Chapter: 10th Social Science : Geography : Chapter 1 : India - Location, Relief and Drainage
Drainage System of India
Drainage
System of India
A drainage system is an integrated system of
tributaries and a trunk stream which collects and drains surface water into the
sea, lake or some other body of water. The total area drained by a river and
its tributaries is known as a drainage basin. The drainage pattern of an area
is the result of the geological structure of the respective areas. The drainage
system of India is broadly divided into two major groups on the basis of their
location. They are Himalayan rivers and the Peninsular rivers.
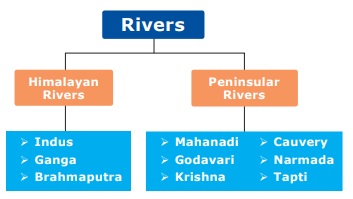
Himalayan Rivers
These
rivers are found in north India and originate from Himalayas. So, they are also
called as Himalayan rivers. These are perennial rivers.
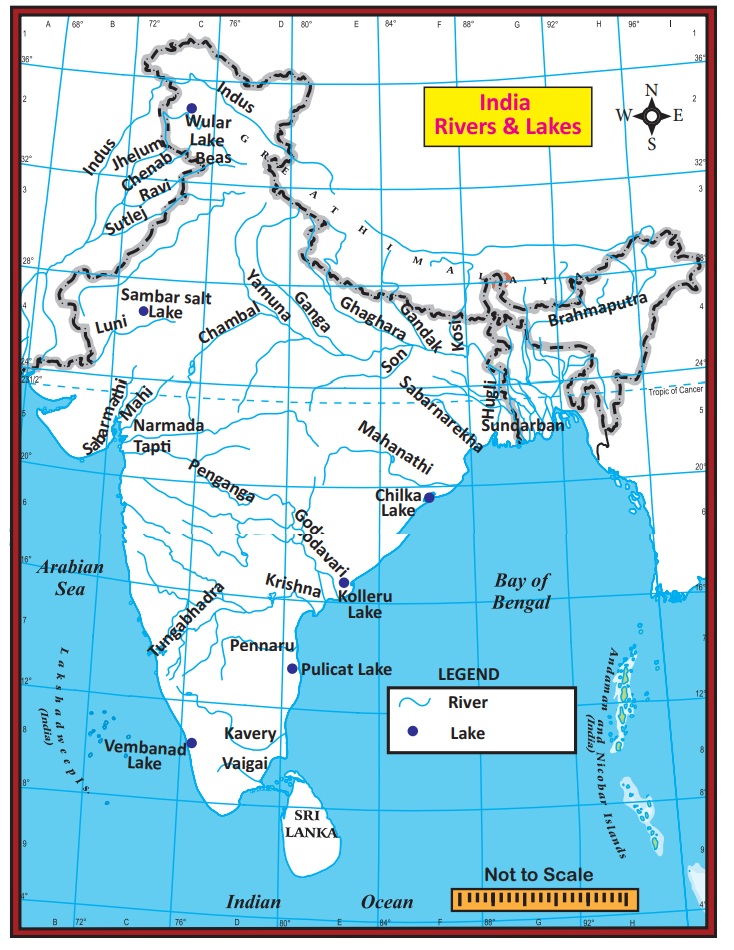
a) The Indus River System
The Indus River is one of the largest rivers of the
world. It originates from the northern slope of the Kailash range in Tibet near
Manasarovar Lake at an elevation of about 5,150 m. Its length is about 2,880 km
(Only 709 km is in India). The river has a total drainage area extending
11,65,500 sq km in which 321,289 sq km areas are drained in India. The river
flows through the Ladakh and Zaskar ranges and creates deep gorges. The river
runs through Jammu and Kashmir, turns south near Chillar and enters Pakistan.
Its major tributaries are Jhelum, Chenab (Largest tributary of Indus), Ravi,
Beas and Sutlej. It enters into with the Arabian Sea.
b) The Ganga River System
The Ganga River system is the largest drainage
system of India. It extends over an area of 8,61,404 sq km. The Ganga plain is
the most densely populated place in India and many towns are developed on the
banks of this river. The river Ganga originates as Bhagirathi from the Gangotri
Glacier in Uttar Khasi District of Uttarkhand state, at an elevation of 7,010
m.

The length of the river Ganga is about 2,525 km. Its major tributaries from the north are Gomti, Gandak, Kosi and Ghaghra and from south, Yamuna (largest tributary of Ganga), Son, Chambal etc. The river Ganga is known as the River Padma in Bangladesh. The combined river of Ganga and Brahmaputra creates the World’s largest delta known as Sundarbans in Bangladesh before joining the Bay of Bengal.
c) The Brahmaputra River System
The river Brahmaputra originates from the
Chemayungdung Glacier of the Kailash range to the east of Lake Manasarovar in
Tibet at an elevation of about 5,150 m. The total area is about 5,80,000 sq km
but the drainage area found in India is 1,94,413 sq km This river is known as
Tsangpo (Purifier) in Tibet. The length of this river is about 2,900 km (900 km
in India). It enters into India through a gorge in Arunachal Pradesh namely
Dihang. It has many tributaries. Tista, Manas, Barak, Subansiri are some of
them. This river is called as Jamuna in Bangladesh. After it joins with the
river Ganga in Bangladesh, the river is called as Meghna.
Characteristics of Himalayan Rivers
1. Long and wide
2. Perennial in nature
3. Unsuitable for hydro power generation
4. Middle and lower courses are navigable
Peninsular Rivers
The
rivers in south India are called the Peninsular rivers. Most of these rivers
originate from the Western Ghats. These are seasonal rivers (non–perennial).
They have a large seasonal fluctuation in volume of water as they are solely
fed by rain. These rivers flow in valleys with steep gradients. Based on the
direction of flow, the peninsular rivers are divided into the
1. West flowing rivers
2. East flowing rivers
East Flowing Rivers
a) Mahanadi
The river
Mahanadi originates near Sihawa in Raipur district of Chattisgarh and flows
through Odisha. Its length is 851 km. Seonath, Telen, Sandur and Ib are its
major tributaries. The main stream of Mahanadi gets divided into several distributaries
such as Paika, Birupa, Chitartala, Genguti and Nun. All these distributaries
form the Delta of Mahanadi which is one of the largest deltas in India. The
Mahanadi empties its water in Bay of Bengal.
b) Godavari
Godavari is the
longest river (1,465 km) with an
area of 3.13 lakh km2 among the Peninsular rivers. It is also called Vridha
Ganga. It originates in Nasik district of Maharashtra, a portion of Western
Ghats. It flows through the states of Telangana and Andhra Pradesh before
joining Bay of Bengal. Purna, Penganga, Pranitha, Indravati, Tal and Salami are
its major tributaries. The river near Rajahmundry gets divided into two
Channels called Vasistha and Gautami and forms one of the largest deltas in
India. Kolleru, a fresh water lake is located in the deltaic region of the
Godavari.
c) Krishna
The river Krishna originates from a spring at a
place called Mahabaleshwar in the Western Ghats of Maharashtra. Its length is
1,400 km and an area of 2.58 lakh sq km. It is the second longest Peninsular
river Bhima, Peddavagu, Musi, Koyna and Thungabhadra are the major tributaries
of this river. It also flows through Andhra Pradesh and joins in Bay of Bengal,
at Hamasaladeevi.
d) Kaveri
The river
Kaveri originates at Talakaveri, Kudagu hills of Karnataka. Its length is 800
km. The river kaveri is called Dhakshin Ganga or Ganga of south. In Karnataka
the river bifurcates twice, forming the sacred islands of Srirangapatnam and
Sivasamudram. While entering Tamil Nadu, the Kaveri continues through a series
of twisted wild gorges until it reaches Hogenakkal Falls and flows through a
straight, narrow gorge near Salem. The Kaveri breaks at Srirangam Island with
two channels, river Coleroon and Kaveri. At last, it empties into the Bay of
Bengal at Poompuhar.
West Flowing Rivers
a) Narmada
This river rises in Amarkantak Plateau in Madhya
Pradesh at an elevation of about 1057 m and flows for a distance of about 1,312
km. It covers and area of 98,796 sq km and forms 27 km long estuary before
outfalling into the Arabian Sea through the Gulf of Cambay. It is the largest
among the west flowing rivers of Peninsular India. Its principal tributaries
are Burhner, Halon, Heran, Banjar, Dudhi, Shakkar, Tawa, Barna and Kolar.
b) Tapti
The Tapti is one of the major rivers of Peninsular
India with the length of about 724 km. It covers an area of 65,145 sq km. Tapti
river rises near Multai tank in the Betul district of Madhya Pradesh at an
elevation of about 752 m. It is one of only the three rivers in Peninsular
India that run from east to west - the others being the Narmada and the Mahi.
The major tributaries are Vaki, Gomai, Arunavati, Aner, Nesu, Buray, Panjhra
and Bori. It outfalls into the Arabian Sea through the Gulf of Cambay.
In which river the Gerosappa (jog)
fall is found?
Characteristics of South Indian Rivers
1. Originate
from Western Ghats
2. Short
and narrow
3. Non
perennial in nature
4. Suitable
for hydro power generation
5. Not useful for navigation
Related Topics