Chapter: 11th Computer Technology : Chapter 13 : Presentation Advanced
Inserting and formatting text - OpenOffice presentation
Inserting
and formatting text
Pasting text
Text
may be inserted into the text box by copying it from another document and pasting
it into Impress. There are several ways to ensure consistency. These methods
are explained below.
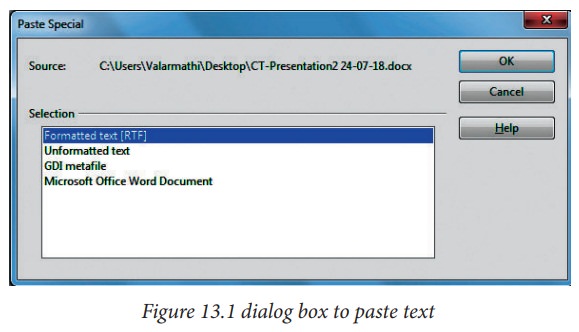
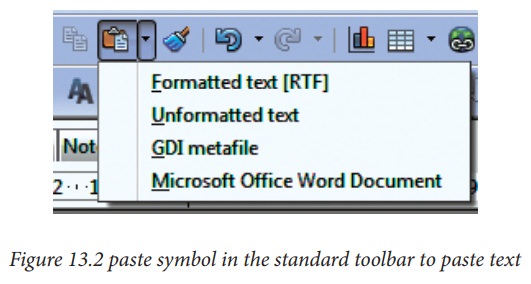
Pasting unformatted text
It
is normally good practice to paste text without formatting and apply the
formatting later. To paste without formatting, press Ctrl+Shift+V or select Unformatted
text from the dialogbox that appears (Figure
13.1), or click on the small black triangle next to the paste symbol in the
standard toolbar (Figure 13.2)and
select Unformatted text.
Formatting pasted text
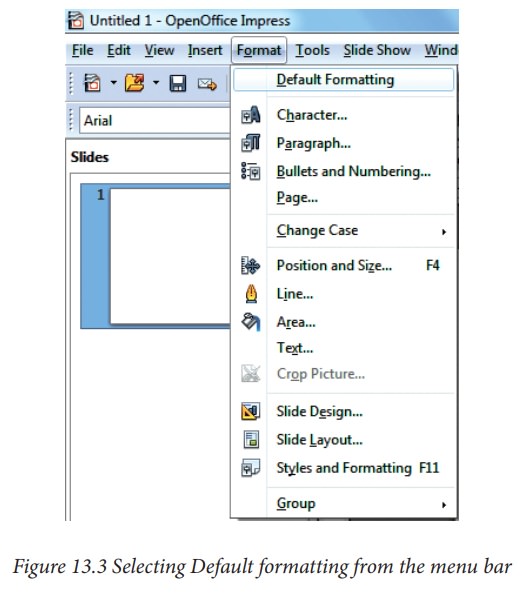
If
pasting the text into an AutoLayout area, then to give the pasted text the same
look and feel of the rest of the presentation apply the appropriate out line
style to the text. To do so:
1.
Paste the text in the desired position.
2.
Select the text you have just pasted .
3.
Select Format → Default formatting
from the menu bar.(Figure 13.3)
4.
Use the four arrow buttons in the Text Formatting toolbar to move the text to
the appropriate position.
Inserting special
characters
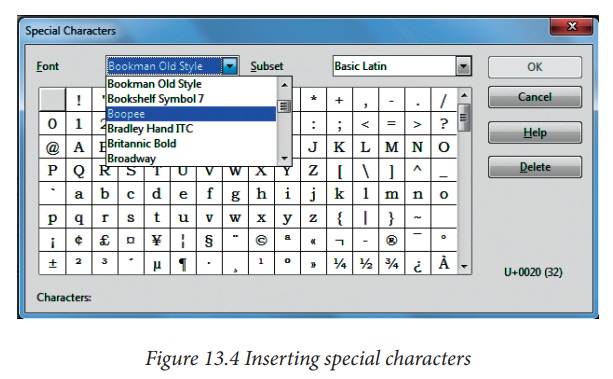
To
insert special characters, such as copyright, math, geometric, ormonetary
symbols, or characters from another language:
1.
Click in the place in the text where you want to insert the character.
2.
Choose Insert → Special Character. The
Special Characters dialog box appears. (Figure
13.4).
3.
Choose the font and character subset from the Font and Subset drop-down menus.
4.
Click the character you want to insert. You may have to scroll to find the one
you want.
5.
Click OK.
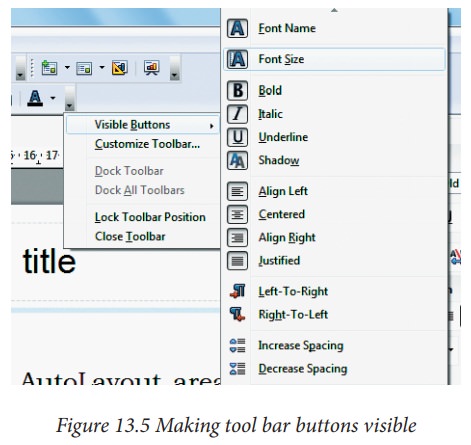
To
show toolbar buttons that are not visible, click on the small down-arrow on the
right end of the tool bar, move the cursor over Visible Buttons and then click
on the icon you wish to make visible (Figure
13.5).
Formatting text
Formatting
text can give a presentation a consistent look and a dynamic feel.
Modifying a style
In
Impress there are two categories of styles: presentation styles and graphics
styles. When inserting text in an Auto
Layout area, the presentation styles become available. When inserting text
in a text box or a graphic object it is possible to apply the graphic styles.
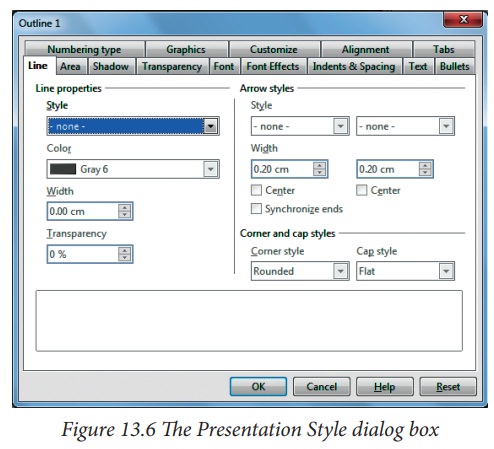
If
you have selected a presentation style, the dialog box in Figure 13.6 will appear. The Presentation Style dialog box
determines the formatting of the text.
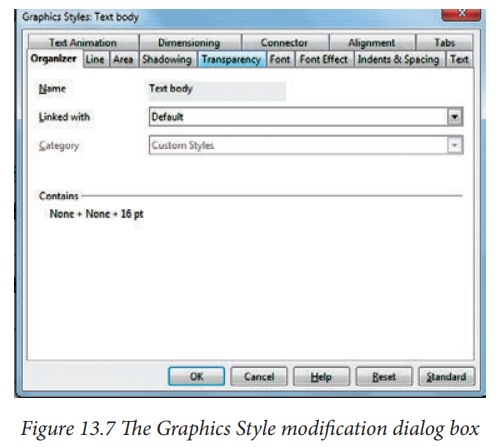
The
dialog box for making modifications to a graphics style is shown in Figure 13.7.
Text
must be selected before it can be formatted manually.
Formatting characters
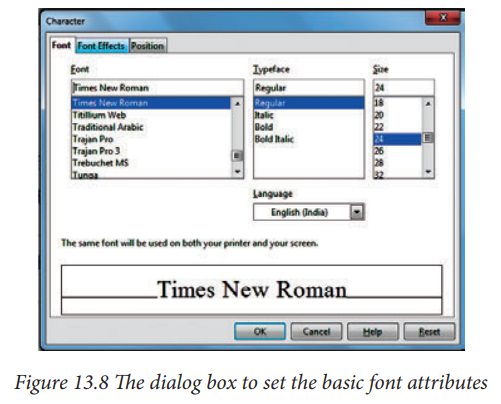
To view the character formatting options, select Format → Characteror click the Character button on the Text Formatting toolbar. (If a toolbar with the text icon is not visible, choose View→ Toolbars → Text Formatting.) The Character dialog box appears.
Font page
Use
the Font page, shown in Figure 13.8,
to select the desired font type, its base attributes (Italic, Bold, etc.) as
well as the size. A sample of the font is displayed in the lower part of the
dialog box. You can also specify the language of this style.This page is
available when creating or modifying a presentation style or a graphics style.
When
writing a presentation in multiple languages, you can make the best of the
language setting by creating two styles that only differ in the language but
are otherwise the same. This allows you to check the spelling of all of the
contents without affecting the appearance.
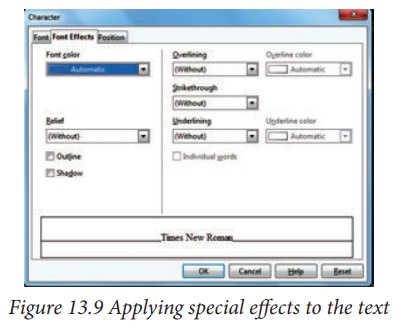
Font Effects page
Use
the Font Effects page, shown in Figure
13.9, to apply special effects to the text, such as underlining, color,
shadow and so on. A sample of the text is displayed in the lower part of the
dialog box allowing a quick visual check of the effects applied. This page is
available when creating or modifying a presentation style or a graphics style.
Position page
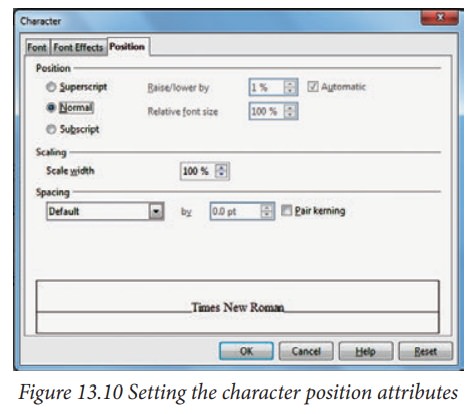
The
Position page, shown in Figure 13.10,
has advanced options to customize text. This page is not available when
creating or modifying a presentation style or a graphics style. Use this page
to set the text position relative to the baseline when you need to insert
subscripts or superscripts.
Formatting paragraphs
To
view the paragraph formatting options, select Format → Paragraph or click the Paragraph button on the Text Formatting
toolbar. If a toolbar with the text icon is not visible, choose View → Toolbars → Text Formatting. The Paragraph dialog box (Figure 13.11) is shown.
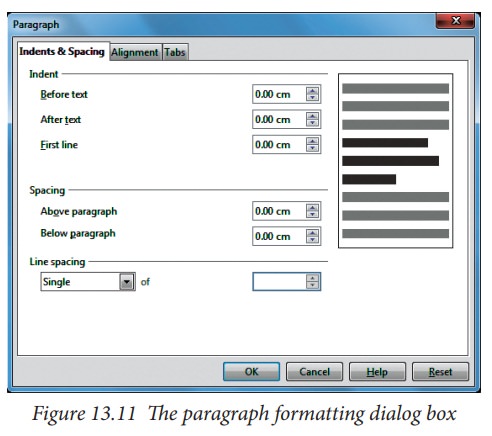
Indents and Spacing page
The
Indents and Spacing page, shown in Figure 13.12, has four sections:
•
Indent: modifies the indentation of
the text (before and after) as well as the indentation of the first line.
•
Spacing: defines the space before
and after each paragraph formatted with the style.
•
Line spacing: determines the spacing
between two lines
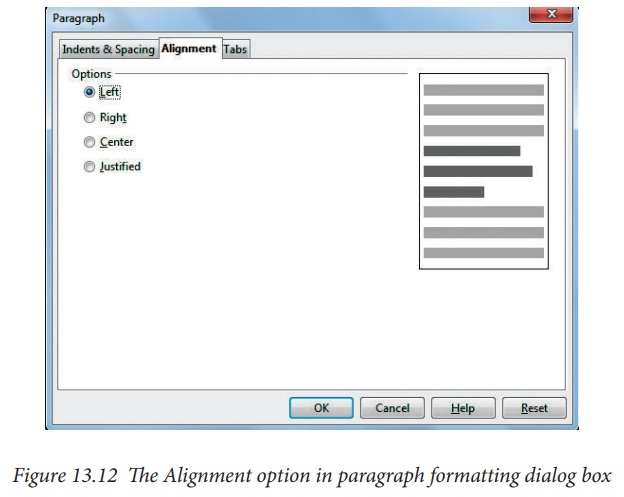
Alignment page
Use
the Alignment page to determine the text alignment: Left, Right,Center, or Justified.
A preview shows the effects of the changes. (Figure 13.12)
Tabs page
Use
the Tabs page, shown in Figure 13.13,
to set tab stops. To delete one existing tab stop, select it in the list and
click the Delete button. To delete all the tab stops, click the Delete All
button.
Creating bulleted and numbered lists
You
can customize the appearance of a list, changing the bullet type or numbering
for the entire list or for single entry. All the changes can be made using the
Bullets and Numbering dialog box. It is accessed by selecting Format → Bullets and Numbering or by clicking on the Bullets and Numbering
icon on the text formatting toolbar. (Figure
13.14)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Workshop -1
1.
Create a presentation using 8 slides and insert the following features in each
slide.
•
Pasting using unformatted text
•
Formatting the text pasted
•
Inserting special characters
•
Formatting text (Changing font attributes)
•
Formatting characters
•
Formatting paragraphs
•
Creating bulleted and numbered lists
Related Topics