categories, being in the range 51 to 60 dBW.
At a Regional Administrative Radio Council (RARC) meeting in 1983, the value
established for DBS was 57 dBW (Mead,2000). Transponders are rated by the power
output of their high-power amplifiers.
Typically,
a satellite may carry 32 transponders. If all 32 are in use, each will operate
at the lower power rating of 120 W.
The
available bandwidth (uplink and downlink) is seen to be 500 MHz. A total number
of 32 transponder channels, each of bandwidth 24 MHz, can be accommodated.
The
bandwidth is sometimes specified as 27 MHz, but this includes a 3- MHz
guardband allowance. Therefore, when calculating bit-rate capacity, the 24 MHz
value is used.
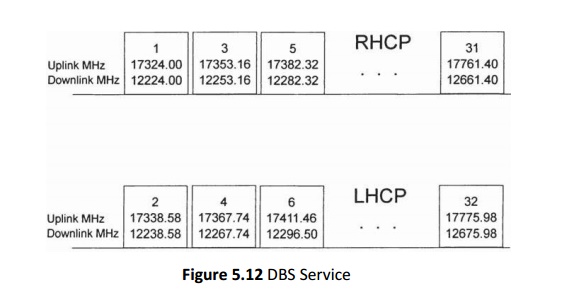
The
total of 32 transponders requires the use of both right- hand circular
polarization (RHCP) and left-hand circular polarization (LHCP) in order to
permit frequency reuse, and guard bands are inserted between channels of a
given polarization.
2. Bit Rates for
Digital Television:
The
bit rate for digital television depends very much on the picture format. One
way of estimating the uncompressed bit rate is to multiply the number of pixels
in a frame by the number of frames per second, and multiply this by the number
of bits used to encode each pixel.
3. MPEG
Compression Standards:
MPEG
is a group within the International Standards Organization and the
International Electrochemical Commission (ISO/IEC) that undertook the job of
defining standards for the transmission and storage of moving pictures and
sound.
The
MPEG standards currently available are MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4, and MPEG-7.
Related Topics