Chapter: Mechanical : Advanced IC Engines : Engine Exhaust Emission Control
HC emission and Smoke
HC emission:
Hydrocarbons
(HC) are the consequence of incomplete combustion of hydrocarbon fuel. The
level of unburned hydrocarbons (HC) in the exhaust gases specified in terms of
total hydrocarbon concentration expressed in parts per million carbon atoms.
Engine exhaust gases contain a wide variety of hydrocarbon compounds.
HC is
basically divided into two classes namely methane and non-methane hydrocarbons.
Below table shows classifications of hydrocarbons according to their relative
reactivity which is the scale of 0 to 100based on their NO2
formation relatively to HC.

Smoke
Formations of smoke and affecting factors:
Engine
Exhaust smoke is the result of incomplete combustion. Smoke from exhaust is a
visible indicator of the combustion process within the engine. It is generated
at any volume in the engine where mixture is rich. The fuel air ratio greater
than 1.5 and pressures developed in diesel engine produced soot. Once soot is
formed, it can burn if it finds sufficient O2 otherwise it comes out
with exhaust. It becomes visible if it is dense. The size of the soot particles
effect the appearance of smoke. The soot particles agglomerate into bigger
particles which have an objectionable darkening effect on diesel exhaust.
Measurement of smoke:
The main
purpose of smoke measurement is to quantify the black smoke from diesel engine.
As visibility is the main criterion in evaluating the intensity of smoke,
development or principle of the smoke meter depends on the light obstruction by
the smoke.
Even
though there are several smoke measuring types, two basic and main types are
discussed in this lecture.
1. Hartridge
smoke meter.
2. Bosch
smoke meter.
Hartridge smoke meter:
The
arrangement is shown in the figure. This consists of two optically identical
tubes, one containing clean air and other the moving sample of the smoke. The
clean air tube is taken as reference. A light source and photo-electric cell
mounted facing each other on swinging arms. Movement of the change-over knob
alters their position from 0-100, indicating the light absorbed by the smoke in
hartridge units. A small fan blows air into the clean air-tube. The air flow
the open ends of the tube across the surfaces of the light source and the
photo-electric cell, to provide cooling and to protect them against sooting by
the smoke.
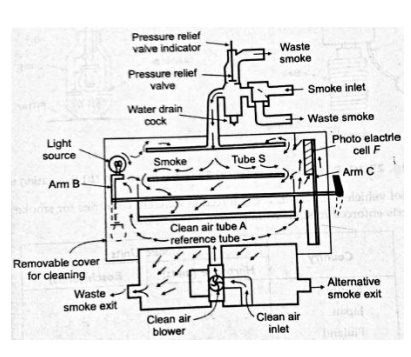
The
sampling probe is connected either to a tapping on the exhaust pipe. The smoke
meter is switched on and control lever set to bring the clean air tube between
light and cell. The smoke meter dial should read zero otherwise the meter is to
adjusted to read zero. The control lever valve, the meter gives continuous and
direct reading of the smoke density.
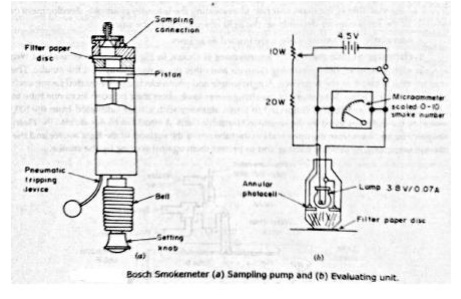
Bosch smoke meter:
The bosch
meter is widely accepted for measuring the diesel engine smoke. This concists
of sampling pump and evaluating unit shown in the figure given below. The
sampling pump is used to draw nearly 300CC of exhaust gas by means of spring
operated pump and released by pneumatic operation of a diaphragm. The gas
sample is drawn is through the filter paper darkening to give precise
assessment of the intensity of the spot. The intensity of the spot is measured
on a scale of 10 arbitary units called arbitrary units, called Bosch smoke units
for white to black.
Related Topics