Chapter: Mechanical : Advanced IC Engines : Compression Ignition Engines
Factors affecting knock
Factors affecting knock
Knocking
is violet gas vibration and audible sound produced by extreme pressure
differentials leading to the very rapid rise during the early part of
uncontrolled second phase of combustion.
In C.I.
engines the injection process takes place over a definite interval of time.
Consequently, as the first few droplets injected are passing through the
ignition lag period, additional droplets are being injected into the chamber.
If the ignition delay is longer, the actual burning of the first few droplets
is delayed and a greater quantity of fuel droplets gets accumulated in the
chamber. When the actual burning
commences,
the additional fuel can cause too rapid a rate of pressure rise, as shown on
pressure crank angle diagram above, resulting in Jamming of forces against the
piston (as if struck by a hammer) and rough engine operation. If the ignition
delay is quite long, so much fuel can accumulate that the rate of pressure rise
is almost instantaneous. Such, a situation produces extreme pressure
differentials and violent gas vibration known as knocking (diesel knock), and
is evidenced by audible knock. The phenomenon is similar to that in the SI
engine. However, in SI Engine knocking occurs near the end of combustion
whereas in CI engine, knocking thatoccurs near the beginning of combustion.
Delay
period is directly related to Knocking in CI engine. An extensive delay
periodcan be due to following factors:
·
A low compression ratio permitting only a marginal
self -ignition temperature to be reached.
·
A low combustion pressure due to worn out piston,
rings and bad valves
·
Low cetane number of fuel
·
Poorly atomized fuel spray preventing early
combustion
·
Coarse droplet formation due to malfunctioning of
injector parts like spring
·
Low intake temperature and pressure of air
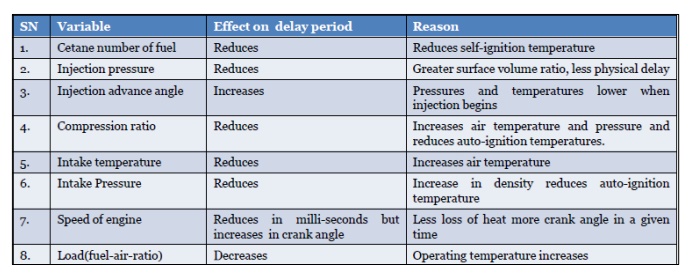
FACTORS AFFECTING KNOCKING
Injection timing
At normal
operating conditions min ignition delay (ID) occurs with start of injection at
10 to 15 OCA BTDC.
Cylinder
temperature and pressure drops if injection is earlier or later (high at first
but decrease as delay proceeds).
Injection quantity (load)
Reducing
engine load changes AFR, cools down the engine, reduces wall temperatures,
reduces residual gas temperatures and increases ID
Droplet size, injection velocity and rate
Ignition
quality within practical limits does not have significant effect on ID
including in injection produces only modest decreasing in ID Injector nozzle
diameter effects droplet size but has no significant effect on ID
Intake air temperature and pressure
Reducing
intake air T and p increases ID.
Strong
dependence of ID on charge temperature below 1000 K – above this value effect
of intake air conditions is not significant.
Engine speed
Increase
in engine speed increases the air motion and turbulence, reduces ID time
slightly (in ms), in terms of CA degrees ID increases almost linearly.A change
in engine speed, changes
“temp~time”
and “pressure~time” relationships.
Combustion chamber design
Spray
impingement on the walls effect fuel evaporation and ID
Increase
in compression ratio, increases pressure and temperature and reduces ID
Reducing
stroke volume, inc surface area to volume ratio, increases engine cooling and
increases ID
Swirl rate
Change
evaporating rate and air-fuel mixing - under normal operating conditions the
effect is small.
At
start-up (low engine speed and temperature) more important, high rate of
evaporation and mixing is obtained by swirl
Oxygen concentration
Residual
gases reduce O2 concentration and reducing oxygen concentration increases ID.
METHODS OF CONTROLING DIESEL KNOCK
We have
discussed the factors which are responsible for the detonation in the previous
sections. If these factors are controlled, then the detonation can be avoided.
·
Using a better fuel. Higher CN fuel has lower delay
period and reduces knocking tendency.
·
Controlling the Rate of Fuel Supply. By injecting
less fuel in the beginning andthen more fuel amount in the combustion chamber
detonation can be controlled to a certain extent. Cam shape of suitable profile
can be designed for this purpose.
·
Knock reducing fuel injector: This type of injector
avoid the sudden increase in pressure inside the combustion chamber because of
accumulated fuel. This can be done by arranging the injector so that only small
amount of fuel is injected first. This can be achieved by using two or more
injectors arranging in out of phase.
·
By using Ignition accelerators : C N number can be
increased by addingchemical called dopes. The two chemical dopes are used are
ethyl-nitrate andamyle –nitrate in concentration of 8.8 gm/Litre and 7.7
gm/Litre. But these twoincrease the NOx emissions.
·
Increasing Swirl : Knocking can be greatly reduced
by increasing swirl ( orreducing turbulence). Swirl helps in knock free
combustion.
Related Topics