Chapter: Physics : Semiconducting Materials
Important Short Questions and Answers: Semiconducting Materials
SHORT QUESTIONS WITH ANSWER
1. What is semiconductor?
The materials in which the electrical conductivity lies between conductors and insulators are called semiconductors. They have resistivity value between 10–4 to 0.5 m . The electrical conductivity of semiconductor increases, when we added to impurities and by increasing the temperature and it is contrary to the metals. They have negative temperature Coefficient of resistance and which are formed by covalent bonds.
2. Distinguish between elemental semiconductors and Compound semiconductors
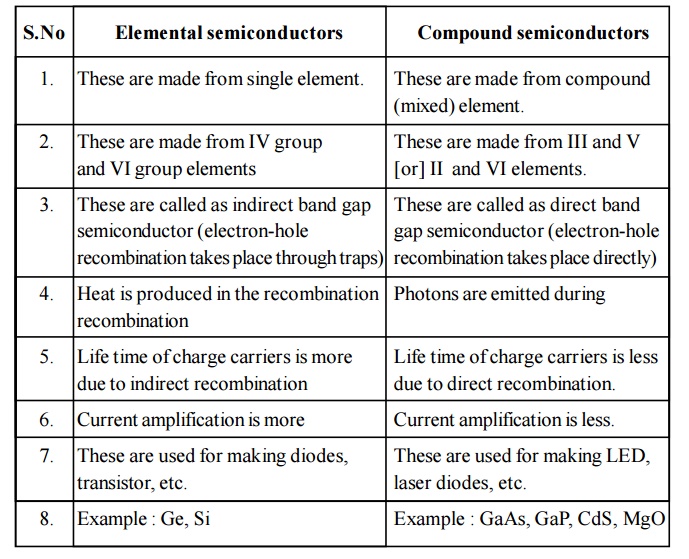
Elemental semiconductors
These are made from single element. (mixed) element.
These are made from IV group and VI group elements
These are called as indirect band gap semiconductor (electron-hole recombination takes place through traps)
Heat is produced in the recombination
Life time of charge carriers is more due to indirect recombination
Current amplification is more
These are used for making diodes, transistor, etc.
Example : Ge, Si
Compound semiconductors
These are made from compound
These are made from III and V [or] II and VI elements.
These are called as direct band gap semiconductor (electron-hole recombination takes place directly)
Photons are emitted during recombination
Life time of charge carriers is less due to direct recombination.
Current amplification is less.
These are used for making LED, laser diodes, etc.
Example : GaAs, GaP, CdS, MgO
3 What are intrinsic semiconductors?
A semiconductor in which holes and electrons are created only by thermal excitation across the energy gap is called an intrinsic semiconductor. A pure crystal of silicon or germanium is an intrinsic semiconductor. In an intrinsic semiconductor the number of holes in the valence band is equal to number of electrons in the conduction band. The Fermi level for an intrinsic semiconductor lies at midway in the forbidden gap.
4 What is meant by compound semiconductor? Give an example.
The compound Semiconductor is a semiconductor compound composed of elements from two or more different groups of the periodic table.
i.e., III-V group, II-Vi group and IV-VI group.
Example: GaAs, GaP, CdS, MgO.
5 What are extrinsic semiconductors? (or) What is the effect of impurity states over intrinsic semiconductor?
It is an impure semiconductor made by doping process thereby reducing the band gap up to 0.01 eV.
In this case of N-type semiconductor, the donar energy level is very close to the unfilled energy band (Conduction band). So it can easily donate an electron to that unfilled state.
In this case of P-type semiconductor, the acceptor energy level is very close to the filled energy band (Valance band). So it can easily accept the electrons from the filled state.
6 Differentiate N-type and P-type semiconductor.
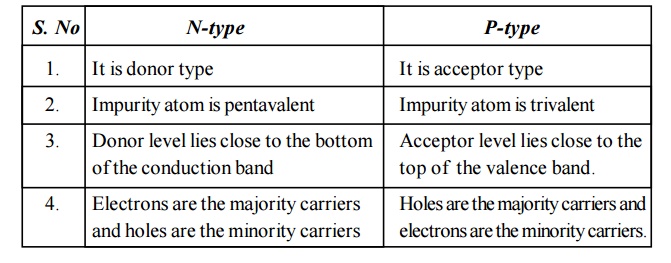
N-type
1. It is donor type
2. Impurity atom is pentavalent
3. Donor level lies close to the bottom of the conduction band
4. Electrons are the majority carriers and holes are the minority carriers
P-type
1. It is acceptor type
2. Impurity atom is trivalent
3. Acceptor level lies close to the top of the valence band.
4. Holes are the majority carriers and electrons are the minority carriers.
7. Sketch the variation of Fermi level in intrinisic semiconductor.
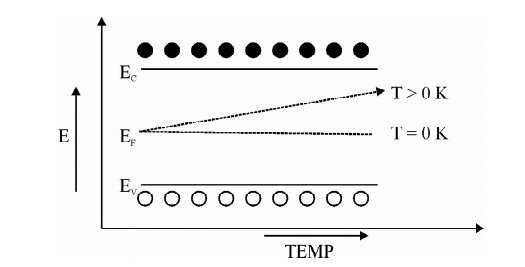
At T = 0 K, the Fermi level lies exactly in midway between conduction band and Valence band.
At T > 0 K, the Fermi level rises slightly upward since.
8.What are donor and acceptor impurities?
A semiconductor in which the impurity atoms are added by doping process is called Extrinsic semiconductor. The addition of impurities increases the carrier concentration and conductivity. There are two types of impurities.
Donor impurity which leads to N-type semiconductor.
Acceptor impurity which leads to P-type semiconductor.
Donor impurity means it donates the electron to the semiconductor materials and Acceptor impurity means it ready to accepts an electron to form the covalent bond in semiconductor materials.
9.State law of mass action.
Therefore for intrinsic semiconductor even it impurity is added to increase ne there will be decrease in nh and hence the product nenh will remain constant. This is called Law of mass action.
Ne Nh = ni2
10. Sketch the variation of Fermi level with temperature for various concentration in P-type semiconductor.
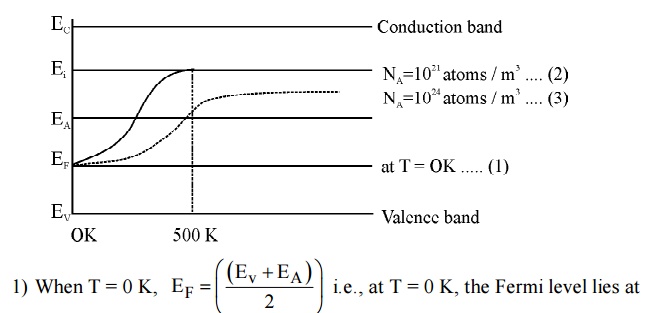
mid way between the acceptor level and valence level.
When temperature increases, some of the electrons from valence band will go to acceptor energy level [EA]. Therefore the Fermi level shifts upward. At high temperature 500 K, the Fermi level reaches intrinsic level Ei.
If the impurity atoms are increased from 10 21 atoms / m3 to 10 24 atoms / m3, the hole concentration increases and hence the Fermi level decrease.
11. Sketch the variation of Fermi level with temperature for various concentration in N-type semiconductor.
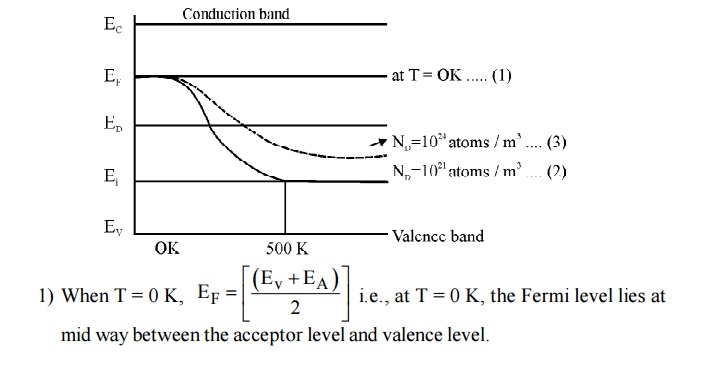
When temperature increases, some of the electrons from valence band will go to acceptor energy level [EA]. Therefore the Fermi level shifts upward. At high temperature 500 K, the Fermi level reaches intrinsic level Ei.
If the impurity atoms are increased from 10 21 atoms / m3 to 10 24 atoms / m3 , the hole concentration increases and hence the Fermi level decrease.
12.What is pair production or generation?
When an energy is supplied to the semiconductor, the covalent bonds are broken and the electrons are raised from valence band to conduction band and a vacant site is created in the valence band. It is called pair production or generation of electron-hole pair.
13.What is Recombination?
Recombination is the conversion of a free electron into a bound electron by occupying a vacant site. An electron jumps from the conduction band to the valence band vacant site is called as band to band recombination of electron-hole pair.
During band to band combination the excess energy is released in the form of light photon. The recombination also occurs via recombination centre and traps.
14.Define Hall effect?
If a semiconductor or a conductor carrying current (I) is placed in a magnetic field (B), an electric field is produced in the direction normal to both the current and magnetic field. The generated voltage is called the Hall voltage (VH) and the field is called Hall field(EH).
15. What are the applications of hall effect?

It can be used to determine whether the given material is metal, insulator, or semiconductor and the type of the semiconductor.
It can be used to determine the power flow in an electromagnetic wave.
16. Give on externisic semiconductor. How will you find whether it is n-type (or) P type.
If pentavalent (Phosphorous, Arsenic, Antimony) impurities are doped with pure semiconducting material the free electrons are produced, this is called n-type semiconductor. In n-type semiconductor majority charge carriers is electron.
If trivalent [Aluminium, Gallium, Indium] impurities are doped with pure semiconducting material the holes are produced, this is called p - type semiconductor. In p - type semiconductor the majority charge carrier is holes.
17. Define diffusion current
In addition to drift current, there is also another current called diffusion current. Diffusion current does not takes place in metals.
Diffusion current is defined as the motion of charge carriers from the region of higher concentration to the region of lower concentration.
18. State the properties of Semiconductors.
They are formed by covalent bonds.
They have small energy gap.
They have an empty conduction band and almost filled valence band 0K.
They have negative temperature coefficient of resistance.
They resistivity of semiconductors lies between a semiconductor and Insulator. (10–4 to 0.5 Ohms m).
At 0 K it behave as insulator.
19.What are the differences between conductor and a semiconductor?
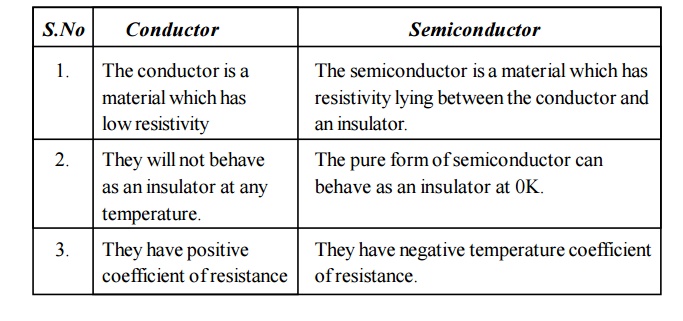
Conductor
The conductor is a material which has low resistivity
They will not behave as an insulator at any temperature.
They have positive coefficient of resistance
Semiconductor
The semiconductor is a material which has resistivity lying between the conductor and an insulator.
The pure form of semiconductor can behave as an insulator at 0K.
They have negative temperature coefficient of resistance.
20. Why do we prefer silicon for transistor and Ga As for Laser diodes?
Silicon in an indirect band gap semiconductor for which the life time of the charge carriers is more and the current amplification is also very high. Hence it is preferable for use it in transistor.
Ga As is a direct band gap semiconductor, in which electrons and holes recombine directly to produce photons and hence used in laser diodes.
21. What happens when the temperature increase in the case of semiconductor and conductor?
With increase of temperature the conductivity of semiconductor increase and hence resistivity decrease because more and more charge carriers are created by the temperature.
22. Write the expression for electrical conductivity of an intrinsic semiconductor.

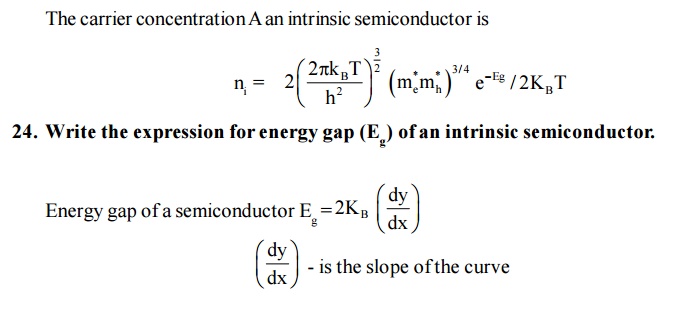
23.Give the carrier concentration of an intrinsic semiconductor.
The carrier concentration A an intrinsic semiconductor is
Related Topics