Chapter: 11th Microbiology : Chapter 7 : Morphology of Bacteria
Cell Envelope of Bacteria
Cell Envelope of Bacteria
Cell envelope is an external
covering that lies outside the
cytoplasm. It is composed of two or three basic layers: the cell wall, the cell
membrane and in some bacteria the outer membrane.
Structure of Prokaryotic Cell Wall
Prokaryotic cells almost always are bounded by a chemically
complex cell wall. Cell wall lies beneath the external structures (capsules,
sheaths and flagella). Cell wall lies external to the plasma membrane (cell
membrane). Cell wall of eubacteria is made up of peptidoglycan or murein, whereas that of Archaeobacteria is composed of proteins,
glycoproteins or polysaccharides. A few genera such as Methanobacterium, have cell walls composed of pseudomurein, a polymer whose structure superficially resemble eubacteria
peptidoglycan of eubacteria but differs markedly in chemical composition.(Note:
Ordinary or typical bacteria are sometimes called eubacteria to distinguish
them from the phylogenetically distinct group known as archaeobacteria).
Peptidoglycan is a cross linked polymer of enormous strength and rigidity. It
is a polymer composed of many identical subunits (Figure 7.11). Peptidoglycan
differs somewhat in composition and structure from one species to another, but
it is basically a polymer of N-acetylglucosamine(NAG), N-acetylmuramic
acid(NAM), L-alanine, D-alanine, D-glutamate, and a diamino acid (LL- or
meso-diaminopimelic acid, L-lysine, L-ornithine, or L- diaminobutyric acid).
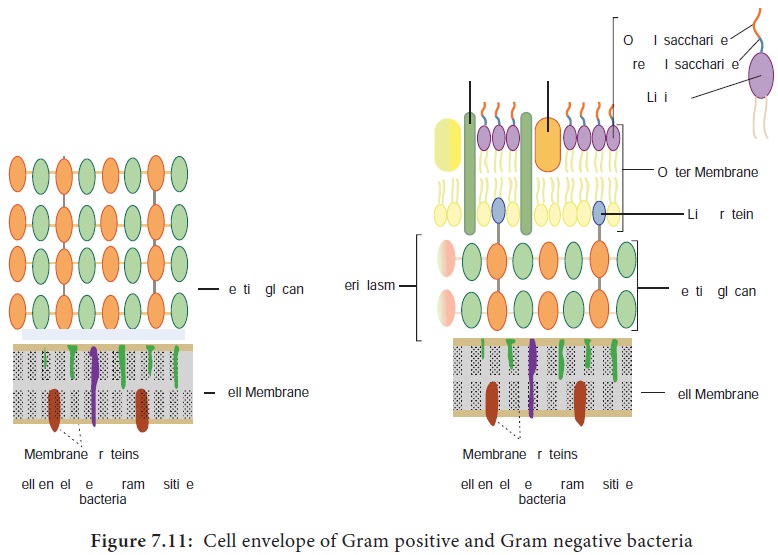
Cell wall may contain other substances in addition to
peptidoglycan. For instance, Staphylococcus
aureus and Streptococcus fecalis contain teichoic acids (polymer of acidic
polysaccharides) covalently linked to peptidoglycan. Cell wall of Gram positive
bacteria contain very little lipid but Mycobacterium
and Corynebacterium cell walls are
rich in mycolic acid (or Cord factor) which make them acid fast.
When stained, the cells cannot be decolorized easily despite treatment with
dilute acids. Mycoplasma lack cell
wall.
Protoplast is a bacterial cell
consisting of cell material bound by a cytoplasmic membrane.
Spheroplast is a bacterial cell
with two membranes namely the cytoplasmic membrane and the outer
membrane but no cell wall.
Functions of cell wall
·
It gives shape to bacteria like a bicycle tyre that maintains
the necessary shape and prevents the more delicate inner tube (the cytoplasmic
membrane) from bursting when it is expanded.
·
It protects bacteria from osmotic lysis in dilute solutions
(hypotonic environment).
·
It protects cell from toxic substances.
Related Topics