Chapter: Physics : Semiconducting Materials
Solved Problems: Semiconducting Materials
SOLVED PROBLEMS
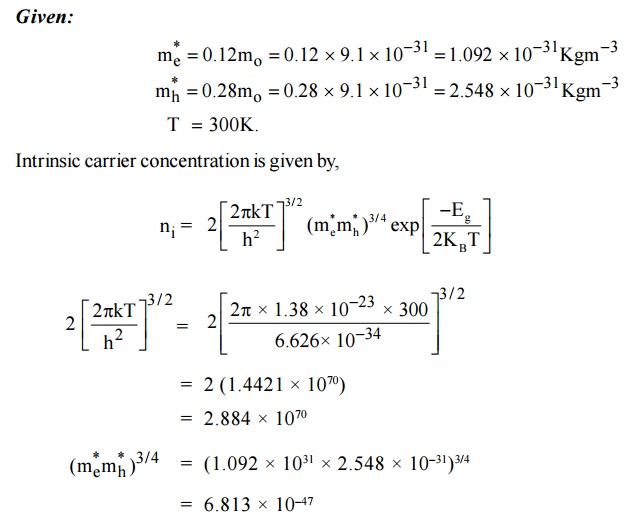
1.Calculate the intrinsic
concentration of charge carriers at 300 K given that m *e
=0.12m o ,m *h =0.28mo and the
value of brand gap = 0.67 eV. Solution:
Given:
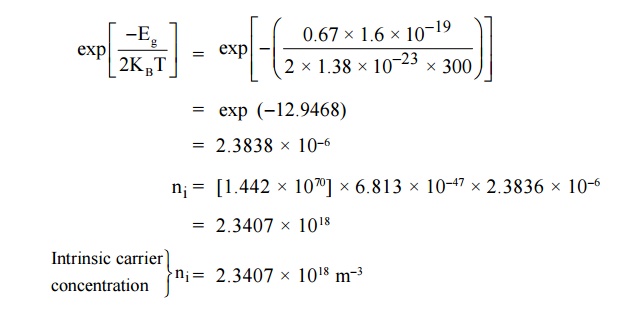
2.The intrinsic carrier density is 1.5 × 1016
m–3. If the mobility of electron and hole are 0.13 and 0.05 m2
V–1 s–1, calculate the conductivity.
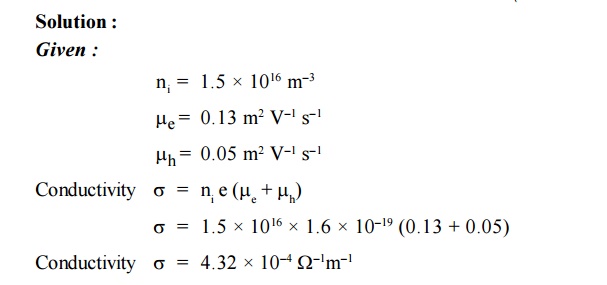
3. The Intrinsic carrier density at room temperature in Ge is 2.37 × 1019
m3 if the electron and hole mobilities are 0.38 and 0.18 m2
V–1 s–1 respectively, calculate the resistivity.

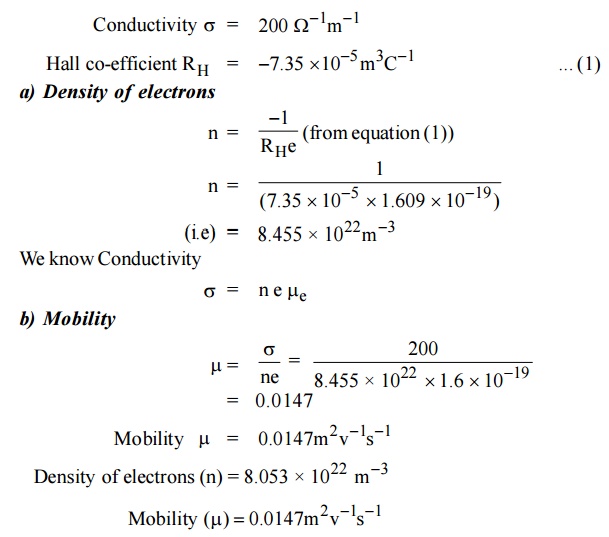
4.The Hall coefficient of certain silicon
specimen was found to be –7.35 × 10–5 m3 C–1
from 100 to 400 K. Determine the nature of the semiconductor. If the
conductivity was found to be 200 –1 m–1. Calculate the
density and mobility of the charge carrier.
Solution:
5. In a P-type germanium, ni = 2.1 ×
1019 m–3density of boran 4.5 × 1023 atoms /m3.
The electron and hole mobility are 0.4 and 0.2 m2 v–1 s–1
respectively. What is its conductivity before and after addition of boron
atoms.

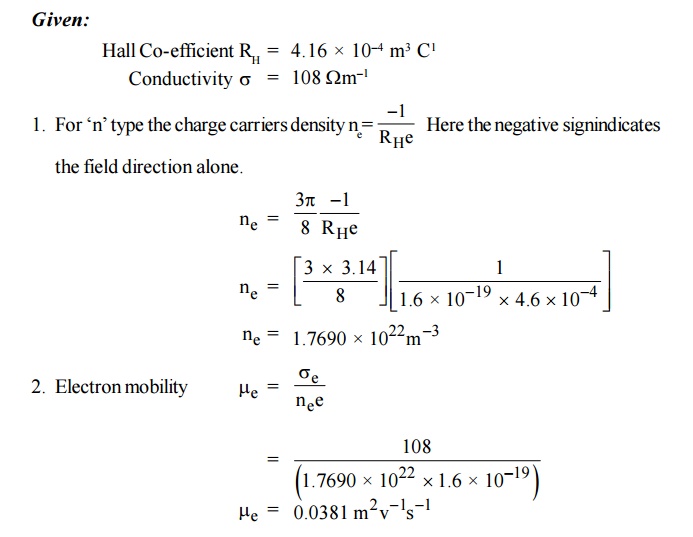
6. An N-type semiconductor has hall coefficient
= 4.16 × 10–4 m3 C–1. The conductivity is 108 –1
m–1. Calculate its charge carrier density ‘ne’and
electron mobility at room temperature.
Solution:
Given:
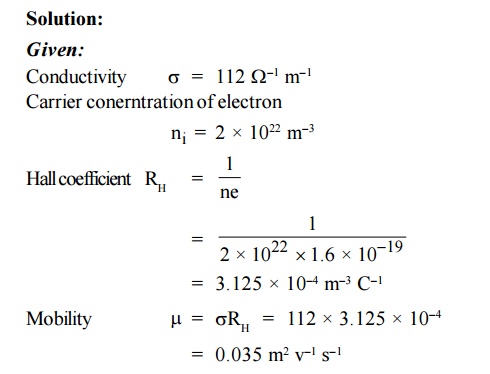
7. In an N-type semiconductor, the
concentration of electron is 2 × 1022 m–3 . Its electrical
conductivity is 112 –1 m–1. Calculate the mobility of
electrons.
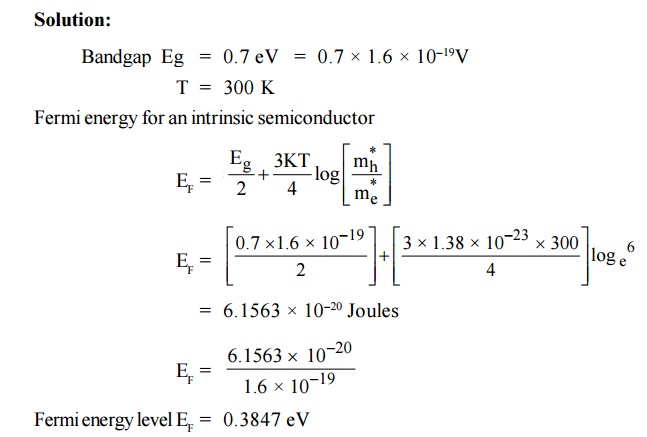
8. For an intrinsic Semiconductor with a band gap
of 0.7 eV, determine the position of EF at T = 300 K if m*h = 6m*e.
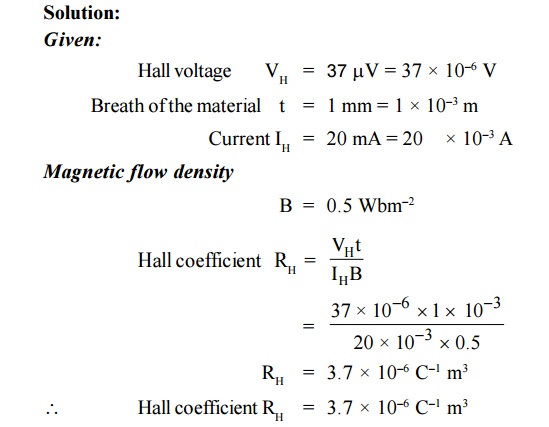
9.A semiconducting crystal with 12 mm long, 5
mm wide and 1 mm thick has a magnetic density of 0.5 Wbm–2 applied
from front to back perpendicular to largest faces. When a current of 20 mA
flows length wise through the specimen, the voltage measured across its width
is found to be 37μV . What is the
Hall coefficient of this semiconductor?
Solution:
Given:
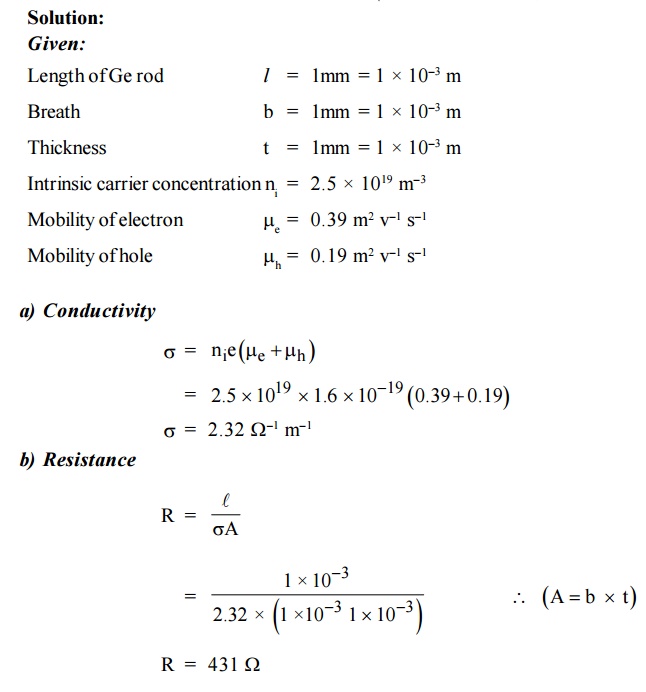
10. Find the resistance of an intrinsic Ge rod
1 mm long, 1 mm wide and 1 mm thick at 300 K. the intrinsic carrier density 2.5
×1019 m–3 is at 300 K and the mobility of electron and hole are 0.39
and 0.19 m2 v–1 s–1.
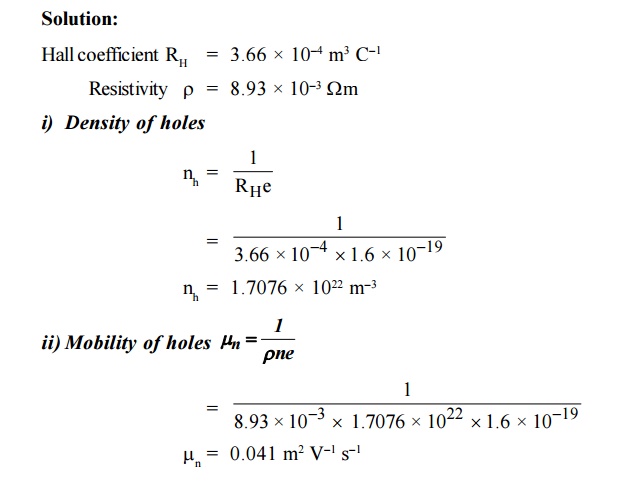
11. Hall coefficient of a specimen of depend
silicon found to be 3.66 × 10–4 m3 C–1. The
resistivity of the specimen is 8.93 × 10–3 m. Find the mobility and
density of the charge carriers.
12. The intrinsic carrier density of a
semiconductor is 2.1 × 1019 m–3. The electron and hole
mobilities are 0.4 and 0.2 m2 V–1 s–1
respectively. Calculate the conductivity.
Solution:

13. The electron mobility and hole mobility in
Si are 0.135 m2 V–1 s–1 and 0.048 m2
V–1 s–1 respectively at room temperature. If the carrier
concentration is 1.5 × 1016 m–3. Calculate the
resistivity of Si at room temperature.

ASSIGNMENT PROBLEMS
1. Find the resistance of an intrinsic germanium
rod 1 cm long, 1mm wide and 1mm thick at 300 K. the intrinsic carrier density
is 2.5 × 1019 / m–3 at 300 K and the mobility of electron
and hole are 0.39 and 0.19 m2 V–1 S–1. (Ans: 4.31 × 103)
Calculate the position of
Fermi level EF and the conductivity at 300 K for germanium crystal
containing 5 × 1022 arsenic atoms / m3. Also calculate
the conductivity if the mobility of the electron is 0.39 m2 V–1
S–1.
(Ans : EF is 0.16 eV below Ec = 3210 –1 m–1)
In a Hall experiment a
current of 25 A is passed through a long foil of silver which is 0.1mm thick
and 3cm wide. If the magnetic field of flux density 0.14 Wb/m2 is
applied perpendicular to the foil, calculate the Hall voltage development and
estimate the mobility of electrons in silver. The conductivity the Hall
coefficient is (–8.4 × 10–11)m3 / coulomb. (Ans : 29.4 V and 57.7 × 10–4
m2 V–1)
The intrinsic carrier density
at room temperature in Ge is 2.37 × 1019 m3. If the
electron and hole motilities are 0.38 and 0.18 m2 V1 S1
respectively, calculate the resistivity.
(Ans : 0471 m)
5. For silicon semiconductor with band gap1.12
eV, determine the position of the Fermi level at 300 K, if m*e
0.12m0 and m*h 0.28m0 (Ans : 0.576 eV)
For an intrinsic
semiconductor with gap width Eg = 0.7 eV, calculate the
concentration of intrinsic charge carriers at 300 K assuming that m*e
m*h m0 .
(Ans :
33.49 × 1018 / m3)
A silicon plate of thickness
1mm, breadth 10mm, and length 100mm is placed magnetic field of 0.5 wb/m2
acting perpendicular to its thickness. If A 10–2 current flows along
its length, calculate the Hall voltage developed if the Hall coefficient is
3.66 × 10–4 m3 / coulomb. (Ans : 3.7 ×
106 C–1 m3)
A N-type
semiconductor has Hall coefficient = 4.16 × 10–4 C–1 m3.
The conductivity is 108 ohm–1 m–1. Calculate its charge
carrier density and electron mobility at room temperature. (Ans
: 0.038 m2 V–1 S–1)
Related Topics