Anatomy and Plant Physiology - Book Back Questions with Answers | 10th Science : Chapter 12 : Anatomy and Plant Physiology
Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 12 : Anatomy and Plant Physiology
Book Back Questions with Answers
Anatomy and Plant Physiology (Science)
I. Choose the correct answer
1. Casparian strips are present in the _____________ of the root.
a) cortex
b) pith
c) pericycle
d) endodermis
2. The endarch condition is the characteristic feature of
a) root
b) stem
c) leaves
d) flower
3. The xylem and phloem arranged side by side on same radius is called _________
a) radial
b) amphivasal
c) conjoint
d) None of these
4. Which is formed during anaerobic respiration
a) Carbohydrate
b) Ethyl alcohol
b) Acetyl CoA
d) Pyruvate
5. Kreb’s cycle takes place in
a) chloroplast
b) mitochondrial matrix
c) stomata
d) inner mitochondrial membrane
6. Oxygen is produced at what point during photosynthesis ?
a) when ATP is converted to ADP
b) when CO2 is fixed
c) when H2O is splitted
d) All of these
II. Fill in the blanks.
1. Cortex lies between epidermal and vascular tissues.
2. Xylem and phloem occurring on the same radius constitute a vascular bundle called conjoint.
3. Glycolysis takes place in cytoplasm.
4. The source of O2 liberated in photosynthesis is water.
5. Mitochondria is ATP factory of the cells
III. State whether the statements are true or false. Correct the false statement.
1. Phloem tissue is involved in the transport of water in plant. - False
Phloem tissue is involved in the transport of food in plant.
2. The waxy protective covering of a plant is called as cuticle. - True
3. In monocot stem cambium is present in between xylem and phloem.
In dicot stem cambium is present between xylem and phloem.
4. Palisade parenchyma cells occur below upper epidermis in dicot root.
Palisade parenchyma cells occur below upper epidermis in dicot leaf.
5. Mesophyll contains chlorophyll.
6. Anaerobic respiration produces more ATP than aerobic respiration.
Aerobic respiration produces more ATP than anaerobic respiration.
IV. Match the following
1. Amphicribal - Dracaena
2. Cambium - Translocation of food
3. Amphivasal - Fern
4. Xylem - Secondary growth
5. Phloem - Conduction of water
Answer:
1. Amphicribal - Fern
2. Cambium - Secondary growth
3. Amphivasal - Dracaena
4. Xylem - Conduction of water
5. Phloem - Translocation of food
V. Answer in a sentence
1. What is collateral vascular bundle?
Collateral vascular bundle is one type of conjoint vascular bundle in which Xylem lies towards the centre and phloem lies towards the periphery. Eg : Dicot stem.
2. Where does the carbon that is used in photosynthesis come from?
The carbon that is used in photosynthesis comes from carbon dioxide in the air.
3. What is the common step in aerobic and anaerobic pathway?
Glycolysis is the common step in aerobic and anaerobic pathway.
4. Name the phenomenon by which carbohydrates are oxidized to release ethyl alcohol.
Fermentation or anaerobic respiration.
VI. Short answer questions
1. Give an account on vascular bundle of dicot stem.
The central part of the stem inner to endodermis is known as stele. It consists of pericycle, vascular bundle and pith. Vascular bundle : Vascular bundles are conjoint, collateral, endarch and open. They are arranged in the form of a ring around the pith.
2. Write a short note on mesophyll.
(i) The tissue present between the upper and lower epidermis of a dicot leaf is called mesophyll.
(ii) It is differentiated into Palisade parenchyma and Spongy parenchyma.
Palisade parenchyma :
(i) It is found just below the upper epidermis. The cells are elongated.
(ii) These cells have more number of chloroplasts. The cells do not have intercellular spaces and they take part in photosynthesis.
Spongy parenchyma :
(i) It is found below the palisade parenchyma tissue.
(ii) Cells are almost spherical or oval and are irregularly arranged.
(iii) Cells have intercellular spaces. It helps in gaseous exchange.
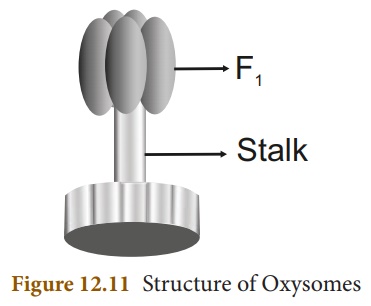
3. Draw and label the structure of oxysomes.
4. Name the three basic tissues system in flowering plants.
The three basic tissue systems in flowering plants are
(i) Epidermal tissue system
(ii) Ground tissue system
(iii) Vascular tissue system
5. What is photosynthesis and where in a cell does it occur?
(i) Photosynthesis is a process by which autotrophic organisms like green plants, algae and chlorophyll containing bacteria utilize the energy from sunlight to synthesize their own food. In this process, carbon dioxide combines with water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll to form carbohydrates. During this process oxygen is released as a byproduct.
6CO2 + 12 H2O –Light--chlorophyll→ C6H12O6 + 6H2O + 6O2 ↑
Carbon dioxide + Water → Glucose + Water + Oxygen
(ii) Photosynthesis occurs in green parts of the plant such as leaves, stems and floral buds.
6. What is respiratory quotient?
Respiratory quotient is the ratio of volume of carbon dioxide liberated and the volume of oxygen consumed during respiration. It is expressed as
RQ = Volume of CO2 liberated / Volume of O2 consumed
7. Why should the light dependent reaction occur before the light independent reaction?
(i) Light dependent reaction of photosynthesis refers to the light reaction / Hill reaction. This reaction occurs in the presence of light in the grana of chloroplast.
(ii) During this process photosynthetic pigments absorb the light energy, and convert it into chemical energy ATP and NADPH2.
(iii) The Light Independent reaction refers to the Dark reaction of photosynthesis or the biosynthetic pathway which occurs in stroma of chloroplast.
(iv) During this reaction CO2, is reduced into carbohydrates with the help of light generated ATP and NADPH2.
(v) Thus light dependent reaction occurs before the light independent reaction.
8. Write the reaction for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 12 H2O –Light--chlorophyll→ C6H12O6 + 6H2O + 6O2 ↑
Carbon dioxide + Water → Glucose + Water + Oxygen
VII. Long answer questions
1. Differentiate the following
a) Monocot root and Dicot root
b) Aerobic and Anaerobic respiration
Answer:
a) Monocot root and
dicot root
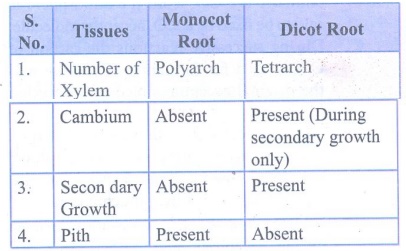
Monocot
Root
1. Number of Xylem : Polyarch
2. Cambium : Absent
3. Secondary Growth : Absent
4. Pith : Present
Dicot
Root
1. Number of Xylem : Tetrarch
2. Cambium : Present
(During secondary growth only)
3. Secondary Growth : Present
4. Pith : Absent
b) Aerobic respiration and anaerobic Respiration:
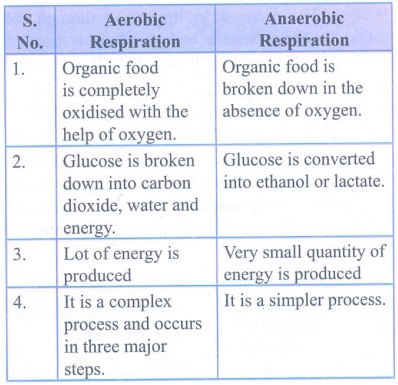
Aerobic
Respiration
1.
Organic food is completely oxidised with the help of oxygen.
2.
Glucose is broken down into carbon dioxide, water and energy.
3.
Lot of energy is produced
4.
It is a complex process and occurs in three major steps.
Anaerobic
Respiration
1.
Organic food is broken down in the absence of oxygen.
2.
Glucose is converted into ethanol or lactate.
3.
Very small quantity of energy is produced
4. It is a simpler process.
2. Describe and name three stages of cellular respiration that aerobic organisms use to obtain energy from glucose.
Answer:
Stages of aerobic respiration :
(a) Glycolysis (Glucose splitting):
(i) It is the breakdown of one molecule of glucose (6
carbon) into two molecules of pyruvic acid (3 carbon).
(ii) Glycolysis takes place in cytoplasm of the cell.
It is the first step of both aerobic and anerobic respiration.
(b) Krebs Cycle :
(i) This cycle occurs in mitochondria matrix. At the
end of glycolysis, 2 molecules of pyruvic acid enter into mitochondria.
(ii) Ihe oxidation of pyruvic acid into CO2
and water takes place through this cycle. It is also called Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (TCA).
(c) Electron Transport Chain :
(i) This is accomplished through a system of electron
carrier complex called electron transport chain
(ETC) located on the inner membrane of the mitochondria.
(ii) NADH2 and FADH2 molecules
formed during glycolysis and Krebs cycle are oxidised to NAD+ and
FAD+ to release the energy via electrons.
(iii) The electrons, as they move through the system,
release energy which is trapped by ADP to synthesize ATP. This is called oxidative phosphorylation.
(iv) In this process, O2 the ultimate
acceptor of electrons gets reduced to water.
3. How does the light dependent reaction differ from the light independent reaction? What are the end product and reactants in each? Where does each reaction occur within the chloroplast?
Answer:

Light
dependent reaction
1.
It takes place in the presence of light and is called as Light reaction of photosynthesis or Hill reaction.
2.
It takes place in the grana of the chloroplast.
3.
During light reaction, photosyntetic pigments absorb the light energy and
convert it into chemical energy ATP and NADPH2.
4.
The inputs are water, solar energy, photosynthetic pigments. The end products
are ATP and NADPH2.
Light
Independent reaction
1.
This takes place in the absence of light and is called dark reaction of photosynthesis or biosynthetic phase.
2. It takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast.
3. During dark reaction CO2 from the
atmosphere is reduced into carbohydrates with the help of light generated ATP
and NADPH2.
4.
The inputs are CO2 from the atmosphere and ATP and NADPH2
from the light reaction. The end product is glucose.
VIII. Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS)
1. The reactions of photosynthesis make up a biochemical pathway.
a) What are the reactants and products for both light and dark reactions.
b) Explain how the biochemical pathway of photosynthesis recycles many of its own reactions and identify the recycled reactants.
(A)
Both light and dark reactions :
Reactant - Product
Light Reaction
Water - Oxygen
Solar energy in presence of chlorophyll pigment. - ATP, NADPH,
Dark Reaction
CO2 - Glucose
ATP and NADPH2 - Glucose
(B)
The ATP and NADPH2 are generated during light reaction of photosynthesis.
(i) They help in reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates and during the process they are converted to ADP and NADP . They are sent back to the grana of chloroplast to form ATP and NADPH2.
(ii) Similarly the CO2 from the atmosphere is said to be fixed by a CO2 acceptor molecule. During successive reactions the carbon of CO2 is used for formation of glucose and the original acceptor molecule is recycled so that it can again help in CO2 fixation.
(iii) Water is split during light reaction and oxygen is produced as a by-product. At the same time water is again released as a by-product of dark reaction.
(iv) Thus many molecules such as ATP, NADPH2, water, CO2 acceptor molecules are recycled during the biochemical pathway of photosynthesis.
2. Where do the light dependent reaction and the Calvin cycle occur in the chloroplast?
(i) The light dependent reaction refers to the light reaction of photosynthesis or Hill reaction and occurs in the grana of chloroplast.
(ii) The Calvin cycle occurs in the stroma of chloroplast.
Related Topics