Chapter: Essentials of Psychiatry: Antipsychotic Drugs
Effects of Antipsychotic Agents on Symptoms of Schizophrenia
Effects
of Antipsychotic Agents on Symptoms of Schizophrenia
Positive Symptoms
Antipsychotic
agents have a specific effect on positive symptoms of schizophrenia including
hallucinations, delusions and thought disorder (Hirsch and Barnes, 1995).
First-generation antipsy-chotic drugs (e.g., chlorpromazine and haloperidol)
are effective for alleviating positive symptoms and in preventing their recur-rence
in many schizophrenic patients (Miyamoto et
al., 2000, 2002a).
Although
the proportion of patients who improve and the magnitude of therapeutic effects
vary greatly, second-generation antipsychotics appear to be at least as
effective for psychotic symptoms as conventional drugs (Markowitz et al., 1999; Remington and Kapur,
2000).
Within a
short period of time, clozapine, risperidone, olanzapine, quetiapine and
ziprasidone have become the drugs of choice over conventional antipsychotic
drugs in the treatment of schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder (Buckley,
2001). There is, however, still considerable debate with regard to the clinical
superiority of second-generation over conventional antipsychotics. The CATIE
study (Lieberman, 2005) failed to resolve this debate, with all medications
tested demonstrating comparable clinical efficacy.
Negative Symptoms
Negative
symptoms can be divided into three components that are usually difficult to
distinguish: 1) primary or deficit-enduring negative symptoms, 2) primary
nonenduring negative symptoms, and 3) secondary negative symptoms that may be
associated with positive symptoms, EPS, depression and environmental
depriva-tion (Buchanan and Gold, 1996; Collaborative Working Group on Clinical
Trial Evaluations, 1998a). Studies of the early course of illness have shown
that about 70% of schizophrenics develop pri-mary negative symptoms, such as
affective blunting, emotional withdrawal, poverty of speech, anhedonia and
apathy, before the onset of positive symptoms (Hafner et al., 1992). Negative symptoms may represent core features of the
illness, and may be associated with poor outcome and prolonged hospitalization
for patients (Buchanan and Gold, 1996).
Conventional
antipsychotics are generally less effective against negative than positive
symptoms of schizophrenia (Miyamoto et
al., 2002a). Thus, the efficacy of second-generation antipsychotics on
negative symptoms compared with that of first-generation drugs has received
much attention. Although second-generation antipsychotics have been shown to be
more effective than conventional agents in treating negative symptoms, there is
a continuing debate as to whether these effects are related to a reduction in
EPS, or to a direct effect on primary negative symptoms (Marder and Meibach,
1994; Kane et al., 2001; Remington
and Kapur, 2000; Carpenter et al.,
1995; Conley et al., 1994; Meltzer,
1995).
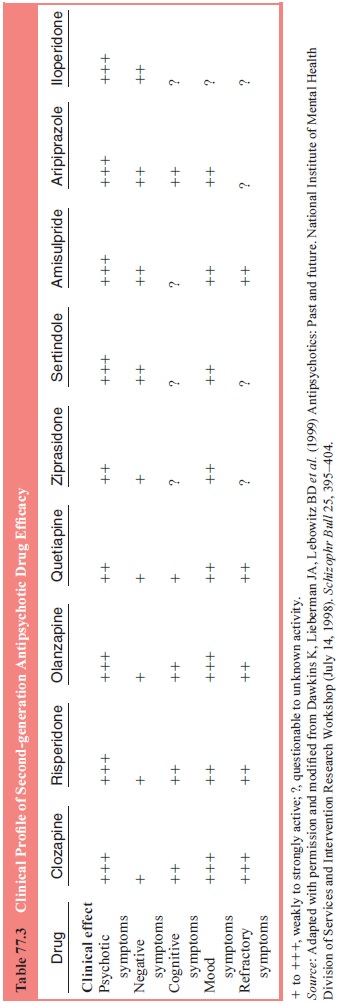
A summary
of the clinical profile of second-generation drugs on a range of symptoms is
provided in Table 77.3.
Mood Symptoms and Suicidal Behavior
Depressive
symptoms frequently occur in the context of psy-chotic symptoms or
intercurrently between psychotic episodes (Siris, 2001). Antidepressant
medication used adjunctively to antipsychotic drugs is generally indicated and
effective (Siris, 2001). Atypical antidepressants have been reported to have
se-lective benefits against mood symptoms in schizophrenia, both manic and
depressive (Sartorius et al., 2002).
Suicidal
behavior presents a particular problem in patients with schizophrenia. Recently
the FDA approved clozapine for use in suicidal patients with schizophrenia on
the basis of results in the InterSePT study. This study found that clozapine
treatment produced a lower rate of suicidal behavior than the comparison
treatment olanzapine in patients with active or histories of sui-cidal behavior
(Meltzer et al., 2003).
Related Topics