Chapter: Analog and Digital Communication
Frequency Spectrum and Bandwidth Requirement of Angle Modulated Wave
FREQUENCY SPECTRUM AND BANDWIDTH REQUIREMENT OF
ANGLE MODULATED WAVE.
Frequency
Spectrum of Angle Modulated Waves
We know that AM
contains only two sidebands per modulating frequency. But angle modulated
signal contains large number of sidebands depending upon the modulation index.
Since FM and PM have identical modulated waveorms, their frequency content is
same. Consider the PM equation or spectrum analysis,
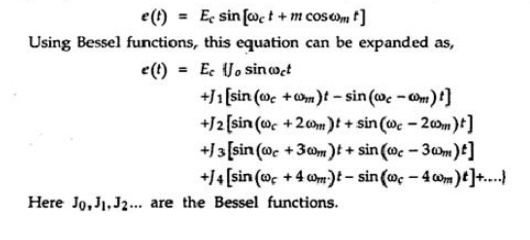
The
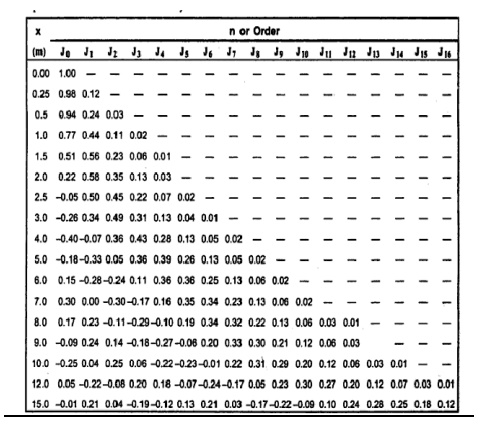
values of Bessel functions depend upon modulation index m, They are listed in
Table 2.1.1
It is clear from the
above discussion that, angle modulated signal has infinite number of sidebands
as well as carrier in the output. The sidebands are separated from the carrier
by fm, 2fm, 3fm … etc. The frequency
separation between successive sidebands is fm. All the sidebands are
symmetric around carrier frequency. The
amplitude of the sidebands are Ecf0, Ecf1,
Ecf2, Ecf3, Ecf4,
… and so on.
Bandwidth
Requirement
The bandwidth
requirement of angle modulated waveforms can be obtained depending upon
modulation index. The modulation index can be classified as low (less than 1),
medium (1 to 10) and high (greater than 10). The low index systems are called
narrowband FM. For such system the frequency spectrum resembles AM. Hence
minimum bandwidth is given as,

Here ‘n’ is the number
of significant sidebands obtained from Bessel table.
Carson’s
Rule:
Carson’s
Rule gives appoximate minimum banndwith of angle modulated signal as
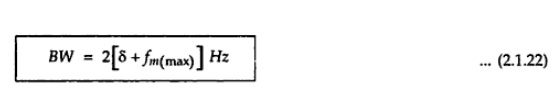
Here fm(max)
is the maximum modulating frequency. As per Carson’s rule, the bandwidth
accommodates almost 98% of the total transmitted power.
Related Topics