Chapter: Digital Principles and System Design : Asynchronous Sequential Circuits
Important Short Questions and Answers: Asynchronous Sequential Circuits
1.
Define Asynchronous sequential circuit?
In asynchronous sequential circuits change in input signals
can affect memory element at any instant of time.
2.
Give the comparison between synchronous &
Asynchronous sequential circuits?
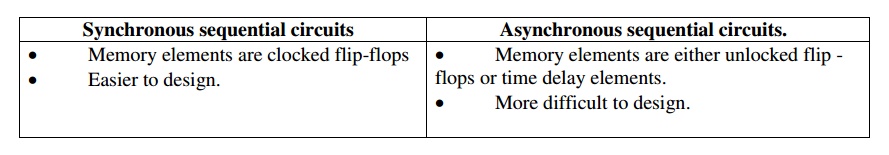
Synchronous
sequential circuits
• Memory elements are clocked flip-flops
• Easier to design.
Asynchronous
sequential circuits.
• Memory elements are either unlocked flip
- flops or time delay elements.
• More difficult to design.
3.
What is race around condition?
In the JK latch, the output is feedback to the input, and
therefore changes in the output results change in the input. Due to this in the
positive half of the clock pulse if J and K are both high then output toggles
continuously. This condition is known as race around condition.
4.
What is fundamental mode sequential circuit?
Input variables changes if the circuit is stable -inputs are
levels, not pulses -only one input can change at a given time
5.
What are pulse mode circuits?
Inputs are pulses -widths of pulses are long for circuit to
respond to the input -pulse width must not be so long that it is still present
after the new state is reached
6.
What are the significance of state
assignment?
In synchronous circuits-state assignments are made with the
objective of circuit reduction Asynchronous circuits-its objective is to avoid
critical races.
7.
What are the different techniques used in
state assignment?
Shared row state assignment -one hot state assignment
8.
What are the steps for the design of
asynchronous sequential circuit?
Construction of primitive flow table
Reduction of flow table -state assignment is made Realization
of primitive flow table
9.
What is hazard?
Unwanted
switching transients
10.
What is static 1 hazard?
Output
goes momentarily 0 when it should remain at 1
11.
What is static 0 hazard?
Output
goes momentarily 1 when it should remain at 0
12.
What is dynamic hazard?
Output changes 3 or more times when it changes from 1 to 0 or
0 to 1
13.
What is the cause for essential hazards?
Unequal delays along 2 or more
path from same input
14.
What is flow table?
State table of an synchronous sequential network
15.
What is primitive flow chart?
One stable state per row
16.
What is combinational circuit?
Output depends on the given input. It has no storage element.
17.
Define merger graph.
The merger graph is defined as
follows. It contains the same number of vertices as the state table contains
states. A line drawn between the two state vertices indicates each compatible
state pair. It two states are incompatible no connecting line is drawn.
18.
Define closed covering
A Set of compatibles is said to
be closed if, for every compatible contained in the set, all its implied
compatibles are also contained in the set. A closed set of compatibles, which contains
all the states of M, is called a closed covering.
19.
Define state table.
For the design of sequential
counters we have to relate present states and next states. The table, which
represents the relationship between present states and next states, is called
state table.
20.
Define total state
The combination of level signals
that appear at the inputs and the outputs of the delays define what is called
the total state of the circuit.
21.
What are the steps for the design of
asynchronous sequential circuit?
1. Construction
of a primitive flow table from the problem statement.
2. Primitive
flow table is reduced by eliminating redundant states using the state reduction
3. State
assignment is made
4. The
primitive flow table is realized using appropriate logic elements.
22.
Define primitive flow table
It is defined as a flow table
which has exactly one stable state for each row in the table. The design
process begins with the construction of primitive flow table.
23. What are the types of asynchronous circuits?
1. Fundamental
mode circuits
2. Pulse
mode circuits
24.
Give the comparison between state Assignment
Synchronous circuit and state assignment asynchronous circuit.
In synchronous circuit, the state
assignments are made with the objective of circuit reduction. In asynchronous
circuits, the objective of state assignment is to avoid critical races.
25.
What are races?
When 2 or more binary state
variables change their value in response to a change in an input variable, race
condition occurs in an asynchronous sequential circuit. In case of unequal
delays, a race condition may cause the state variables to change in an
unpredictable manner.
26.
Define non critical race.
If the final stable state that
the circuit reaches does not depend on the order in which the state variable
changes, the race condition is not harmful and it is called a non critical
race.
27.
Define critical race?
If the final stable state depends
on the order in which the state variable changes, the race condition is harmful
and it is called a critical race.
28.
What is a cycle?
A cycle occurs when an
asynchronous circuit makes a transition through a series of unstable states. If
a cycle does not contain a stable state, the circuit will go from one unstable
to stable to another, until the inputs are changed.
29.
Define secondary variables
The delay elements provide a
short term memory for the sequential circuit. The present state and next state
variables in asynchronous sequential circuits are called secondary variables.
30.
Define flow table in asynchronous sequential
circuit.In asynchronous sequential circuit state table is known
as flow table because of the behavior of the asynchronous sequential circuit.
The stage changes occur in independent of a clock, based on the logic
propagation delay, and cause the states to
.flow. from one to another.
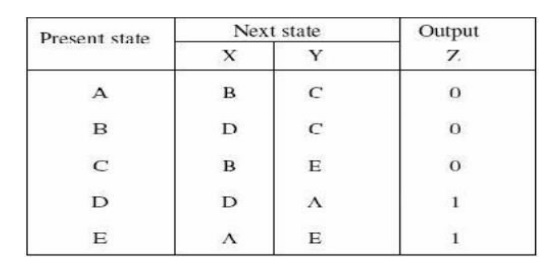
31. A pulse mode asynchronous
machine has two inputs. If produces an output whenever two consecutive pulses
occur on one input line only. The output remains at 1 until a pulse has
occurred on the other input line. Write down the state table for the machine.
32.
Write short note on shared row state
assignment.
Races can be avoided by making a proper binary assignment to
the state variables. Here, the state variables are assigned with binary numbers
in such a way that only one state variable can change at any one state variable
can change at any one time when a state transition occurs. To accomplish this,
it is necessary that states between which transitions occur be given adjacent
assignments. Two binary are said to be adjacent if they differ in only one variable.
33.
Write short note on one hot state assignment.
The one hot state assignment is another method for finding a
race free state assignment. In this method, only one variable is active or hot
for each row in the original flow table, ie, it requires one state variable for
each row of the flow table. Additional row are introduced to provide single
variable changes between internal state transitions.
GLOSSARY TERMS
1.
Fundamental mode-A
transition from one stable state to another occurs only in response to a change
in the input state.
2.
Pulse mode-Inputs are pulses -widths
of pulses are long for circuit to respond to the input -pulse width must
not be so long that it is still present after the new state is reached
3.
State assignment- In synchronous
circuits-state assignments are made with the objective of circuit reduction
Asynchronous circuits-its objective is to avoid critical races.
4.
Primitive flow table-It is
defined as a flow table which has exactly one stable state for each row in
the table. The design process begins with the construction of primitive flow
table.
5.
Hazards- Unwanted switching
transients at the output
6.
Essential hazards-Unequal
delays along 2 or more path from same input
7.
Critical race- If the
final stable state that the circuit reaches does not depend on the order in
which the state variable changes, the race condition are not harmful and
it is called a non critical race.
8.
Non critical race-If the
final stable state that the circuit reaches does not depend on the order in which
the state variable changes, the race condition is not harmful and it is called
a non critical race
9.
Cycles- A cycle occurs when an
asynchronous circuit makes a transition through a series of unstable
states. If a cycle does not contain a stable state, the circuit will go from
one unstable to stable to another, until the inputs are changed.
10. Merger graph-The merger graph is defined as follows. It contains the same number of vertices as the state table contains states. A line drawn between the two state vertices indicates each compatible state pair. It two states are incompatible no connecting line is drawn.
Related Topics