Chapter: Essentials of Psychiatry: Antipsychotic Drugs
Drug Interactions and Antipsychotic Agents
Drug
Interactions and Antipsychotic Agents
Most
antipsychotics are metabolized by hepatic microsomal oxidases (cytochrome P450
system). The major isoenzyme sys-tems involved are CYP1A2, CYP2C19, CYP2D6 and
CYP3A4 (Ereshefsky, 1996). Induction or inhibition of these enzymes by other
drugs may occasionally produce clinically important drug interactions (Burns,
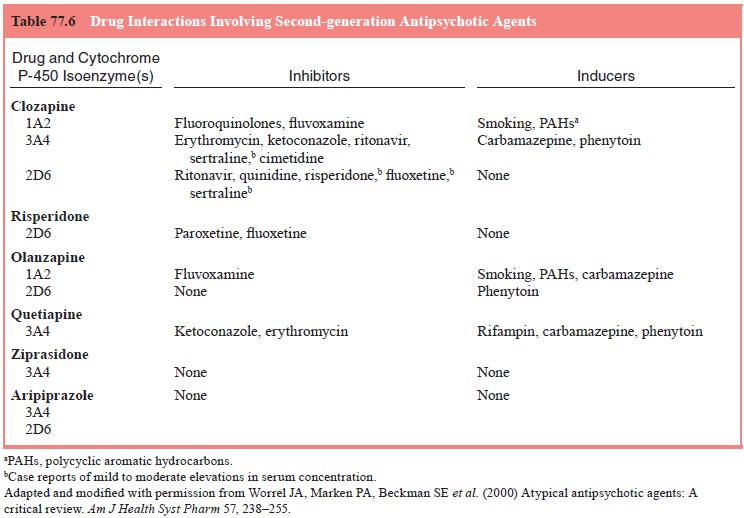
2001). Table 77.6 summarizes clinically significant pharmacokinetic drug
interactions involving second-generation antipsychotic drugs.
There are
other common interactions that will concern clinicians. Antacids can decrease
the absorption of the antip-sychotic agent from the gut. Antipsychotic
medications can antagonize the effects of dopamine agonists or levodopa when
these drugs are used to treat parkinsonism. Antipsychotic agents may also
enhance the effects of central nervous system depressants such as analgesics,
anxiolytics and hypnotics. If patients require preanesthetic medication or
general anesthet-ics, the doses of these drugs may need to be reduced (Marder,
1997).
Related Topics