Chapter: Electronic Devices and Circuits : Multistage Amplifiers and Differential Amplifier
D.C. Analysis of Differential Amplifier
D.C. Analysis of Differential Amplifier
The d.c. analysis means to obtain the operating
point values i.e. I Cq and V CEQ for the transistors
used. The supply voltages are d.c. while the input signals are a.c., so d.c.
equivalent circuit can be obtained simply by reducing the input a.c. signals to
zero. The d.c. equivalent circuit thus obtained is shown in the Fig.. Assuming
Rs 1 = R S2, the source resistance is simply denoted by
Rs ,
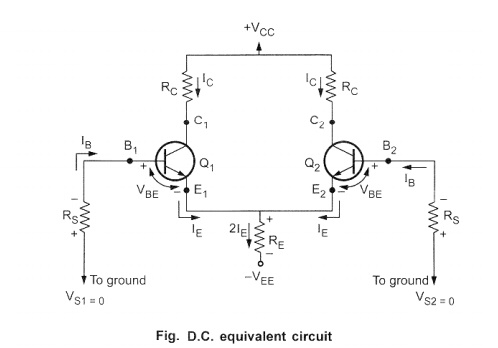
The transistors Q1 and Q 2
are matched transistors and hence for such a matched pair we can assume :
i)
Both the
transistors have the same characteristics.
ii)
R E1
= R E2 hence R E=
R E1 ll R E2.
iii)
R C1
= R c 2 hence denoted as R C.
iv)
lV CCI
= lV EE I and both are measured with respect to ground.
As the two transistors are matched and circuit
is symmetrical, it is enough to find out
operating point I CQ and V CEQ,
for any one of the two transistors. The same is applicable for the other
transistor.
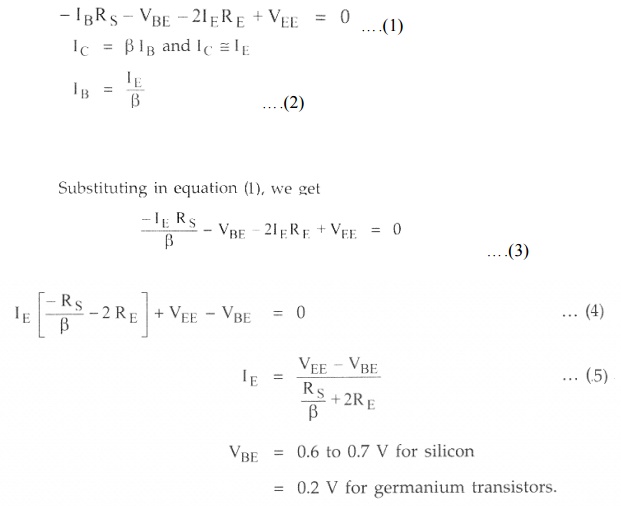
Apply-g KVL to base-emitter loop of the
transistor Q1,

Related Topics