Chapter: Mechanical : Advanced IC Engines : Engine Exhaust Emission Control
Formation of CO
Formation of CO:
Carbon
monoxide (CO) emissions from internal combustion engines are controlled
primarily by the fuel/air equivalence ratio. Figure 11-20 shows CO levelsin the
exhaust of a conventional spark-ignition engine for several different
fuel compositions. 27 When the data are plotted against the relative air/fuel
ratio orthe equivalence ratio, they are correlated by a single curve. For
fuel-rich mixtures CO concentrations in the exhaust increase steadily with
increasing equivalence ratio, as the amount of excess fuel increases. For
fuel-lean mixtures, CO concentrationsin the exhaust vary little with
equivalence ratio and are of order 10-3
mole fraction. Since spark-ignition engines often operate close to stoichio
metric at partload and fuel rich at full load, CO emissions are significant and
mustbe controlled. Diesels, however, always operate well on the lean side of
stoichiometric;CO emissions from diesels are low enough to be unimportant,
therefore, and will not be discussed further.
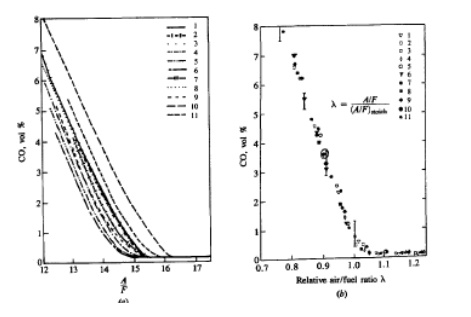
The
levels of CO observed in spark-ignition engine exhaust gases are lower than the
maximum values measured within the combustion chamber, but arehigher than
equilibrium values for the exhaust conditions. Thus the processes which govern
CO exhaust levels are kinetically controlled. In premixed hydrocarbon-air
flames, the CO concentration increases rapidly in the flame zoneto a maximum
value, which is larger than the equilibrium value for adiabatic of the fuel-air
mixture. CO formation is one of the principal reaction steps in the hydrocarbon
combustion mechanism, which may be summarized by
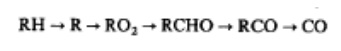
Where R stands for the hydrocarbon radical.
The CO formed in the combustion process via this path is then oxidized to CO,
at a slower rate. The principal CO oxidation reaction in hydrocarbon-air flames
is
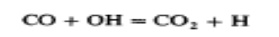
CO
increases rapidly as the inlet mixture becomes richer than stoichiometric
ratio. And also improved cylinder-to-cylinder fuel/air ratio distribution has
become essential. In addition to this, it is necessary to enrich the fuel-air
mixture when the engine is cold since CO emission is higher at engine warm up.
Related Topics