Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Nursing Health Care Hospital Hygiene Higher secondary school College Notes
Dietary Management In Urinary Calculi(kidney stones) - Urolithiasis
DIETARY MANAGEMENT IN
URINARY CALCULI - UROLITHIASIS
Urinary
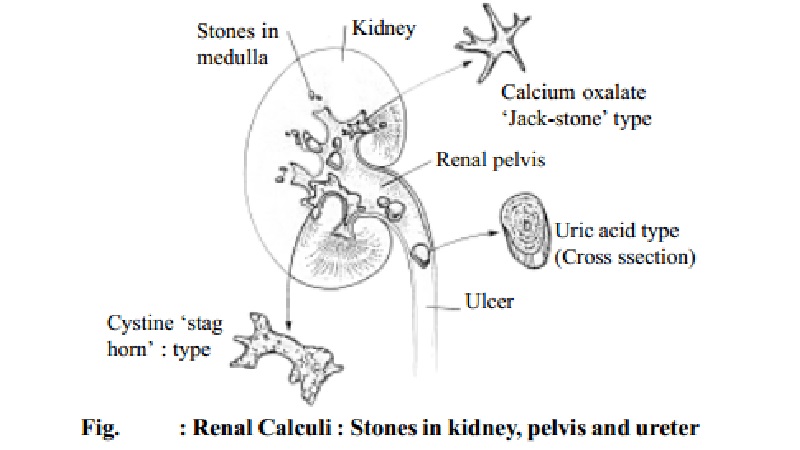
calculi (kidney stones) may be found in the kidney, ureter, bladder or urethra
as presented in Fig. 15-B. About 90% of all stones contain calcium. The
occurrence of kidney stones may be due to an outcome of different nutritional
status, dietary habits and environmental factors such as temperature and
humidity.
In warm climates, the urine volume is low and concentrated with urates,
oxalates and calcium salts. Frequent urinary tract infection may contribute to
the formation of stones. In India the most common type of calculi is calcium
oxalate.
The diet should be low in oxalic acid and purine. Intake of calcium and
phosphates should be reduced. Large amounts of fluid should be consumed to
increase urine output. A dilute urine prevents the formation of stones.
When
stones are composed of calcium, magnesium phosphates and carbonates the urine
is alkaline and acid - ash diet is used. The acid ash diet should maintain the
urine pH between 4.5 and 5 and with an alkaline ash diet, a urinary pH of 7.6
to 8 is maintained.
a. Planning acid ash
Diet
A liberal fluid intake is important. Salt is
used in moderation. Fruits and vegetables should not contribute more than 25 ml
of base daily.
b. Planning alkaline -
ash diet
If stones
of uric acid or cystine type occur, an alkaline - ash diet is given. Alkaline
producing foods like fruits, vegetables and milk are given while acid producing
foods like meat, eggs and cereals are restricted Table 15.2 gives the list of
Acid producing, Alkali producing and neutral foods.
c. Low oxalate diets
In the case of oxalate stones, foods that are a good source such as
beans, chocolate, cocoa, potatoes, spinach, tea and tomatoes should be omitted.
Fluid
A liberal fluid intake of 3000 ml or more daily is essential to prevent
the production of concentrated urine. Coconut and barely water, fruit juice and
weak tea are given.
Related Topics