Chapter: Obstetrics and Gynecology: Isoimmunization
Isoimmunization
Isoimmunization
When any fetal blood group factor
inherited from the father is not possessed by the
mother, antepartumor intrapartum fetal–maternal bleeding may stim-ulate an
immune reaction in the mother. Maternal immune reactions also can occur
from blood product transfusion. The
formation of maternal antibodies is called isoimmuniza-tion.
It can lead to various degrees of transplacental passage ofthese antibodies
into the fetal circulation, causing an anti-body
response sufficient to destroy fetal red cells.Althoughearly exposures
to maternal antigens during pregnancy may occur in the same pregnancy,
isoimmunization more commonly occurs in a subsequent pregnancy. The bind-ing of
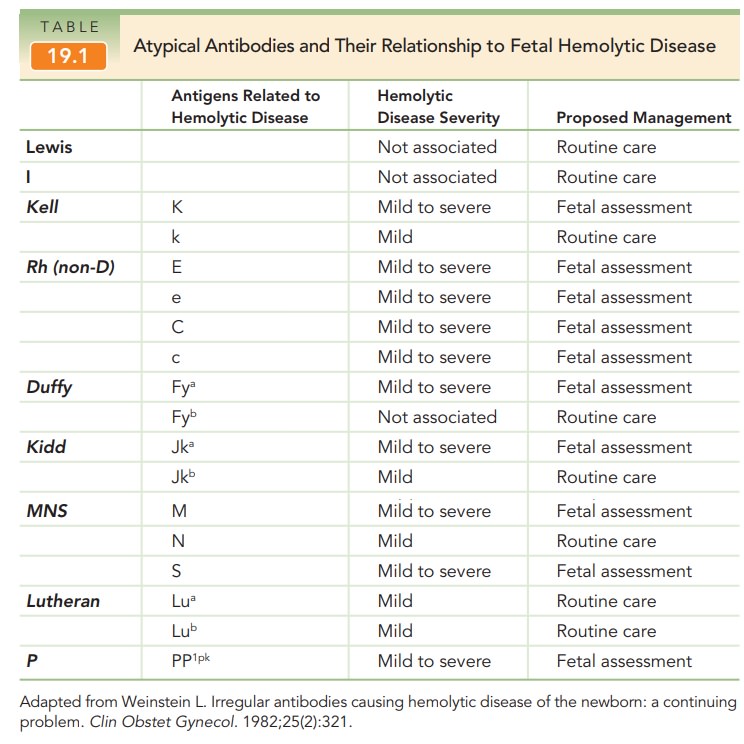
maternal antibodies to fetal red blood cells leads to hemolytic disease in the fetus or newborn, characterizedby hemolysis, bilirubin release, and anemia. The sever-ity of the illness
encountered by the fetus or newborn is determined by a number of factors,
including the degree of immune response elicited (i.e., how much antibody is
pro-duced), how strongly the antibody binds the antigen, the gestational age at
which the diagnosis is made, and the abil-ity of the fetus to replenish the
destroyed red cells to main-tain a hematocrit sufficient for growth and
development (Table 19.1).
Related Topics