Coordinate Geometry - Introduction | 10th Mathematics : UNIT 5 : Coordinate Geometry
Chapter: 10th Mathematics : UNIT 5 : Coordinate Geometry
Introduction
COORDINATE GEOMETRY
“A line is breadthless
length” – Euclid
Apollonius was born at Perga, in modern day Turkey. His greatest work was called
“conics” which introduced curves
like circle, parabola geometrically. He wrote six other books all related to
the basics of modern day
coordinate geometry.
His ideas were applied to study planetary theory and solve
practical problems. He developed the sundial and contributed to other branches
of science using his exceptional geometric skills. For this reason, Apollonius
is hailed as “The
Great Geometer”.

Learning Outcomes
·
To find area of a triangle formed by three given points.
·
To find area of a quadrilateral formed by four given points.
·
To find the slope of a straight line.
·
To determine equation of a straight line in various forms.
·
To find the equation of a line parallel to the line ax + by
+c = 0 .
·
To find the equation of a line perpendicular to the line ax
+ by +c = 0
Introduction
Coordinate geometry, also called Analytical geometry is a branch
of mathematics, in which curves in a plane are represented by algebraic
equations. For example, the equation x2 + y2
= 1 , describes a circle of unit radius in the plane. Thus coordinate geometry
can be seen as a branch of mathematics which interlinks algebra and geometry,
where algebraic equations are represented by geometric curves. This connection
makes it possible to reformulate problems in geometry to problems in algebra
and vice versa. Thus, in coordinate geometry, the algebraic equations have
visual representations thereby making our understanding much deeper. For
instance, the first degree equation in two variables ax + by +c
= 0 represents a straight line in a plane. Overall, coordinate geometry is a
tool to understand concepts visually and created new branches of mathematics in
modern times.
In the earlier classes, we initiated the study of coordinate
geometry where we studied about coordinate axes, coordinate plane, plotting of
points in a plane, distance between two points, section formulae, etc. All
these concepts form the basics of coordinate geometry. Let us now recall some
of the basic formulae.
Recall
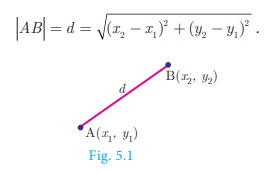
Distance between two points
Distance between two points A(x1 , y1
) and B (x2, y2) is
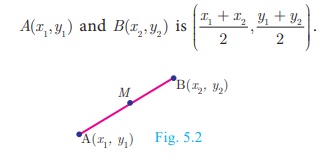
Mid-point of line segment
The mid-point M, of the line segment joining
Section Formula
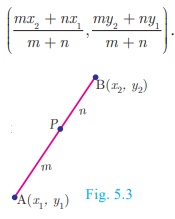
Internal Division
Let A(x 1 , y1 ) and B(x
2 , y2 ) be two distinct points such that point P
(x, y) divides AB internally in the ratio
m:n.
Then the coordinates of P are given by
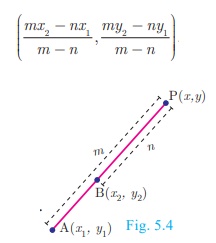
External Division
A(x 1 , y1 ) and B(x
2 , y2 ) be two distinct points such that the
point P (x, y) divides AB externally in the ratio m:n.
Then the coordinates of P are given by
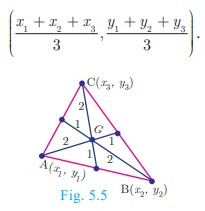
Centroid of a triangle
The coordinates of the centroid (G) of a triangle with vertices A(x 1 , y1 ), B(x 2 , y2 ) and C(x 3 , y3 ) are given by
Related Topics