Chapter: Digital Signal Processing : IIR Filter Design
IIR Filter Design
IIR FILTER DESIGN
INTRODUCTION
To remove
or to reduce strength of unwanted signal like noise and to improve the quality
of required signal filtering process is used. To use the channel full bandwidth
we mix up two or more signals on transmission side and on receiver side we
would like to separate it out in efficient way.
Hence
filters are used. Thus the digital filters are mostly used in
1.
Removal of undesirable noise from the desired
signals
2.
Equalization of communication channels
3.
Signal detection in radar, sonar and communication
4.
Performing spectral analysis of signals.
![]()
Analog and digital filters
In signal
processing, the function of a filter is to remove unwanted parts of the signal,
such as random noise, or to extract useful parts of the signal, such as the
components lying within a certain frequency range.
The
following block diagram illustrates the basic idea.
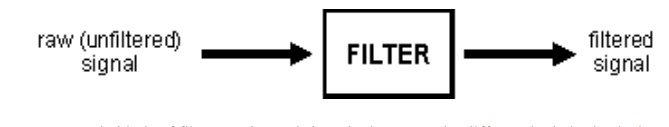
There are
two main kinds of filter, analog and digital. They are quite different in
their physical makeup and in how they work.
An analog
filter uses analog electronic circuits made up from components such as
resistors, capacitors and op amps to produce the required filtering effect.
Such filter circuits are widely used in such applications as noise reduction,
video signal enhancement, graphic equalizers in hi-fi systems, and many other
areas.
In analog
filters the signal being filtered is an electrical voltage or current which is
the direct analogue of the physical quantity (e.g. a sound or video signal or
transducer output) involved.
A digital
filter uses a digital processor to perform numerical calculations on sampled
values of the signal. The processor may be a general-purpose computer such as a
PC, or a specialized DSP (Digital Signal Processor) chip.
The
analog input signal must first be sampled and digitized using an ADC (analog to
digital converter). The resulting binary numbers, representing successive
sampled values of the input signal, are transferred to the processor, which
carries out numerical calculations on them. These calculations typically
involve multiplying the input values by constants and adding the products
together. If necessary, the results of these calculations, which now represent
sampled values of the filtered signal, are output through a DAC (digital to
analog converter) to convert the signal back to analog form.
In a
digital filter, the signal is represented by a sequence of numbers, rather than
a voltage or current.
The following diagram shows the
basic setup of such a system.
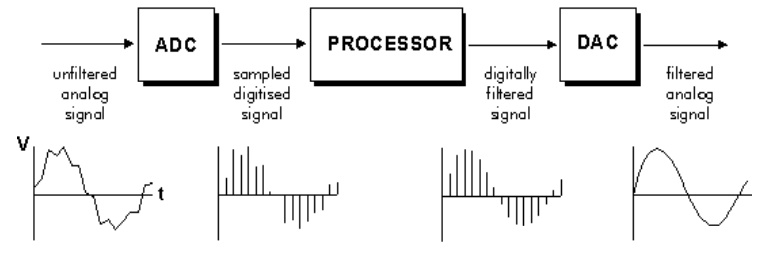
BASIC
BLOCK DIAGRAM OF DIGITAL FILTERS
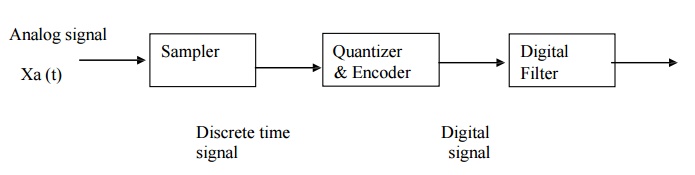
a. Samplers
are used for converting continuous time signal into a discrete time signal by
taking samples of the continuous time signal at discrete time instants.
b. The
Quantizer are used for converting a discrete time continuous amplitude signal
into a digital signal by expressing each sample value as a finite number of
digits.
c. In
the encoding operation, the quantization sample value is converted to the
binary equivalent of that quantization level.
d. The
digital filters are the discrete time systems used for filtering of sequences.
e. These
digital filters performs the frequency related operations such as low pass,
high pass, band pass and band reject etc. These digital Filters are designed
with digital hardware and software and are represented by difference equation.
DIFFERENCE
BETWEEN ANALOG FILTER AND DIGITAL FILTER
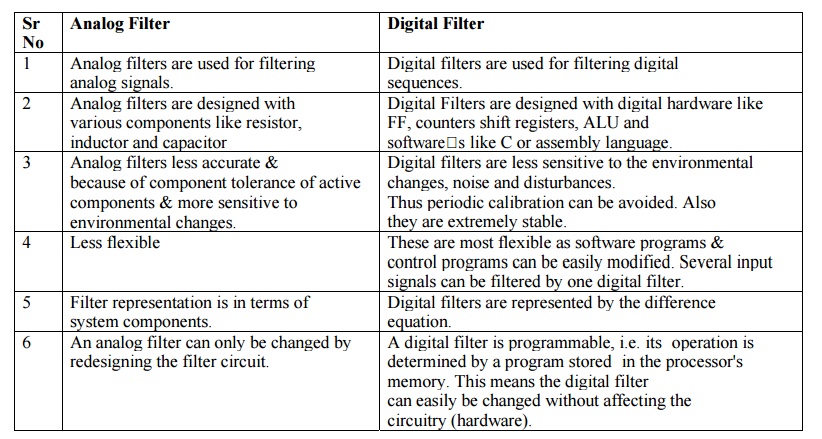
Analog Filter
1 Analog filters are used for filtering analog
signals.
2 Analog filters are designed with various
components like resistor, inductor and capacitor
3 Analog filters less accurate & because
of component tolerance of active components & more sensitive to
environmental changes.
4 Less flexible
5 Filter representation is in terms of system
components.
6 An analog filter can only be changed by
redesigning the filter circuit.
Digital Filter
1 Digital filters are used for filtering
digital sequences.
2 Digital Filters are designed with digital
hardware like FF, counters shift registers, ALU and software s like C or
assembly language.
3 Digital filters are less sensitive to the
environmental changes, noise and disturbances. Thus periodic calibration can be
avoided. Also they are extremely stable.
4 These are most flexible as software programs
& control programs can be easily modified. Several input signals can be
filtered by one digital filter.
5 Digital filters are represented by the
difference equation.
6 A digital filter is programmable, i.e. its
operation is determined by a program stored in the processor's memory. This
means the digital filter can easily be changed without affecting the circuitry
(hardware).
FILTER TYPES AND IDEAL FILTER CHARACTERISTIC
Lowpass Filter
A lowpass
filter is made up of a passband and a stopband, where the lower frequencies Of
the input signal are passed through while the higher frequencies are
attenuated.
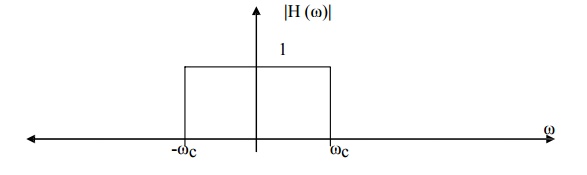
Highpass Filter
A
highpass filter is made up of a stopband and a passband where the lower
frequencies of the input signal are attenuated while the higher frequencies are
passed.

Bandpass Filter
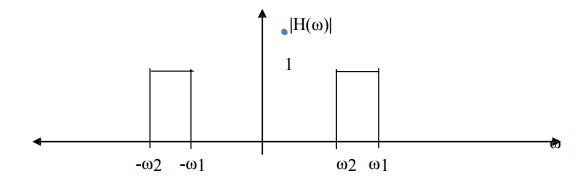
A
bandpass filter is made up of two stopbands and one passband so that the lower
and higher frequencies of the input signal are attenuated while the intervening
frequencies are passed.
Bandstop Filter
A
bandstop filter is made up of two passbands and one stopband so that the lower
and higher frequencies of the input signal are passed while the intervening
frequencies are attenuated. An idealized bandstop filter frequency response has
the following
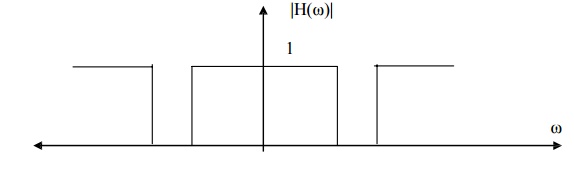
Multipass Filter
A
multipass filter begins with a stopband followed by more than one passband. By
default, a multipass filter in Digital Filter Designer consists of three
passbands and
four
stopbands. The frequencies of the input signal at the stopbands are attenuated
while those at the passbands are passed.
Multistop Filter
A
multistop filter begins with a passband followed by more than one stopband. By
default, a multistop filter in Digital Filter Designer consists of three
passbands and two stopbands.
All Pass Filter
An all
pass filter is defined as a system that has a constant magnitude response for
all frequencies.
|H(ω)| = 1 for 0 ≤ ω < ∏
The
simplest example of an all pass filter is a pure delay system with system
function H(z) = Z-k. This is a low pass filter that has a linear
phase characteristic.
All Pass
filters find application as phase equalizers. When placed in cascade with a
system that has an undesired phase response, a phase equalizers is designed to
compensate
for the poor phase characteristic of the system and therefore to produce an
overall linear phase response.
IDEAL FILTER CHARACTERISTIC
1. Ideal filters have a constant gain (usually
taken as unity gain) passband characteristic and zero gain in their stop band.
2. Ideal filters have a linear phase
characteristic within their passband.
3. Ideal filters also have constant magnitude
characteristic.
4. Ideal filters are physically unrealizable.
Related Topics