Chapter: Civil : Structural Analysis : Plastic Analysis Of Structures
Important Questions and Answers: Plastic Analysis Of Structures
P
LASTIC ANALYSIS OF STRUCTURES
1. What is
a plastichinge?
When a section attains full plastic moment Mp, it acts as
hinge which is called a plastic hinge. It is defined as they ieldedzone due to
bending at which large rotation s can occur with a constant value of plastic moment
Mp.
2. What is
a mechanism?
When an-degree indeterminate structure develops n plastic
hinges, it becomes determinate and the formation of an additional hinge will
reduce the structure to a mechanism. Once a structure becomes a mechanism, it
will collapse.
3. What is difference between
plastic hinge and mechanical hinge?
Plastic hinges modify the behavior of structures in the same way
as mechanical hinges. The only difference is that plastic hinges permit
rotation with a constant resisting moment equal to the plastic moment Mp. At
mechanical hinges, theresisting moment is equal to zero.
4. Define
collapse load.
The load that causes the(n +1) th hinge to form a mechanism is
called collapse load where n is the degree of statically indeterminacy. Once the
structure becomes a mechanism
5. List out
the assumptions m adefor plastic analysis.
The assumptions for plastic analysis are:
·
Plane transverse sections remain plane and normal
to the longitudinal axis before and after bending.
· Effect of
shear is neglected.
· The
material is homogeneous and isotropic both in the elastic and plastic state.
· Modulus
of elasticity has the same value both in tension and compression.
· There is
no resultant axial force in the beam.
·
The cross-section of the beam is symmetrical about
an axis through its centroid and parallel to the plane of bending.
6. Define shape
factor.
Shape factor(S) is defined as the ratio of plastic
moment of the section to the yield moment of the section.
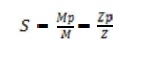
Where Mp
= Plastic moment
M=Yield
moment
Zp = Plastic
section modulus
Z= Elastic
section modulus
7. List out
the shape factors for the following sections.
(a)Rectangular section S =1.5 (b)Triangular section S =2 .346
(c)Circular section S =1.697 (d)Diamond section S =2
8. Mention
the section having maximum shape factor.
The section
having maximum shape factor is a triangular section, S =2.345.
9. Define
load factor.
Load factor is defined as the ratio of collapse load
to working load and is given by
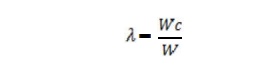
10.
State upper bound theory.
Upper bound theory states that of all the assumed mechanisms
the exact collapse mechanism is that which requires a minimum load.
11.
State lower bound theory .
Lower bound theory states that the collapse load is determined
by assuming suitable moment distribution diagram. The moment distribution
diagram is drawn in such away that the conditions of equilibrium are satisfied.
12.
What are the different types of mechanisms?
The different types of mechanisms are:
·Beam mechanism
·Column mechanism
·Panel orsway mechanism
·Cable mechanism
·Combined or composite mechanism
13Depending on the support and load conditions indicate
the possible locations of plastic hinges.
14.
Mention the types of frames.
Frames are broadly of two types:
(a)Symmetric frames
(b)Un-symmetric frames
15.
What are symmetric frames and how they
analyzed?
Symmetric frames are frames having the same support conditions,
lengths and loading conditions on the columns and beams of the frame. Symmetric
frames can be analyzed by:
(a)Beam mechanism
(b)Column mechanism
16.
What are unsymmetrical frames and how are they
analyzed?
Un-symmetric frames have different support conditions, lengths
and loading conditions on its columns and beams. These frames can be analyzed
by:
(a)Beam mechanism
(b)Column mechanism
(c)Panel orswaymechanism (d)Combined mechanism
17.
Define plastic modulus of a section Zp.
The plastic modulus of a section is the first moment of the area
above and below the equal are a axis. It is the resisting modulus of a fully plasticized
section.
Zp =A/2
(Z1+Z2)
18.
How is the shape factor of a hollow circular section
related to the shape factor of a ordinary circular section?
The shape factor of a hollow circular section =A factor K x shape
factor of ordinary circular section.
SF of hollow circular section =SF of circular section x{(1- c3)/(1- c4)}
19.
Give the governing equation for bending.
The governing equation for bending is given by
M/I=s/y
Where M=Bending moment I=Moment of inertia
s=Stress
y=c.g. distance
20.
Give the theorems for determining the collapse
load.
The two theorems for the determination of collapse
load are:
(a)Static Method [Lower bound Theorem]
(b)Kinematic Method [Upper bound Theorem]
Related Topics