Chapter: 11th Microbiology : Chapter 7 : Morphology of Bacteria
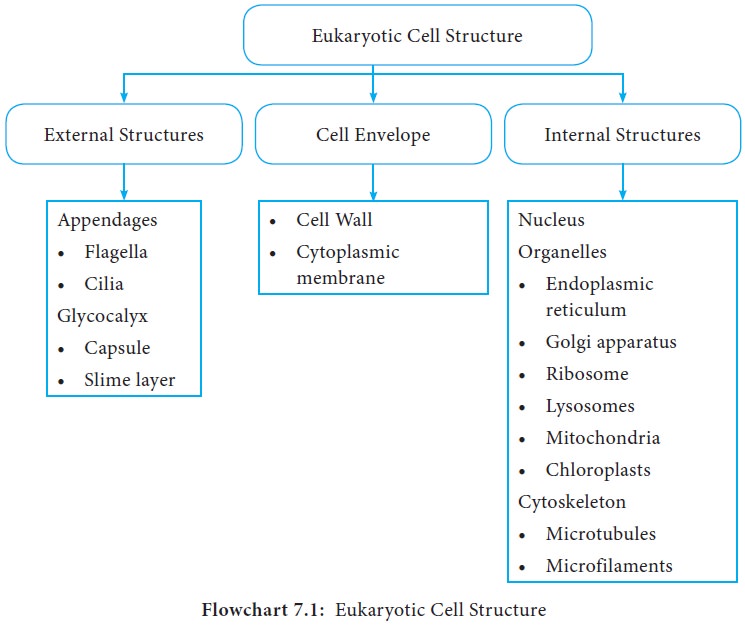
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
As mentioned earlier, eukaryotic organisms include algae,
protozoa, fungi, higher plants and animals. The eukaryotic cell is typically
larger and structurally more complex than the prokaryotic cell (Flowchart 7.1).
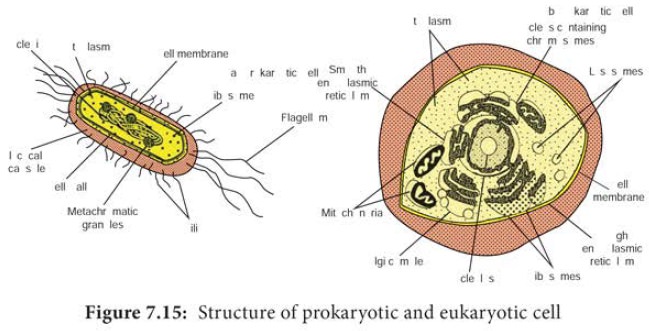
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes are chemically similar, in the sense
that they both contain nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates
(Figure 7.15). They use the same kinds of chemical reactions to metabolize
food, build proteins, and store energy.
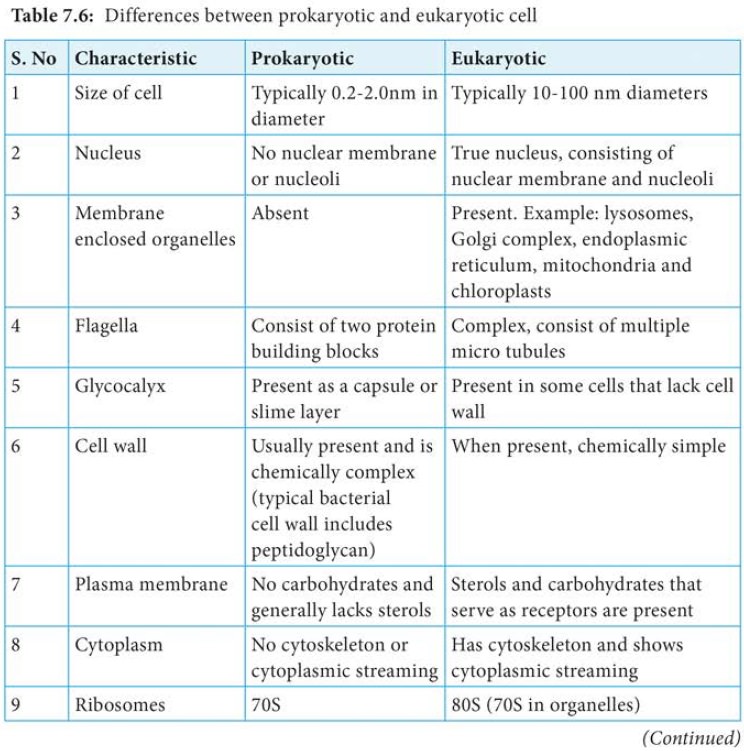
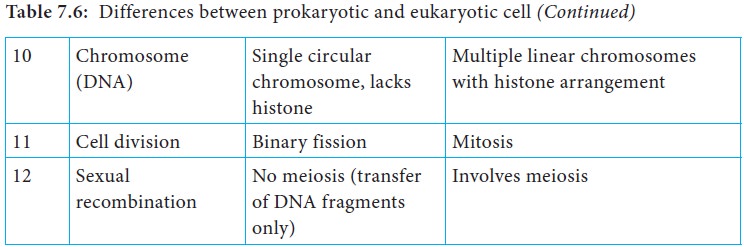
It is primarily the structure of cell walls and membranes, and
the absence of organelles (specialized cellular structures that have specific
functions), that distinguish prokaryotes from eukaryotes (Table 7.6).
The general, eukaryotic microbial cells have a cytoplasmic membrane,
nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuoles,
cytoskeleton, and glycocalyx. A cell wall, locomotor appendages and
chloroplasts are found only in some groups. The structure and functions of the
eukaryotic cells are discussed in (Table 7.7).
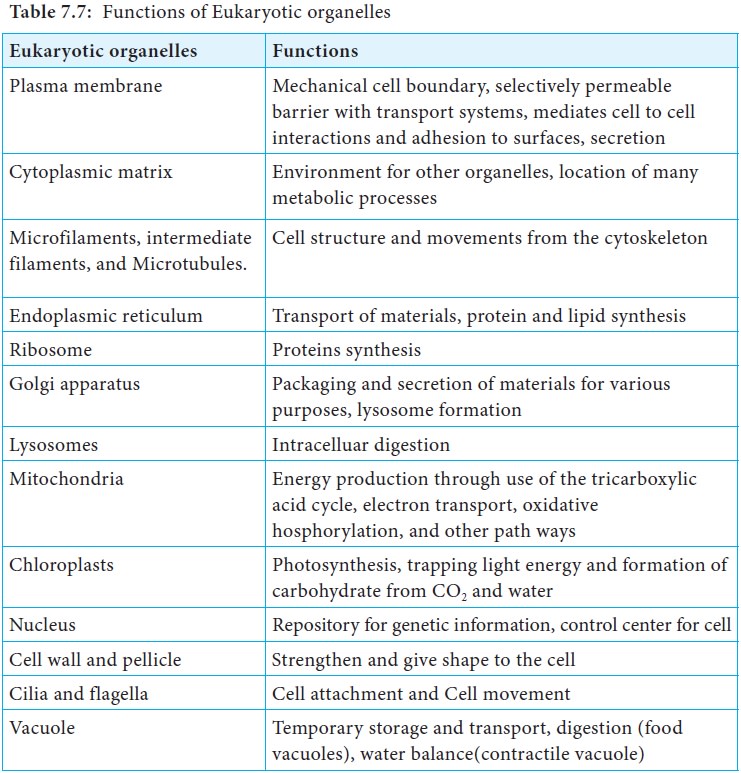
Table 7.7: Functions of Eukaryotic organelles
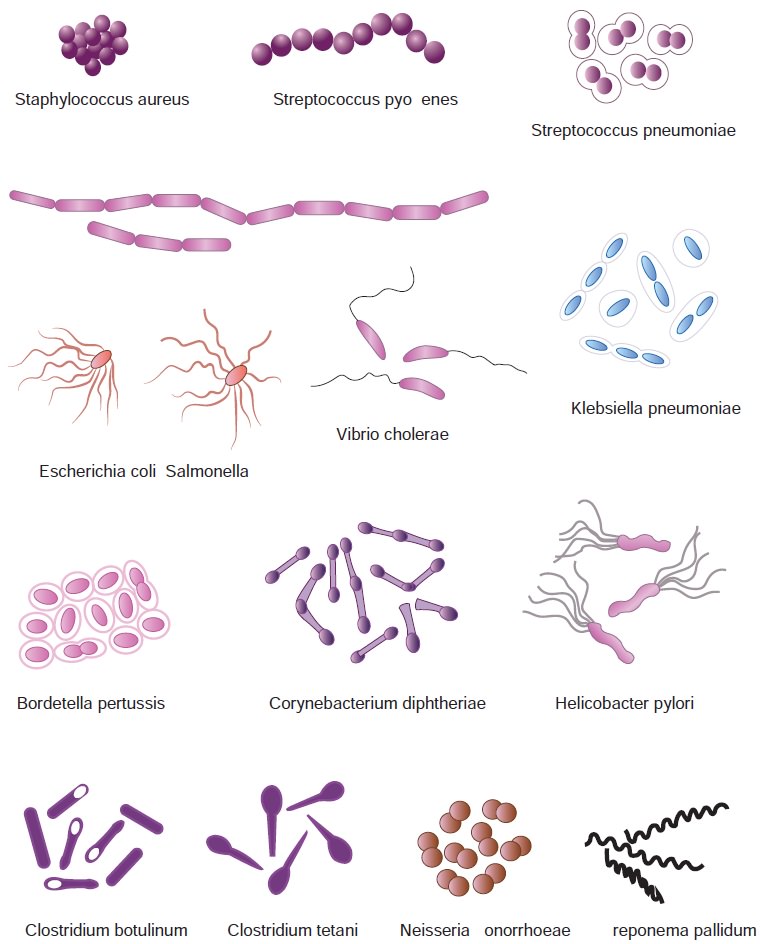
Different Shapes of Bacteria
Related Topics