Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio zoology Human Body higher secondary school
Human Kidney stone (Calculus) And Kidney transplantation
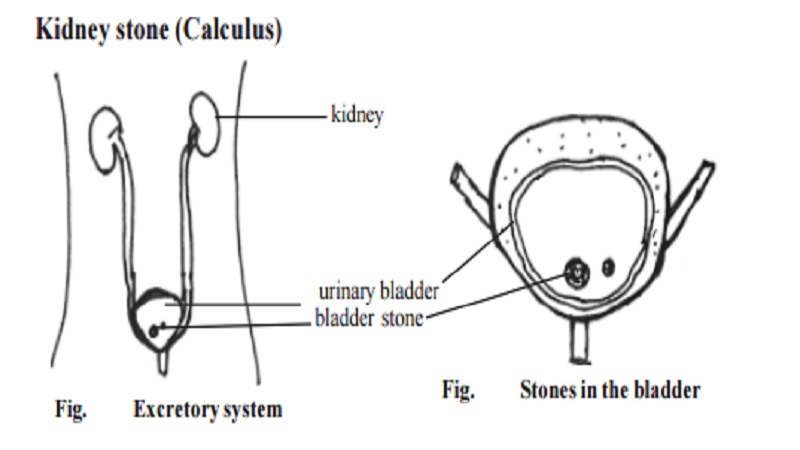
Kidney stone (Calculus)
Stone formation in the kidneys, Ureters or Bladder, is caused by the precipitation from the solution of the substances in urine. Kidney and Ureter stones are more common than Bladder stones. The incidence of stone formation is highest in summer months as the urine is more concentrated due the loss of fluid in the sweat. The stones tend to be a recurrent problem. Chronic dehydration is the main cause for kidney stones. Kidney stone consists mainly of calcium oxalate and/or phosphate.
Stone consists mainly of uric acid and may occur in people with GOUT.
Bladder stone usually develops as a result of a diet that is low in phosphate and protein. The most common symptom of a stone in the kidney or ureter is renal cholic (a severe pain) and the symptom for the bladder stones manifest with difficulty in passing urine. Stones in the bladder and lower ureter can be crushed and removed by cystoscopy or by ureterorenoscopy. The first line of treatment is lithotripsy which disintegrates stones by focusing shock waves on them from outside the body.
Kidney transplantation
Kidney transplantation refers to an operation in which a diseased kidney is replaced by a transplanted healthy kidney, either from a living donor or from a person who has just died (cadaver). One healthy donor kidney is sufficient to maintain the health of the recipient.
Factors in improving the results of transplant surgery are
(1) To prevent rejection, effective immune suppressant drug treatment is given.
(2) Tissue typing is necessary to help in matching recipient and donor tissue for transplant surgery thus minimizing the risk of rejection of a donor organ by the recipient's immune system.
(3) After removal of organ from the donor it should be washed with an oxygenated fluid and cooled. This reduces the risk of damage.
Related Topics