Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio zoology Human Body higher secondary school
Haemocytometer
Haemocytometer
The counting of blood cells after proper dilution is known as haemocytometry and the instrument used to count the blood cells is called haemocytometer. Using haemocytometry method, red cells, platelets and eosinophils are often counted. Now-a-days it is also used for counting cells of bacteria, yeast, or algae.
Haemocytometer - instruments description
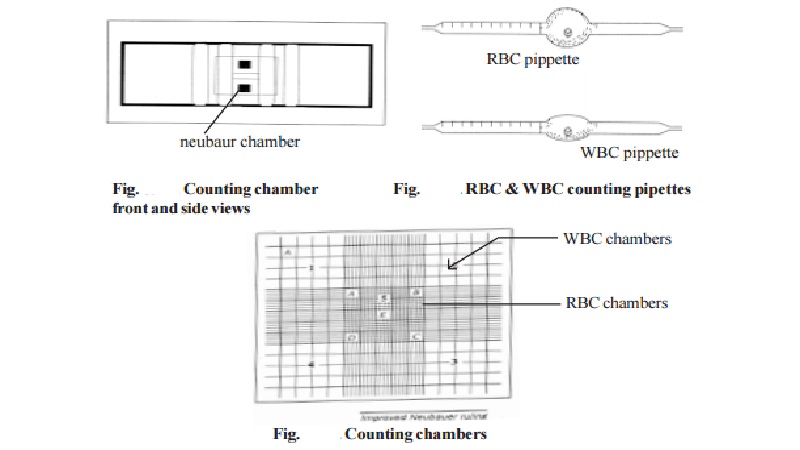
A haemocytometer consists of a counting chamber, a coverglass for the counting chamber and diluting pipettes. Many types of counting chambers are available. Improved Neubauer and Fauchs Rosenthal are the two most commonly used counting chambers in laboratories.
RBCs and WBCs in blood cannot be counted as such. The blood has to be diluted in specific isotonic solutions. RBC, diluting fluid is called Hayem's solution. For WBC counting Turk's solution or Toisson solution can be used.
The total number of cells is expressed per mm3. The isotonic diluting fluid keeps up the cells intact. In WBC counting, the solution will lyse the red blood cells and the remaining nucleated WBCs are counted. Venous blood is used in blood cells counting.
Normal Range of RBCs in human is as follows :
Men : 4.5 - 5.9 million/mm3
Women : 4.1 - 5.1 million/mm3
At birth : 4.0 - 5.6 million/mm3
Normal Range of WBCs in human is as follows :
Adults : 4,500 - 11,000/mm3
Neonates : 10,000 - 25,000/mm3
Clinical significance :
1.Decrease in the number of circulating erythrocytes indicates anaemia.
2. An increased number of erythrocytes indicates the possibility of polycythemia.
3.An increase in WBC count for a transient period indicates bacterial infection.
4. Progressive increase in abnormal WBC count indicates the possibility of leukemia.
Related Topics