Chapter: Computer Graphics and Architecture
Illumination and Colour Models
ILLUMINATION
AND COLOUR MODELS
PREREQUISITE DISCUSSION:
In this
unit going to discuss about graphics color models and general computer
animation and three dimensional object scenes.
1. COLOR MODELS
CONCEPTS:
Color Model is a method
for explaining the properties or behavior of color within some particular
context. No single color model can explain all aspects of color, so we make use
of different models to help describe the different perceived characteristics of
color.
2. PROPERTIES OF LIGHT
Light
is a narrow frequency band within the electromagnetic system.
Other frequency bands
within this spectrum are called radio waves, micro waves, infrared waves and
x-rays. The below fig shows the frequency ranges for some of the
electromagnetic bands.
Each frequency value within the visible band
corresponds to a distinct color.
At the low frequency end is a red color (4.3*104 Hz)
and the highest frequency is a violet color (7.5 *10 14Hz)
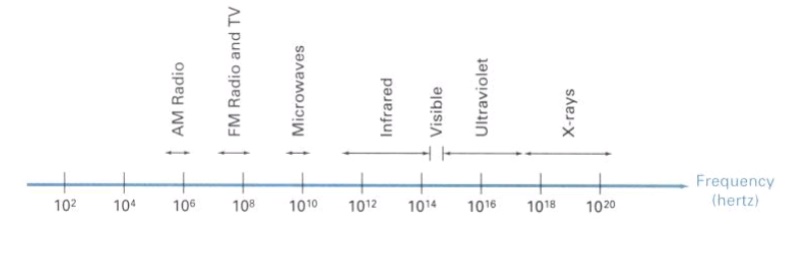
Spectral colors range
from the reds through orange and yellow at the low frequency end to greens,
blues and violet at the high end.
Since light is an
electro magnetic wave, the various colors are described in terms of either the
frequency for the wave length λ of the wave.
The wave length ad
frequency of the monochromatic wave are inversely proportional to each other,
with the proportionality constants as the speed of light C where C = λ f
A
light source such
APPLICATIONS:
1.Implement a color models.
2.Implement a realistic scenes and
objects
3.OPENGL is a easy way
to make a real objects. as the sun or a light bulb emits all frequencies within
the visible range to produce white light. When white light is incident upon an
object, some frequencies are reflected and some are absorbed by the object. The
combination of frequencies present in the reflected light determines what we
perceive as the color of the object.
If low frequencies are
predominant in the reflected light, the object is described as red. In this
case, the perceived light has the dominant frequency at the red end of the
spectrum. The dominant frequency is also called the hue, or simply the color of
the light.
Brightness is another property, which in the
perceived intensity of the light.
Intensity in the
radiant energy emitted per limit time, per unit solid angle, and per unit
projected area of the source.
Radiant energy is related to the luminance of the
source.
The next property in the purity or saturation of the
light.
- Purity
describes how washed out or how pure the color of the light appears.
- Pastels
and Pale colors are described as less pure.
The term chromaticity is used to refer collectively
to the two properties, purity and dominant frequency.
SIGNIFICANCE:
Color
Model is a method for explaining the properties or behavior of color within
some particular
context.
3. STANDARD PRIMARIES
CONCEPTS
4. XYZ
COLOR MODEL
The set of primaries is
generally referred to as the XYZ or (X,Y,Z) color model where X,Y and Z
represent vectors in a 3D, additive color space.
Any color Cλ is expressed as
Cλ = X X + YY
+ ZZ -------------(1) Where X,Y and Z designates the amounts of the
standard primaries needed to match Cλ.
It is convenient to
normalize the amount in equation (1) against luminance (X + Y+ Z). Normalized
amounts are calculated as,
x = X/(X+Y+Z), y = Y/(X+Y+Z), z = Z/(X+Y+Z) with x +
y + z = 1
Any color can be
represented with just the x and y amounts. The parameters x and y are called
the chromaticity values because they depend only on hue and purity.
5. RGB Color Model
Based on the
tristimulus theory of our eyes perceive color through the stimulation of three
visual pigments in the cones on the retina.
These visual pigments
have a peak sensitivity at wavelengths of about 630 nm (red), 530 nm (green)
and 450 nm (blue).
By comparing intensities in a light source, we
perceive the color of the light.
This is the basis for
displaying color output on a video monitor using the 3 color primaries, red,
green, and blue referred to as the RGB color model.
The sign represents black, and the vertex with
coordinates (1,1,1) in white.
Vertices of the cube on
the axes represent the primary colors, the remaining vertices represents the
complementary color for each of the primary colors.
The RGB color scheme is
an additive model. (i.e.,) Intensities of the primary colors are added to
produce other colors.
Each color point within
the bounds of the cube can be represented as the triple (R,G,B) where values
for R, G and B are assigned in the range from 0 to1.
The color Cλ is expressed in RGB component as
Cλ = RR + GG + B
6. YIQ Color Model
The National Television
System Committee (NTSC) color model for forming the composite video signal in
the YIQ model.
In the YIQ color model,
luminance (brightness) information in contained in the Y parameter,
chromaticity information (hue and purity) is contained into the I and Q
parameters.
A combination of red, green and blue intensities are
chosen for the Y parameter to yield the standard luminosity curve.
Since Y contains the luminance information, black
and white TV monitors use only the Y signal.
Parameter I contain
orange-cyan hue information that provides the flash-tone shading and occupies a
bandwidth of 1.5 MHz.
Parameter Q carries green-magenta hue information in
a bandwidth of about 0.6 MHz.
An RGB signal can be converted to a TV signal
7. CMY Color Model
A color model defined
with the primary colors cyan, magenta, and yellow (CMY) in useful for
describing color output to hard copy devices.
It is a subtractive
color model (i.e.,) cyan can be formed by adding green and blue light. When
white light is reflected from cyan-colored ink, the reflected light must have
no red component. i.e., red light is absorbed or subtracted by the link.
Magenta ink subtracts the green component from
incident light and yellow subtracts the blue component.
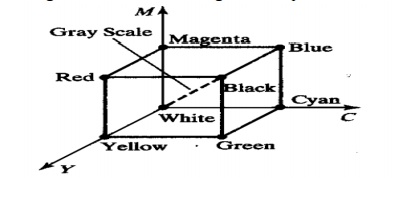
In CMY model, point (1,1,1) represents black because
all components of the incident light are subtracted.
The origin represents white light.
Equal amounts of each of the primary colors produce
grays along the main diagonal of the cube.
A combination of cyan
and magenta ink produces blue light because the red and green components of the
incident light are absorbed.
The printing process
often used with the CMY model generates a color point with a collection of 4
ink dots; one dot is used for each of the primary colors (cyan, magenta and
yellow) and one dot in black.
8. HSV Color Model
The HSV model uses color descriptions that have a
more interactive appeal to a user.
Color parameters in this model are hue (H),
saturation (S), and value (V).
The 3D representation of the HSV model is derived
from the RGB cube. The outline of the cube has the hexagon shape.
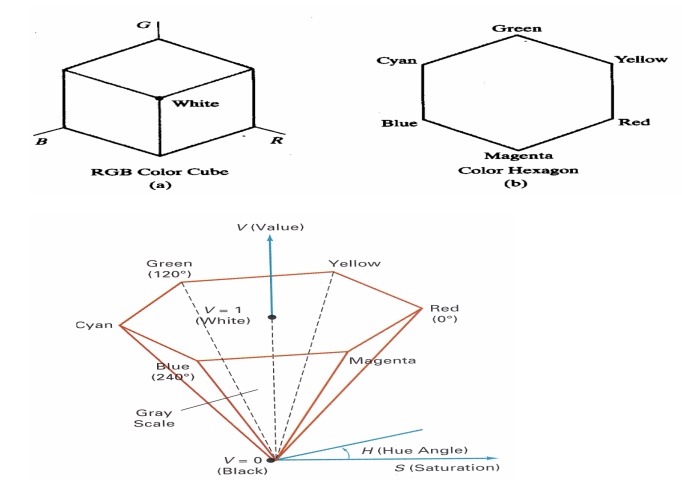
9. HLS Color Model
HLS model is based on intuitive color parameters used by Tektronix.
It has the double cone representation shown in the below figure. The 3 parameters in this model are called Hue (H), lightness (L) and saturation (s).
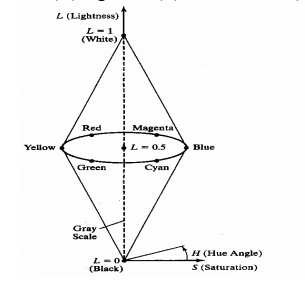
SIGNIFICANCE:
Different types of color models provide how the color displays in different form.
APPLICATIONS:
1.Implement
a color models.
2.Implement
a realistic scenes and objects
3.OPENGL is a easy way to make a real
objects.
Related Topics