Chapter: Digital Logic Circuits : Synchronous Sequential Circuits
Important Short Questions and Answers: Synchronous Sequential Circuits
SYNCHRONOUS SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS
1. What
are shift register counters? List two widely used shift register counters.
Solution:
If the output of a shift register is
fed back to the input. a ring counter results. The data pattern contained
within the shift register will recirculate as long as clock pulses are applied.
2. Why
is FlipFlop also known as Latch?
Solution:
The difference between a latch and a
flip-flop is that a latch does not have a clock signal, whereas a flip-flop
always does. Latch is a level sensitive device while flip-flop is an edge sensitive
device. Latch is sensitive to glitches on enable pin, whereas flip-flop is
immune to that.
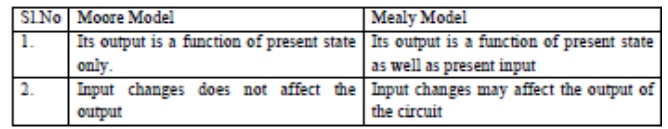
3.
Compare Moore and Mealy Machine.
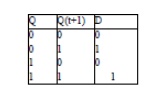
4.
Obtain the excitation table of D-FlipFlop
4. What
are state diagram and state tables?
Solution:
The time sequence of inputs, outputs
and flip-flop states may be enumerated in a state table and the information
available in a state table may be represented graphically called a state
diagram. For the design of sequential counters we have to relate present states
and next states. The table, which represents the relationship between present
states and next states, is called state table.
5. Give
the excitation table for JK FlipFlop
Solution:

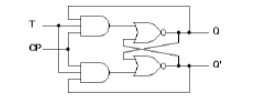
6.
Draw the logic diagram for T FlipFlop
Solution:
7. How
many flip-flops are required to design a mod-7 up-down counter?
Solution:
Flip Flops required are 2n >= N
where N=7
2n >= 7 n = Number of Flip Flops.
n = 3 Hence 3 Flip Flops are
required
8. What
is a sequential circuit?
Solution:
The logic circuits whose outputs at
any instant of time depend not only on the present inputs but also on the past
outputs are called sequential circuits. Example : flip-flops.
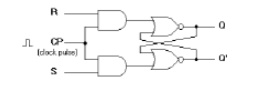
10.
Draw the logic diagram of SR
flip-flop.
Solution:
11.
Draw the timing diagram of 4-bit ring counter.
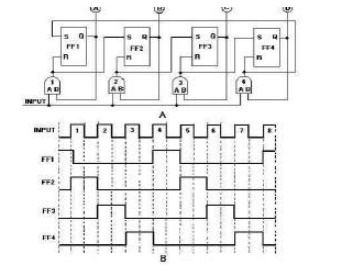
12.
Write the characteristic equation of JK flip-flop.
Solution:
Q(t + 1) = JQ' + K'Q
13.State
a limitation of SR flip-flop.
Solution:
The last input condition in SR
flip-flop is S=1 and R=1. This Condition will produce 0 at the output of both
the NOR gate. Hence Qn+1=0 and Q'n+1= 0. This condition violates the fact that
the outputs Qn+1 and Q'n+1 are the complements of each other. In normal
operation, this condition must be avoided by making sure that 1s are not a
applied to both inputs simultaneously.
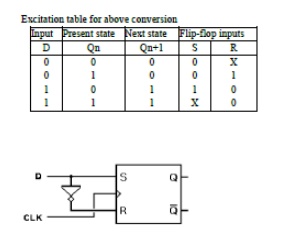
14.
Convert a D flip-flop into T flip-flop.
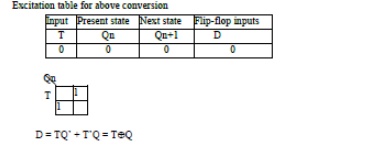
15.
What is the race- around condition?
Solution:
In JK FF output is fedback to the
input and therefore change in the output results in change in the input.If the
FF is level trigged, in the positive half of the clock pulse if j and k are
both high then output toggles continuously. This condition is known as race
around condition.
Related Topics