Nursing Education and Management - Curriculum planning | 12th Nursing : Chapter 12 : Nursing Education and Management
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 12 : Nursing Education and Management
Curriculum planning
Curriculum planning
The term curriculum is derived from the latin word “currere” which
means ‘run’. Thus, curriculum is a runway for attaining the goals of education.
Curriculum may be considered as the blue print of an educational programme. It
is the base of education on which the teaching-learning process is planned and
implemented.
Meaning of curriculum
The systematic arrangement of certain courses designed with
certain objectives for the pupil.
Curriculum refers to the totality of activity and experiences
planned by the school with a view to achieve the objectives of education.
Definition
According to Cunningham,’ Curriculum is a tool in the hands of an
artist to mould his material, according to his ideals in his studio. In this
definition, artist is the teacher, material is the student, ideals are the
objectives and studio is the educational institute.
Nursing curriculum is the learning opportunities (subject matter)
and the learning activities (clinical experiences and practices) that the
faculty plans and implement in various settings for particular group of
students, for a specified period of time in order to attain the objectives.
Three facets of curriculum are
·
Goals and purposes of
education
·
Process of curriculum
·
Evaluation of products
The four C’ s of curriculum planning
Cooperative: A programme prepared jointly by group of persons.
Continuous: Preparation of programme and its revision should be
continuous.
Comprehensive: All the components of the programme
should be included.
Concrete: Concrete professional tasks must constitute the essential
structure of a relevant programme.
Components of curriculum
·
Philosophy
·
Objectives
·
Total duration
·
Detailed course plan
·
Programme evaluation.
·
The statement of
philosophy of the educational programme.
·
The statement of the
objectives of educational programme.
·
Total duration of the
educational programme. (theortical ,practical ,clinical components.)
·
Detailed course plan for
each course. (placement, sequences and learning situations, instructional
methods)
·
Programme evaluation
(evaluation methods, plan and schedule of evaluation, results of evaluation).
1. Levels of curriculum planning
Goodland names curriculum in 3 levels.
·
Societal
·
Institutional
·
Instructional
Societal curriculum
This curriculum which is planned for a large group or class of
students, e.g BSc(N) It is planned by groups outside of an educational institution,
e.g. National league for nursing. They are more immediately concerned with
There is significant relationship between curriculum and nature of
society. According to the needs of the society curriculum will be changed.
 The institutional curriculum
The institutional curriculum
·
It is planned by faculty
or teacher for a clearly identified group of students who will spend a
specified period in a particular institution.
·
Cooperative planning
through curriculum committee of the particular institution.
·
More active participation
of each teachers generally brings about change and improvement.
The instructional curriculum
It consists of the content (subject matter and learning
activities) planned day by day and week by week by a particular teacher for a
particular group of students.
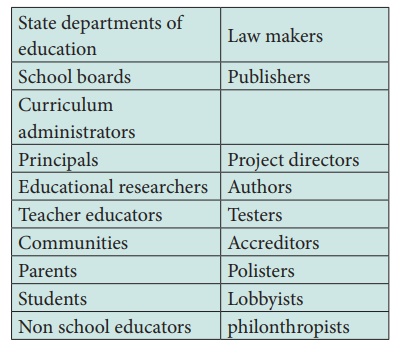
2. Curriculum committee
The committee comprises the following members
3. Grading of curriculum content
E- Essential or must learn.
D- Desirble or useful to learn.
S- Supportive or nice to learn.
4. Principles of curriculum development
The conservative principles: this means that the present, the
past, and the future needs of the community should be taken into
considerations.
The forward- looking principles: Children of today
are the citizens of tomorrow.
The creative principle: Curriculum should enable the child to
exercise his creative and constructive powers.
Principle of totality form: The curriculum should be total learning
experience and total learning opportunity.
The activity principles: The curriculum should be developed in
terms of activity and experience.
Principle of preparation of life: Enable the child
to fulfil his responsibilities when he becomes an adult.
Principle of connecting to life:
Curriculum should provide worthwhile life experiences.
Child centered curriculum: Consideration should be given to the
student’s age, their educational level, needs and individual differences.
Priniciple of integration and correlation: While developing
curriculum, each year’s course should be built on what has been done in
previous years and at the same time should serve as basis for subsequent
learning.
Priniciple of comprehensiveness and balance. The curriculum should be
framed in such a way as every aspect of life, like economic
relationships, social activities and occupations.
Principle of loyalties: Curriculum should be planned in such a
manner that it teaches a true sense of loyalty to the family, the school, the
country and the international community at large
Priniciple of variety and flexibility: Variety should be
provided in terms of learning and teaching activities. Its not so rigid.
Priniciple of connecting to community needs: Curriculum should
address the community needs.
Principle of connecting with social life:
Curriculum has to maintain to relation with social life.
Training for leisure: The curriculum should have some provision
for the co-curricular activities, relaxation, and library utilization according
to choice.
Principle of core or common subjects: Broad areas of
knowledge, skills and appreciation should be included. Co subjects, like maths,
science etc.
Principle of all round development of body, mind and spirit: All kinds of experiences
should be provided.
Prinicples of dignity of labour: Curriculum should help
students to develop a positive attitude towards all kinds of jobs.
Principle of character building: Curriculum should
promote human and social values.
Principle of democracy, secularism and socialism: Curriculum should train
the child to imbibe ideals and values of a democratic, secular and
socialist state. Principle of connecting with social life: curriculum has to
maintain a relations with social life.
Types of curiculum
·
Legitimate curriculum
·
Illegitimate curriculum
·
Hidden curriculum
·
Null curriculum
Principles related to the Development of Nursing curriculum
·
Nursing curriculum
should equip the students with the essential knowledge, skills and attitude.
·
Curriculum should be
clear to the students as well as to the teacher.
·
Consider the community
needs.
·
Curriculum should
inculcate right attitude to students.
·
Frame adequate teaching
– learning activities in the classroom, clinical area and community settings.
·
Consider the guidelines
laid down by the statutory bodies line INC, Universities, examination boards .
·
High-Tech-High-Touch
approach in the nursing
care.
·
Participatory approach
in the teaching-learning process.
·
The learning environment
should resemble the life situation.
Related Topics