Chapter: Linear Integrated Circuits : Analog Multiplier and PLL
Important Questions and Answers: Linear Integrated Circuits : Analog Multiplier and PLL
ANALOG MULTIPLIER AND PLL
PART-A
1. List the basic building blocks of
PLL
1.
Phase detector/comparator
2.
Low pass filter
3.
Error amplifier
4.
Voltage controlled oscillator
2. Define FSK modulation.
FSK
is a type of frequency modulation, in which the binary data or code is
transmitted by means of a carrier frequency that is shifted between two fixed
frequencies namely mark (logic1) and space frequency (logic 0).
3. What is analog multiplier?
A
multiplier produces an output v0, which is proportional to the product of two
inputs vx and vy V0= kvxvy
4. List out the various methods
available for performing for analog multiplier.
•
Logarithmic summing technique
•
Pulse height /width modulation technique
•
Variable Tran’s conductance technique
•
Multiplication using gilbert cell
•
Multiplication technique using Trans conductance technique
5. Mention some areas where PLL is
widely used.
1.
Radar synchronizations
2.
Satellite communication systems
3.
Air borne navigational systems
4.
FM communication systems
5.
Computers.
6. What are the three stages through
which PLL operates?
1.
Free running
2.
Capture
3.
Locked/ tracking
7. Define lock-in range of a PLL.
The
range of frequencies over which the PLL can maintain lock with the incoming
signal is called the lock-in range or tracking range. It is expressed as a
percentage of the VCO free running frequency.
8. Define capture range of PLL.
The
range of frequencies over which the PLL can acquire lock with an input signal
is called the capture range. It is expressed as a percentage of the VCO free
running frequency.
9. Define Pull-in time.
The
total time taken by the PLL to establish lock is called pull-in time. It
depends on the initial phase and frequency difference between the two signals
as well as on the overall loop gain and loop filter characteristics.
10. Write the expression for FSK
modulation.
∆vf=f2-f1/k0
11. Define free running mode.
An
interactive computer mode that allows more than one user to have Simultaneous
use of a program.
12. For perfect lock, what should be
the phase relation between the incoming signal and VCO output signal?
The
VCO output should be 90 degrees out of phase with respect to the input signal.
13. Give the classification of phase
detector:
1.
Analog phase detector.
2.
Digital phase detector
14. What is a switch type phase
detector?
An
electronic switch is opened and closed by signal coming from VCO and the input
signal is chopped at a repetition rate determined by the VCO frequency. This
type of phase detector is called a half wave detector since the phase
information for only one half of the input signal is detected and averaged.
15. What is a voltage controlled
oscillator?
Voltage
controlled oscillator is a free running multivibrator operating at a set
frequency called the free running frequency. This frequency can be shifted to
either side by applying a dc control voltage and the frequency deviation is
proportional to the dc control voltage.
16. Define Voltage to Frequency
conversion factor.
Voltage to Frequency conversion factor is
defined as,
Kv
= fo / Vc= 8fo /Vcc
Vc
is the modulation voltage fo-frequency shift
17. What is the purpose of having a
low pass filter in PLL?
*It
removes the high frequency components and noise.
*Controls
the dynamic characteristics of the PLL such as capture range, lock-in range,
band-width and transient response.
*The
charge on the filter capacitor gives a short- time memory to the PLL
18. Discuss the effect of having
large capture range.
The
PLL cannot acquire a signal outside the capture range, but once captured, it
will hold on till the frequency goes beyond the lock-in range. Thus, to
increase the ability of lock range, large capture range is required. But, a
large capture range will make the PLL more susceptible to noise and undesirable
signal.
19.Mention some typical applications
of PLL:
•
Frequency multiplication/division
•
Frequency translation
•
AM detection
•
FM demodulation
•
FSK demodulation.
20. What is a compander IC? Give
some examples.
The
term companding means compressing and expanding. In a communication system, the
audio signal is compressed in the transmitter and expanded in the receiver.
Examples: LM 2704-LM 2707; NE 570/571.
21. What are the merits of
companding?
*The
compression process reduces the dynamic range of the signal before it is
transmitted.
*Companding
preserves the signal to noise ratio of the original signal and avoids non
linear distortion of the signal when the input amplitude is large.
*It
also reduces buzz, bias and low level audio tones caused by mild interference.
22. What is a VCO?
VCO
is a free running multivibrator which operates at free running frequency.
23.Draw the relation between the
capture ranges and lock range in a PLL.
24. What is lock range and capture
range of PLL?
Range
of frequencies over which PLL can maintain lock with the incoming signal is
called lock range. Range of frequencies over which PLL can acquire lock with
the incoming signal is called capture range.
25. With reference to a VCO, define
voltage to frequency conversion factor Kv.
Kv
= ∆fo / ∆Vc
26. What are the advantages of
variable transconductance technique?
1.
Provides four quadrant operation.
2.
Good accuracy.
3.
High speed operation.
4.
Less error.
27.VCO is called v-f
converter? why?
The frequency deviation is directly proportional
to the dc control voltage and hence it is called a V-f converter.
28. A PLL frequency multiplier has
an input frequency of “f” and a decade counter is included in the loop. What
will be the frequency of the PLL output?
Output
of PLL = 10f
29. Mention any two applications of
PLL.
Frequency
Translation & AM Detection.
30. What is meant by Frequency
synthesizing.
Large
number of desired frequencies can be produced from a single crystal controlled
oscillator
32. What is the need for Frequency
Synthesizer.
To
produce precise series of frequencies from a stable crystal oscillator
33. What is the function of phase
detector in PLL?
The
phase detector produces a DC or low frequency signal which is proportional to
the phase difference between the input signal and VCO output signal
34. Under what condition the gilbert
cell will function as a multiplier?
When
both the input to the gilbert cell are very small, it will work as a
multiplier.
35. How do you convert a basic
multiplier to a squaring and square root circuit?
When
the input is connected to both the terminals of the multiplier IC, it will act
as a squaring circuit
36. Mention two application of
analog multiplier.
Gilbert
cell ,two and four quadrant multiplier.
37. With the equations, show how is
a multiplier cab be used for finding phase angle difference between two
signals.
38. What is four quadrant
multiplier?
39. Draw the circuit diagram of PLL
circuit using as a FM detector.
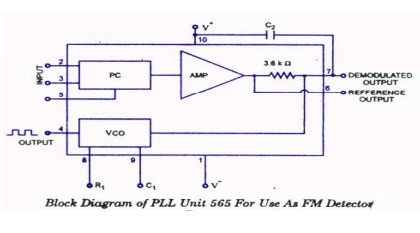
40. Define free running mode.
In
a PLL if the error control voltage is zero then the PLL is said to be operated
in free running mode and its output frequency is called its center frequency f0.
41. What is a four quadrant
multiplier?
In
a multiplier circuit, if both the inputs are allowed to swing in both positive
and negative directions the multiplier is called as a four quadrant multiplier.
42. Mention some areas where PLL is
widely used.
·
Radar
synchronization
·
Satellite
communication systems
·
Air
borne navigational systems
·
FM
communication systems
·
Computers.
43.
List the basic building blocks of PLL
·
Phase
detector/comparator
·
Low
pass filter
·
Error
amplifier
·
Voltage
controlled oscillator
44. What are the three stages
through which PLL operates?
·
Free
running
·
Capture
·
Locked/
tracking
45. Define lock-in range of a PLL.
The
range of frequencies over which the PLL can maintain lock with the incoming
signal is called the lock-in range or tracking range. It is expressed as a
percentage of the VCO free running frequency.
46. Define capture range of PLL.
The
range of frequencies over which the PLL can acquire lock with an input signal
is called the capture range. It is expressed as percentage of the VCO free
running frequency.
47. Define Pull-in time.
The
total time taken by the PLL to establish lock is called pull-in time. It
depends on the initial phase and frequency difference between the two signals
as well as on the overall loop gain and loop filter characteristics.
48. Mention some typical
applications of PLL:
·
Frequency
multiplication/division
·
Frequency
translation
·
AM
detection
·
FM
demodulation
·
FSK
demodulation.
49. What is a voltage controlled
oscillator?
Voltage
controlled oscillator is a free running multivibrator operating at a set
frequency called the free running frequency. This frequency can be shifted to
either side by applying a dc control voltage and the frequency deviation is
proportional to the dc control voltage.
50. Define VCO.
A
voltage controlled oscillator is an oscillator circuit in which the frequency
of oscillations can be controlled by an externally applied voltage.
51. On what parameters does the free
running frequency of VCO depend on?
·
External
timing resistor, RT
·
External
timing capacitor, CT
·
The
dc control voltage Vc.
52. Give the expression for the VCO
free running frequency.
fo
= 0.25 / RT CT
53. Define Voltage to Frequency
conversion factor.
Voltage
to Frequency conversion factor is defined as,
Ky
= fo / Vc= 8fo /Vcc
where,
Vc is the modulation voltage required to produce the frequency shift fo
54. Define FSK modulation.
In
digital data communication, binary data is transmitted by means of a carrier
frequency. FSK employs two different carrier frequencies one for logic 1 and
other for logic 0 states ofbinary data signal. This process is called FSK
modulation.
PART-B
1.
Draw and explain the block diagram of PLL IC 565.
2.
Draw and explain the operation of VCO IC 566 and derive the expression for
fo.
3.
a) Derive the expression for capture range and lock range of PLL. b) Derive the expression for voltage to
frequency conversion factor of VCO.
4.
Explain the application AM detector and FSK demodulator using PLL.
5.
Explain various types of phase detectors used in PLL.
6.
a) Explain the application frequency synthesizer using PLL.
b)
What is the function of LPF in PLL?
7.
Draw and explain the block diagram of PLL IC 565 and derive its transfer
function.
8.
Draw and explain the operation of VCO IC 566 and derive the expression for fo.
9.
a) Derive the expression for capture range and lock range of PLL.
b)
Derive the expression for voltage to frequency conversion factor of VCO.
10.
Explain about Analog multiplier IC.
11.
Sketch and explain the following applications of multipliers.
1.
Squaring
2.
Finding square root
3.
Frequency doubler
4.
Phase angle detector
12.
(i) With a neat diagram explain the variable transconductance technique in
analog multiplier and give its output equation.
(ii) Briefly explain the working of voltage controlled oscillator.
13.
What are important building block of phase locked loop (PLL) explain its
Working?
14.
Draw the functional block schematic of a NE565 PLL and explain the roles of the
low pass filter and VCO. Derive the expression for the capture range and lock
in range of the PLL.
15.
With suitable block diagram, explain the operation of 566 voltage controlled
oscillator. Also derive an expression for the frequency of the output waveform
generated.
16.(i)List
and define the various performance parameters of a multiplier IC. (ii) How the multiplier is used as the
voltage divider? (iii) How the multiplier is used as the frequency doubler?
17.
(i) Explain with neat block diagrams how PLL is used as
(i)
AM detector
(ii)
FM detector
(iii)
Frequency synthesizer
(iv)
FSK Demodulation
18.
a) i) What do you mean by variable Trans conductance Analog multiplier?
ii)
State the advantages of variable Tran‟s conductance technique for analog
multiplication.
iii)
Draw the circuit and explain the working of one quadrant variable Trans
conductance analog multiplier.
19.
Draw the block diagram and explain principle of working, characteristics and
applications of
i)
Frequency synthesizer.
ii)
Frequency shift keying (FSK) Demodulator.
20.
Explain the working of Gilbert Multiplier cell
21.
Explain the principle of operation of PLL?
22.
Explain the working of Analog Multiplier using emitter coupled transistor pair.
Discuss the application of analog multiplier IC.
23.
Explain the application of VCO for FM generation.
24.
With neat simplified internal diagram, explain the working principle of
Operational Tran‟s conductance amplifier. (OTA).
25.
Define capture range and lock range. Explain the process of capturing the lock
and also drive for capture range and lock range.
25.
Derive the expression for the capture range and lock range of Phase Locked
26.
Explain the application of PLL as
(i).Frequency
synthesizer
(ii)AM
demodulator and
(iii)
FM demodulator
27.
Explain the working of Analog Multiplier using emitter coupled transistor with
circuit diagram.
28.
Describe how a PLL could be used as a voltage controlled oscillator.
29.
Draw the basic schematic of the PLL and explain its operation.
30.
Explain the functional diagram the FSK modulation and demodulation operations using
PLL‟s
31.
Explain the working principle of four quadrant variable form trasconductance
multiplier.
32.
Discuss the principle of operation of NE565 PLL circuit.
33.
How can PLL be modeled as a frequency multiplier?
34.
Design a VCO having the maximum range of 1KHz.Assume power supply
Vcc=15V.Required pulse width should not exceed 100µs.
35.
Design PLL 565 as a FSK demodulator in telephone data transmission.
36.
Design a PLL circuit using IC565 to get free running frequency of 4.5 KHz.,Lock
range of 2 KHz, Capture Range of 100Hz.Assume supply voltages of ±10Vare
available.Show diagram with all component values.
37.
In basic multiplier circuit,calculate the output voltage Vo with input voltages
Vi=4V and reference voltage Vref=10V.
38.
For a VCO circuit,assume R2=2.2KΩ ,R1=R3 = 15K and C1= 0.001µF.Assume Vcc=12V.
Determine i) output frequency ii)the change in output frequency if modulating
input Vc is varied from 7 to 8V.
39.
Determine the change in dc control voltage Vc during lock, if input signal frequency
fs=20KHz,the free running frequency is 21KHz and voltage to frequency transfer
coefficient of VCO is 4 KHz/V.
40.
A PLL IC565 connected as an FM demodulator has R1=10KΩ, C1= 0.01µF and C2=
0.04µF.The supply voltage is +12 V. Determine the i) Free running frequency ii)
Lock in range iii) Capture range.
41.
In the given circuit V+= 12V,R2= 1.5K,R1=R3=10K and C1= 0.001µF. i) Determine
nominal frequency of output. Ii) Compute modulation in output frequencies if Vc
is varied between 9.5 and 11.5V. iii) Draw square wave output waveform if the
modulating input is a sinewave.
Related Topics