Chapter: Communication Theory : Noise Characterisation
Important Short Questions and Answers: Noise Characterisation
NOISE CHARACTERISATION
1. Define
noise.
Noise is
defined as any unwanted form of energy, which tends to interfere with proper
reception and reproduction of wanted signal.
2. Give the classification of noise.
Noise is
broadly classified into two types. They are
(i)External
noise
(ii)Internal
noise.
3.
What are
the types of External noise? External noise can be classified into
1. Atmospheric
noiseq
2. Extraterrestrial
noises
3. Man –made
noises or industrial noises
4.
What are
types of internal noise?
Internal
noise can be classified into
1. Thermal
noise
2. Shot
noise
3. Transit
time noise
4. Miscellaneous
internal noise
5.
What are
the types of extraterrestrial noise and write their origin?
The two
type of extraterrestrial noise are solar noise and cosmic noise Solar noise is
the electrical noise emanating from the sun. Cosmic noise is the noise received
from the center part of our galaxy, other distant galaxies and other virtual
point sources.
6. Define transit time of a transistor.
Transit
time is defined as the time taken by the electron to travel from emitter to the
collector.
7. Define flicker noise.
Flicker
noise is the one appearing in transistors operating at low audio frequencies.
Flicker noise is proportional to the emitter current and junction temperature
and inversely proportional to the frequency.
8.
State the
reasons for higher noise in mixers.
1. Conversion
transconductance of mixers is much lower than the transconductance of amplifiers.
2. If
image frequency rejection is inadequate, the noise associated with the image
frequency also gets accepted.
9. Define signal to noise ratio.
Signal to
noise ratio is the ratio of signal power to the noise power at the same point
in a system.
10. Define thermal noise. Give the expression for
the thermal noise voltage across a resistor.
The
electrons in a conductor possess varying amounts of energy. A small fluctuation
in this energy produces small noise voltages in the conductor. These random
fluctuations produced by thermal agitation of the electrons is called thermal
noise.
11. Define noise temperature. (In terms of
hypothetical temperature)
The
available noise power is directly proportional to temperature and it is
independent of value of resistance. This power specified in terms of
temperature is called as noise temperature. It is denoted by Te . It is given
as,
Te = (F −1 )T
12. What is shot noise?
When
current flows in electronic device, the fluctuations number of electrons or
holes generates the noise. It is called shot noise. Shot noise also depends
upon operating conditions of the device.
13. Give the expression for noise voltage in a
resistor.
The Mean
–Square value of thermal noise voltage is given by,
Vn 2
= 4 k TBR
K – Boltz
man constant,
R –
Resistance
T –
Obsolute temperature, B Bandwidth
Many
types of noise sources are Gaussian and have flat spectral density over a wide
frequency range. Such spectrum has all frequency components in equal portion,
and is therefore called white noise. The power spectral density of white noise
is independent of the operating frequency. The Power spectral density of White
Noise is given as,
15. What is narrowband noise?
The
receiver of a communication system usually includes some provision for
preprocessing the received signal. The preprocessing may take the form of a
narrowband filter whose bandwidth is large enough to pass modulated component
of the received signal essentially undistorted but not so large as to admit
excessive noise through the receiver. The noise process appearing at the output
of such filter is called narrow band noise.
16. Define noise equivalent bandwidth.
The noise
equivalent bandwidth of the filter is defined as the bandwidth of an ideal
filter at which the noise power passed by real filter and ideal filter is same.
17. Define noise factor.
Noise
factor (F) is defined as the ratio of signal to noise power ratio at the input
to signal to noise power ratio at the output
18.
Give the
characteristics of shot noise.
(i) Shot
noise is generated due to fluctuations in the number of electrons or holes.
(ii) Shot noise has uniform spectral density.
(iii)
Mean square noise current depends upon direct component of current. (iv) Shot
noise depends upon operating conditions of the device.
19. What is
FM threshold effect?
As the
carrier to noise ratio is reduced, clicks are heard in the receiver output. As
the carrier to noise ratio reduces further, crackling, or sputtering sound
appears at the receiver output. Near the breaking point, the theoretically
calculated output signal to noise ratio becomes large, but its actual value is
very small. This phenomenon is called threshold effect.
20. What is
capture effect in FM?
When the
noise interference is stronger than FM signal, then FM receiver locks to
interference. This suppresses FM signal. When the noise interference as well as
FM signal are of equal strength, then the FM receiver locking fluctuates
between them. This phenomenon is called capture effect.
21. What is meant by figure of merit of a receiver?
The ratio
of output signals to noise ratio to channel signal to noise ratio is called
figure of
merit.,
22. What is
the Purpose of re-emphasis and de-emphasis in FM?
The PSD
of noise at the output of FM receiver sally increases rapidly at high
frequencies but the PSD of message signal falls off at higher frequencies. This
means the message signal doesn‘t utilize the frequency band in efficient
manner. Such more efficient use of frequency band and improved noise
performance can be obtained with the help of re-emphasis and de-emphasis.
Threshold
extension s also called threshold reduction. It is achieved with the help of
FMFB demodulator. In the local oscillator is replaced by voltage controlled
oscillator (VCO).The VC frequency changes as per low frequency variations of
demodulated signal. Thus the receiver responds only to narrow band of noise
centered around instantaneous carrier frequency. This reduces the threshold of
FMFB receiver.
24. What is
threshold effect with respect to noise?
When the
carrier to noise ratio reduces below certain value, the message information is
lost. The performance of the envelope detector deteriorates rapidly and it has
no proportion with carrier to noise ratio. This is called threshold effect.
25. Define
pre-emphasis and de-emphasis.
Pre-emphasis:
It artificially emphasizes the high frequency components before modulation.
This equalizes the low frequency and high frequency portions of the PSD and
complete band is occupied.
De-emphasis:
This circuit attenuates the high frequency components. The attenuation
characteristic is exactly opposite to that of pre-emphasis circuit. De-emphasis
restores the power distribution of the original signal.
The
signal to noise ratio is improved because of pre-emphasis and de-emphasis
circuits.
26. Write
the expression of the SNR for a synchronous detector.
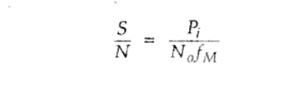
27. Define superheterodyne principle.
It can be
defined as the process of operation of modulated waves to obtain similarly
modulated waves of different frequency. This process uses a locally generated
carrier wave, which determines the change of frequency.
28. Define signal to noise ratio.
Signal to
noise ratio is the ratio of signal power to the noise power at the same point
in a
system.
When a noise is large compared to the signal at the input of the envelope detector, the detected output has a message signal completely mingled with noise. It means that if the input SNR is below a certain level, called threshold level, the noise dominates over the message signal, threshold is defined as value of the input signal to noise ratio (So/No) below which the output signal to noise ratio (Si/Ni) deteriorates much more rapidly than the input signal to noise ratio. The threshold effect in an envelope detector whenever the carrier power-to-noise power ratio approaches unity or less.
GLOSSARY TERMS:
1. Correlated
noise, is a form of internal noise which is correlated to the signal and is
absent in the absence of signal.
2. Noise,
unwanted introduction of energy which interferes with the proper reception and
reproduction of transmitted signals.
3. Coherent
detection, carrier wave at the transmitted side is phase locked within the
carrier wave at the receiver side.
4. Non
Coherent detection, carrier wave at the transmitted side need not phase locked
within the carrier wave at the receiver side.
5. Demodulation,
which is used to recover the original message signals.
6. Mixer,
non linear device which combines RF frequency and local oscillator frequency.
Related Topics