Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Agents Used in Dyslipidemia
Fibric Acid Derivatives (FIBRATES)
FIBRIC ACID DERIVATIVES
(FIBRATES)
Gemfibrozil and fenofibrate decrease
levels of VLDL and, insome patients, LDL as well. Another fibrate, bezafibrate, is not yet available in
the USA.
Chemistry & Pharmacokinetics
Gemfibrozil
is absorbed quantitatively from the intestine and is tightly bound to plasma
proteins. It undergoes enterohepatic circulation and readily passes the
placenta. The plasma half-life is 1.5 hours. Seventy percent is eliminated
through the kidneys, mostly unmodified. The liver modifies some of the drug to
hydroxymethyl, carboxyl, or quinol derivatives. Fenofibrate is an isopropyl
ester that is hydrolyzed completely in the intestine. Its plasma half-life is
20 hours. Sixty percent is excreted in the urine as the glucuronide, and about
25% in feces.
Mechanism of Action
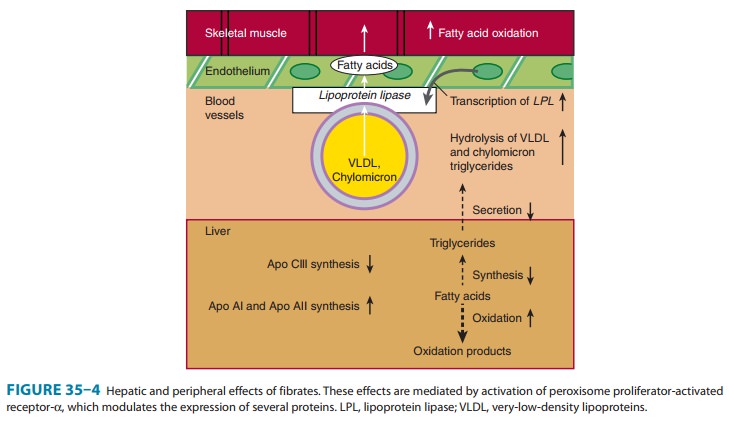
Fibrates function
primarily as ligands for the nuclear transcription receptor, PPAR-α. They
transcriptionally up-regulate LPL, apo A-I and apo A-II, and down-regulate apo
C-III, an inhibitor of lipolysis. A major effect is an increase in oxidation of
fatty acids in liver and striated muscle (Figure 35–4). They increase lipolysis
of lipoprotein triglyceride via LPL. Intracellular lipolysis in adipose
Only modest reductions of LDL occur in most patients.
In others, especially those with combined hyperlipidemia, LDL often increases
as triglycerides are reduced. HDL cholesterol increases moderately. Part of this
apparent increase is a consequence of decreasing triglycerides in plasma, with
reduction in exchange of triglycerides into HDL in place of cholesteryl esters.
Therapeutic Uses & Dosage
Fibrates are useful
drugs in hypertriglyceridemias in which VLDL predominate and in
dysbetalipoproteinemia. They also may be of benefit in treating the
hypertriglyceridemia that results from treat-ment with viral protease
inhibitors. The usual dose of gemfibrozil is 600 mg orally once or twice daily.
The dosage of fenofibrate (as Tricor) is one to three 48 mg tablets (or a
single 145 mg tablet) daily. Absorption of gemfibrozil is improved when the
drug is taken with food.
Toxicity
Rare adverse effects
of fibrates include rashes, gastrointestinal symp-toms, myopathy, arrhythmias,
hypokalemia, and high blood levels of aminotransferases or alkaline
phosphatase. A few patients show decreases in white blood count or hematocrit.
Both agents potenti-ate the action of coumarin and indanedione anticoagulants,
and doses of these agents should be adjusted. Rhabdomyolysis has occurred
rarely. Risk of myopathy increases when fibrates are given with reductase
inhibitors. Fenofibrate is the fibrate of choice for use in combination with a
statin. Fibrates should be avoided in patients with hepatic or renal
dysfunction. There appears to be a modest increase in the risk of cholesterol
gallstones, reflecting an increase in the cholesterol content of bile.
Therefore, fibrates should be used with caution in patients with biliary tract
disease or in those at high risk such as women, obese patients, and Native
Americans.
Related Topics