Term 3 Chapter 1 | 6th Maths - Fractions | 6th Maths : Term 3 Unit 1 : Fractions
Chapter: 6th Maths : Term 3 Unit 1 : Fractions
Fractions
CHAPTER 1
FRACTIONS

Learning Objectives
* To add and subtract
unlike fractions.
* To understand improper
and mixed fractions.
* To express improper
fractions into mixed fractions and vice versa.
* To do fundamental operations on mixed fractions.
Recap
I. Fractions
On Anbu’s birthday function, his father, mother
and uncle have bought one cake each of equal size. At the time of cutting a cake,
two friends were present for the celebration. He divided the cake into 2 equal pieces
and gave the pieces to them. After some time, three of his friends arrived. He took
another cake and divided it into 3 equal pieces and gave the pieces to them. Still
he has one more cake at home. Anbu wanted to share it among his four family members.
Third cake is divided into 4 equal pieces and given to them.
Following table shows how Anbu divided the cake
equally according to the number of persons.
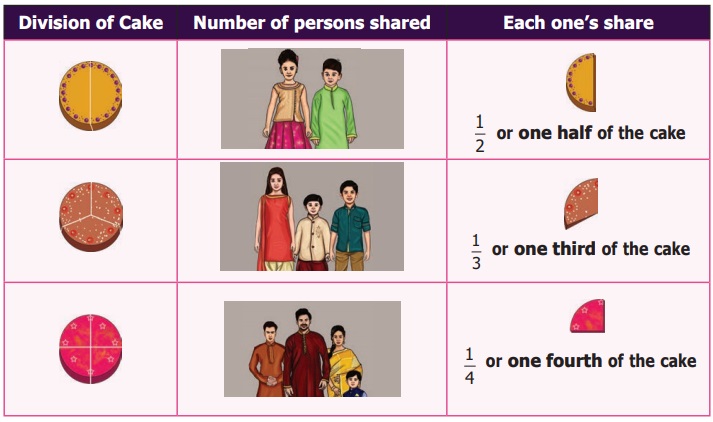
In the above situation, each of 3 cakes was divided
equally according to the number of persons attended the function. When Anbu shared
one cake to 4 persons, each one got quarter of the cake which was comparatively
smaller than the share got by one person when it was divided equally between 2 and
3 persons. When the number of persons increases the size of the cake becomes smaller.
Suppose all the three cakes of equal size are shared
equally with the family members of Anbu, what would be each one’s share?
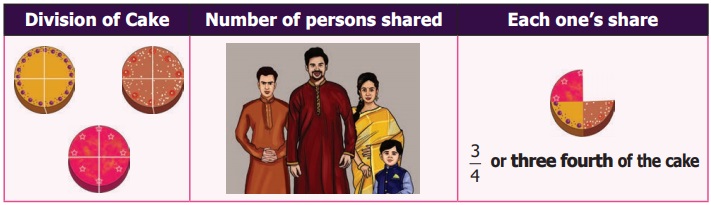
Each one would get ¾ of the cake. Here we have divided
the whole into equal parts, each part is called a Fraction. We say a fraction as selected part(s) out of total
number of equal parts of an object or a group.
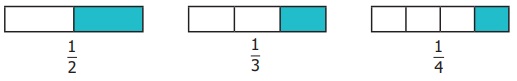
Each one’s share of dividing one cake between 2,
3 and 4 persons respectively can be represented as follows.
Think
If all the three cakes are divided among
the total participants of the function what would be each one's share? Discuss.
Try these
1. Observe the following and represent
the shaded parts as fraction.
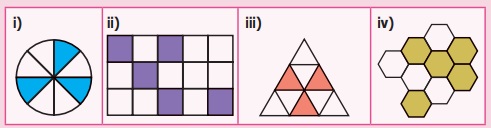
Answer:
i) 3 / 8
ii) 5 / 15
iii) 3 / 9
iv) 5 / 9
2. Look at
the following beakers. Express the quantity of water as fractions and arrange them
in ascending order.
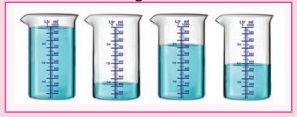
Answer:
100 / 100
25 / 100
75 / 100
50 / 100
Ascending order :
25 / 100, 50 / 100, 75 / 100, 100 / 100

3. Write
the fraction of shaded part in the following.

Answer:
(i) 2/3
(ii) 3/4
(iii) 4/5
4. Write
the fraction that represents the dots in the triangle.
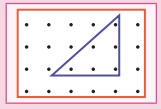
Answer: 6/24
5. Find the
fractions of the shaded and unshaded portions in the following.
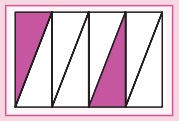
Answer: 2/8, 6/8
II. Equivalent Fractions
Murali has one peanut bar. He wants to share it
equally with Rani. So he divided it into two equal pieces, each one has got 1 piece
out of 2, which is half of the peanut bar. They both decided to have half of their
share in the morning break and another half in the evening break. Now the total
number of pieces becomes 4. Each one has 2 pieces out of 4. That is 2/4 which is
nothing but half of the peanut bar. Look at the figures. In both the type of sharing,
they got only the same half of the peanut bar. Therefore, 1/2 = 2/4. Hence, 2/4
is equivalent
to 1/2.
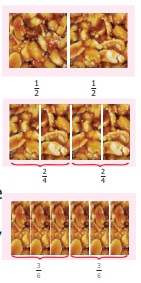
If the peanut bar had been
divided into 6 equal pieces, each one would have got 3/6. What about each one’s
share if it is divided into 8 equal pieces? We can observe that 1/2 = 2/4 = 3/6.
How do we get these equivalent fractions of 1/2?
2/4 = [1 × 2] / [2 × 2],
3/6 = [1 × 3] / [2 × 3]
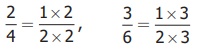
Hence, to get equivalent
fractions of the given fraction, the numerator and denominator are to be multiplied
by the same number.
Activity
Take a rectangular paper. Fold it
into two equal parts. Shade one part, write the fraction. Again fold it into two
halves. Write the fraction for the shaded part. Continue this process 5 times and
write the fraction of the shaded part. Establish the equivalent fractions of 1/2
in the folded paper to your friends.

Example 1.1
Find three equivalent
fractions of 3/4 and 2/7 .
Solution
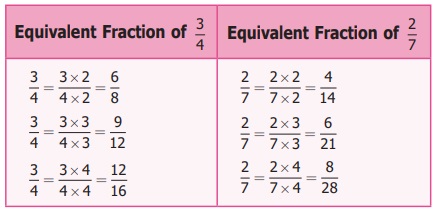
Equivalent
fractions of 3/4: 3/4 = 6/8 = 9/12 =
12/16
Equivalent
fractions of 2/7: 2/7 = 4/14 = 6/21 =
8/28
Try these
Find the unknown in the following
equivalent fractions

Introduction
Fractions are used in life situations such as
* To express time as
quarter past 3, half past 4, quarter to 5.
* To say the quantum
of work completed as quarter / half / three quarters of the work completed.
* To say the distance
between two places as half a kilometre / two and half kilometre.
* To express the quantity of ingredients to be used
in a recipe as half of the rice taken, half of the dhal taken etc.
Mathematics Alive − Fractions in Real Life

Nine-Tenths of water on the earth is salty.
The distance between Chennai Egmore and the Directorate
of Public Instruction Campus (DPI) is nearly 1 ½ kilometre.
Related Topics